Abstract
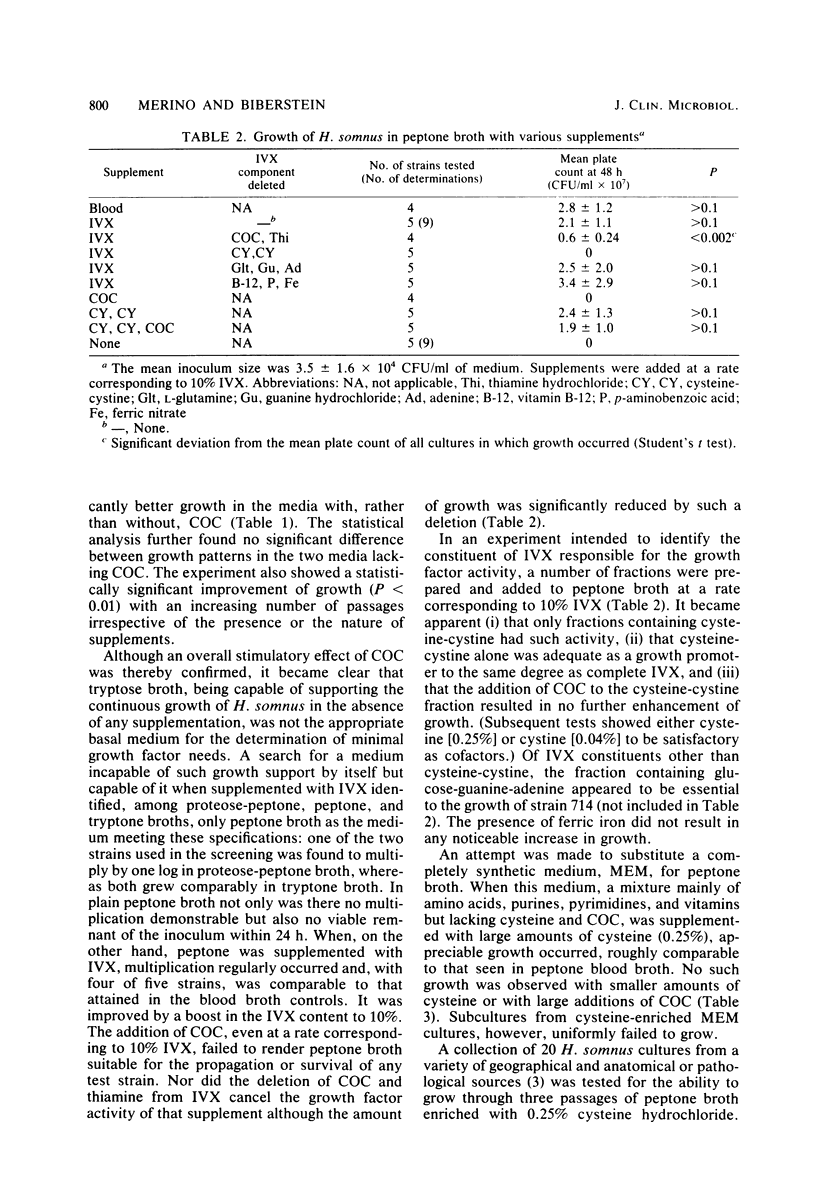
The growth factor needs of Haemophilus somnus, which have not been defined to date, were found to be provided by 1% IsoVitaleX (IVX; BBL Microbiology Systems) in tryptose broth. Some growth, however, occurred in unsupplemented tryptose broth. Of the ingredients of IVX, cocarboxylase was found to stimulate growth to about the same degree as the total supplement. Cocarboxylase was without direct effect in 2% peptone broth, which supported no growth of 25 H. somnus strains until supplemented with IVX, optimally at the 10% level. This could be substituted for by proportional amounts of cysteine or cystine, but by no other IVX ingredient. Cysteine-cystine and IVX but not cocarboxylase supplementation allowed H. somnus to grow in Eagle minimal medium, a completely synthetic medium, but attempts at serial passage were unsuccessful.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asmussen M. D., Baugh C. L. Thiamine pyrophosphate (cocarboxylase) as a growth factor for Haemophilus somnus. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Aug;14(2):178–183. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.2.178-183.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canto G. J., Biberstein E. L. Serological diversity in Haemophilus somnus. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1009–1015. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1009-1015.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corboz L., Pohlenz J. Experimentelle Infektionen mit sogenanntem Haemophilus somnus beim Kalb: Vergleich von Stämmen mit unterschiedlicher Virulenz. Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd. 1976 Oct;118(10):429–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crandell R. A., Smith A. R., Kissil M. Colonization and transmission of Haemophilus somnus in cattle. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Nov;38(11):1749–1751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C., Gorman G. W., Weaver R. E., Mackel D. C., Smith H. W. Primary isolation media for Legionnaires disease bacterium. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):320–325. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.320-325.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Delgado G. A., Little P. B., Barnum D. A. A comparison of various Haemophilus somnus strains. Can J Comp Med. 1977 Oct;41(4):380–388. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNEDY P. C., BIBERSTEIN E. L., HOWARTH J. A., FRAZIER L. M., DUNGWORTH D. L. Infectious meningo-encephalitis in cattle, caused by a haemophilus-like organism. Am J Vet Res. 1960 Mar;21:403–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDade J. E., Shepard C. C., Fraser D. W., Tsai T. R., Redus M. A., Dowdle W. R. Legionnaires' disease: isolation of a bacterium and demonstration of its role in other respiratory disease. N Engl J Med. 1977 Dec 1;297(22):1197–1203. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197712012972202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard D. G., Macleod N. S. The isolation of Haemophilus somnus following sudden deaths in suckler calves in Scotland. Vet Rec. 1977 Feb 12;100(7):126–127. doi: 10.1136/vr.100.7.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigidi M. A., Hoerlein A. B. Characterization of the Haemophilus-like organism of infectious thromboembolic meningoencephalitis of cattle. Am J Vet Res. 1970 Jun;31(6):1017–1022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. P., Biberstein E. L. Septicemia and meningoencephalitis in pastured cattle caused by a Haemophilus-like organism ("Haemophilus somnus"). Cornell Vet. 1977 Jul;67(3):327–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Little P. B., Wilkie B. N., Barnum D. A. Infectious thromboembolic meningoencephalitis in cattle: a review. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1981 Feb 15;178(4):378–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


