Abstract
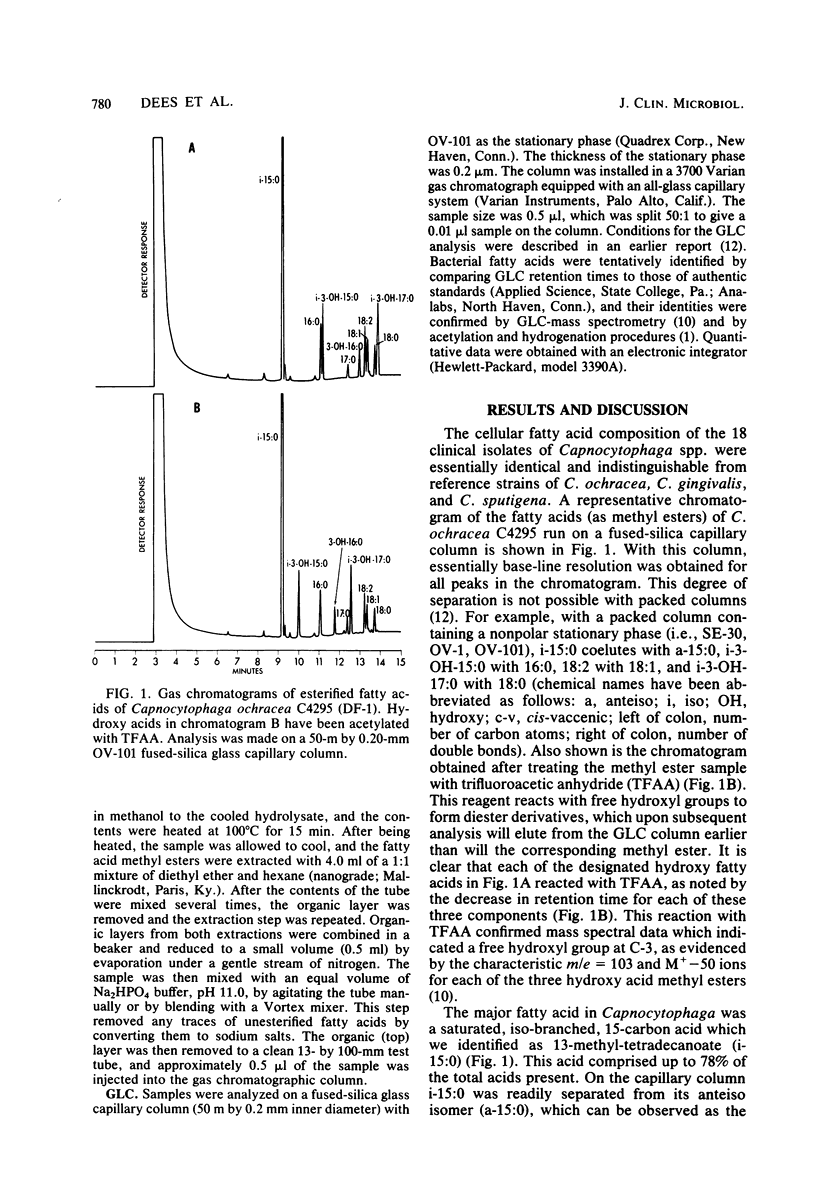
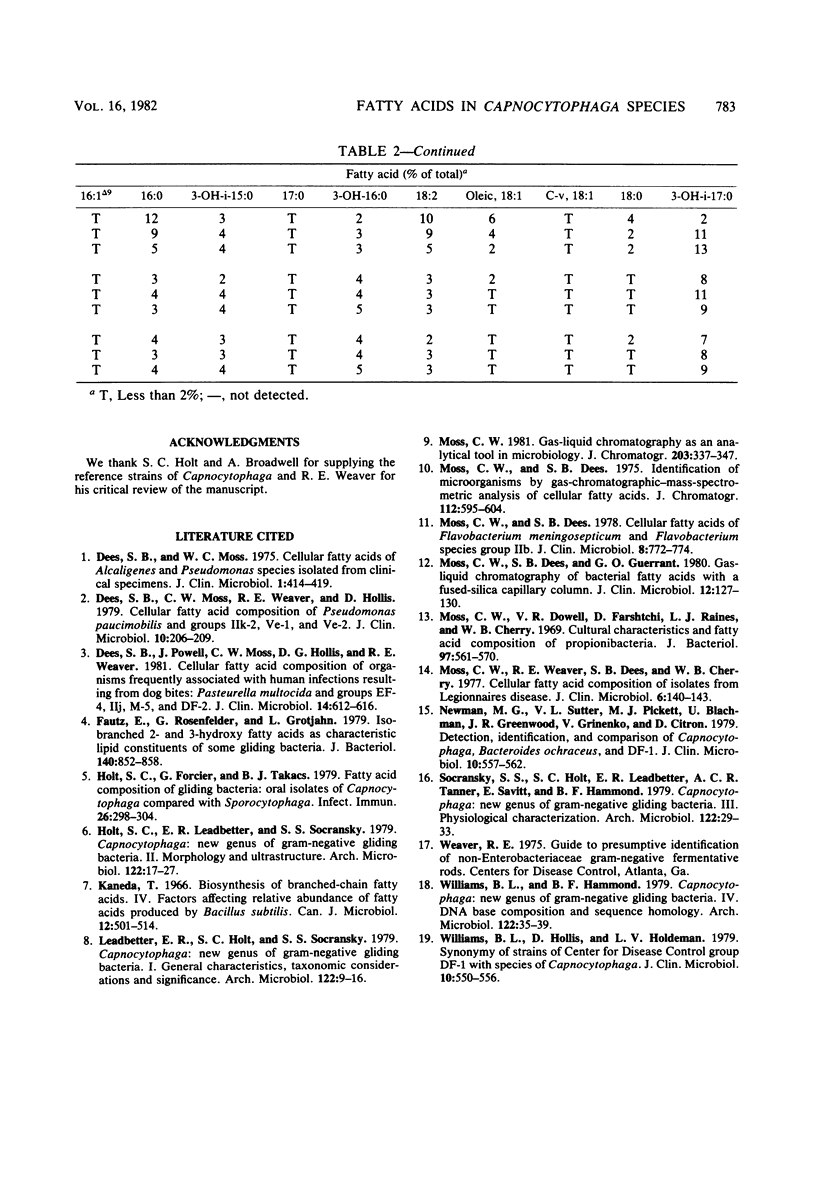
The cellular fatty acid composition of 18 clinical isolates and 4 reference strains of Capnocytophaga species (Capnocytophaga ochracea, Capnocytophaga gingivalis, and Capnocytophaga sputigena) was determined by gas-liquid chromatography. The fatty acid profiles of the 22 cultures were essentially identical and were characterized by major amounts (60% or greater) of a saturated, iso-branched-chain, 15-carbon acid (13-methyl-tetradecanoate) and the presence of two relatively uncommon saturated, iso-branched, 3-hydroxy acids (13-methyl-3-hydroxy-tetradecanoate and 15-methyl-3-hydroxy-hexadecanoate). The presence and relative amounts of these acids distinguish Capnocytophaga spp. from other gliding bacteria.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dees S. B., Moss C. W. Cellular fatty acids of Alcaligenes and Pseudomonas species isolated from clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 May;1(5):414–419. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.5.414-419.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dees S. B., Moss C. W., Weaver R. E., Hollis D. Cellular fatty acid composition of Pseudomonas paucimobilis and groups IIk-2, Ve-1, and Ve-2. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Aug;10(2):206–209. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.2.206-209.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dees S. B., Powell J., Moss C. W., Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E. Cellular fatty acid composition of organisms frequently associated with human infections resulting from dog bites: Pasteurella multocida and groups of EF-4, IIj, M-5, and DF-2. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Dec;14(6):612–616. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.6.612-616.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fautz E., Rosenfelder G., Grotjahn L. Iso-branched 2- and 3-hydroxy fatty acids as characteristic lipid constituents of some gliding bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):852–858. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.852-858.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C., Forcier G., Takacs B. J. Fatty acid composition of gliding bacteria: oral isolates of Capnocytophaga compared with Sporocytophaga. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):298–304. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.298-304.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C., Leadbetter E. R., Socransky S. S. Capnocytophaga: new genus of gram-negative gliding bacteria. II. Morphology and ultrastructure. Arch Microbiol. 1979 Jul;122(1):17–27. doi: 10.1007/BF00408041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneda T. Biosynthesis of branched-chain fatty acids. IV. Factors affecting relative abundance of fatty acids produced by Bacillus subtilis. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Jun;12(3):501–514. doi: 10.1139/m66-073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leadbetter E. R., Holt S. C., Socransky S. S. Capnocytophaga: new genus of gram-negative gliding bacteria. I. General characteristics, taxonomic considerations and significance. Arch Microbiol. 