Abstract
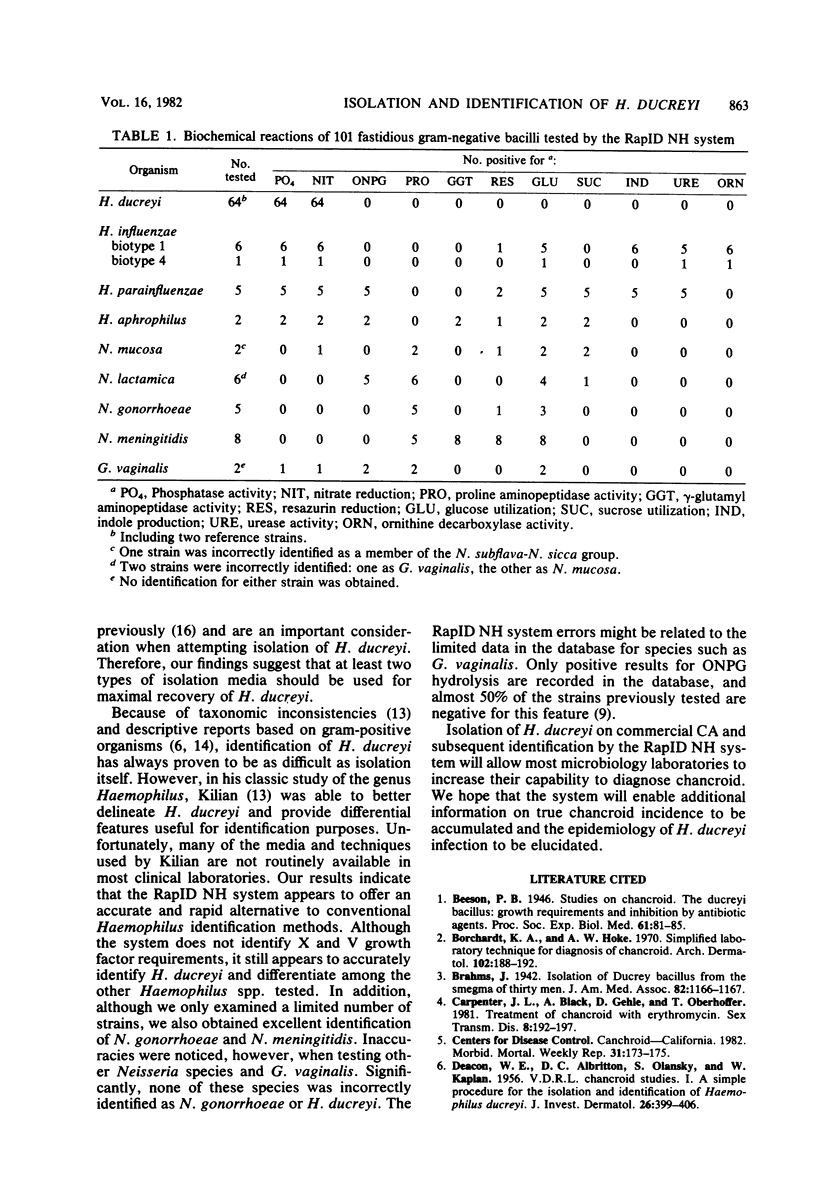
During a 2-month period, 62 strains of Haemophilus ducreyi were isolated from 168 genital lesions and 2 lymph node aspirates. Of these strains, 22 were found on both chocolate agar and fetal bovine serum agar supplemented with vancomycin, 29 were found only on chocolate agar, and 9 were found only on fetal bovine serum agar. Two additional strains were isolated on sheep blood agar. All of these isolates were correctly identified with the RapID NH system (Innovative Diagnostic Systems, Inc., Decatur, Ga.) a new identification kit that has a database for Haemophilus, Neisseria, and other genera that include fastidious gram-negative bacilli.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borchardt K. A., Hoke A. W. Simplified laboratory technique for diagnosis of chancroid. Arch Dermatol. 1970 Aug;102(2):188–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter J. L., Back A., Gehle D., Oberhoffer T. Treatment of chancroid with erythromycin. Sex Transm Dis. 1981 Jul-Sep;8(3):192–197. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198107000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEACON W. E., ALBRITTON D. C., OLANSKY S., KAPLAN W. V.D.R.L. chancroid studies. I. A simple procedure for the isolation and identification of Hemophilus ducreyi. J Invest Dermatol. 1956 May;26(5):399–406. doi: 10.1038/jid.1956.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick J. E., Tyler H., Jr, Gramstad N. D. Treatment of chancroid. Comparison of sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim with recommended therapies. JAMA. 1981 Oct 16;246(16):1804–1805. doi: 10.1001/jama.246.16.1804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood J. R., Pickett M. J. Salient features of Haemophilus vaginalis. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):200–204. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.200-204.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond G. W., Slutchuk M., Scatliff J., Sherman E., Wilt J. C., Ronald A. R. Epidemiologic, clinical, laboratory, and therapeutic features of an urban outbreak of chancroid in North America. Rev Infect Dis. 1980 Nov-Dec;2(6):867–879. doi: 10.1093/clinids/2.6.867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handsfield H. H., Totten P. A., Fennel C. L., Falkow S., Holmes K. K. Molecular epidemiology of Haemophilus ducreyi infections. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Sep;95(3):315–318. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-95-3-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M. A taxonomic study of the genus Haemophilus, with the proposal of a new species. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Mar;93(1):9–62. doi: 10.1099/00221287-93-1-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhofer T. R., Back A. E. Isolation and cultivation of Haemophilus ducreyi. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Apr;15(4):625–629. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.4.625-629.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottnek F. O., Biddle J. W., Kraus S. J., Weaver R. E., Stewart J. A. Isolation and identification of Haemophilus ducreyi in a clinical study. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Aug;12(2):170–174. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.2.170-174.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]