1979 Jul;122(1):9–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00408040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Dees S. B. Cellular fatty acids of Flavobacterium meningosepticum and Flavobacterium species group IIb. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Dec;8(6):772–774. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.6.772-774.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Dees S. B., Guerrant G. O. Gas-liquid chromatography of bacterial fatty acids with a fused-silica capillary column. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jul;12(1):127–130. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.1.127-130.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Dees S. B. Identification of microorganisms by gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric analysis of cellular fatty acids. J Chromatogr. 1975 Oct 29;112:594–604. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)99988-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Dowell V. R., Jr, Farshtchi D., Raines L. J., Cherry W. B. Cultural characteristics and fatty acid composition of propionibacteria. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):561–570. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.561-570.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W. Gas-liquid chromatography as an analytical tool in microbiology. J Chromatogr. 1981 Jan 9;203:337–347. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)80305-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Weaver R. E., Dees S. B., Cherry W. B. Cellular fatty acid composition of isolates from Legionnaires disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Aug;6(2):140–143. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.2.140-143.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman M. G., Sutter V. L., Pickett M. J., Blachman U., Greenwood J. R., Grinenko V., Citron D. Detection, identification, and comparison of Capnocytophaga, Bacteroides ochraceus, and DF-1. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):557–562. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.557-562.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socransky S. S., Holt S. C., Leadbetter E. R., Tanner A. C., Savitt E., Hammond B. F. Capnocytophaga: new genus of gram-negative gliding bacteria. III. Physiological characterization. Arch Microbiol. 1979 Jul;122(1):29–33. doi: 10.1007/BF00408042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. L., Hammond B. F. Capnocytophaga: new genus of gram-negative gliding bacteria. IV. DNA base composition and sequence homology. Arch Microbiol. 1979 Jul;122(1):35–39. doi: 10.1007/BF00408043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. L., Hollis D., Holdeman L. V. Synonymy of strains of Center for Disease Control group DF-1 with species of Capnocytophaga. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):550–556. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.550-556.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


