Abstract
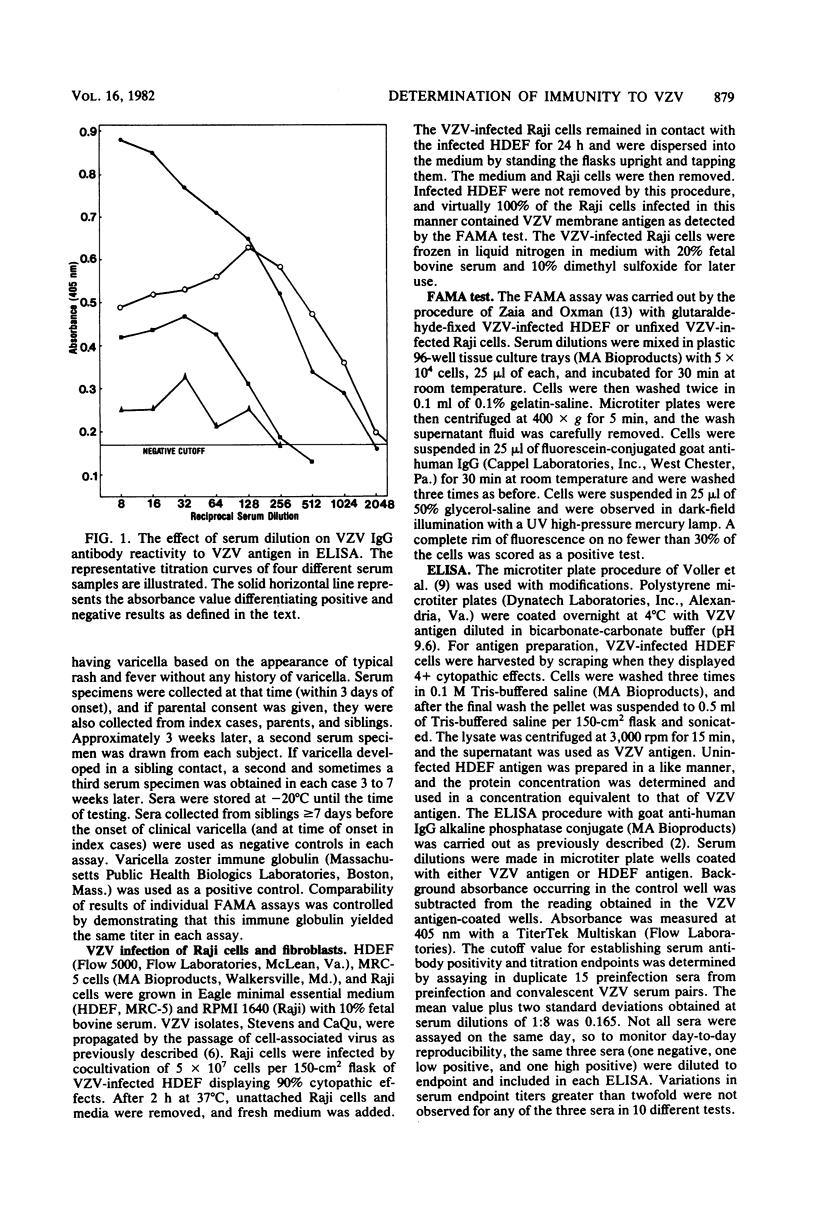
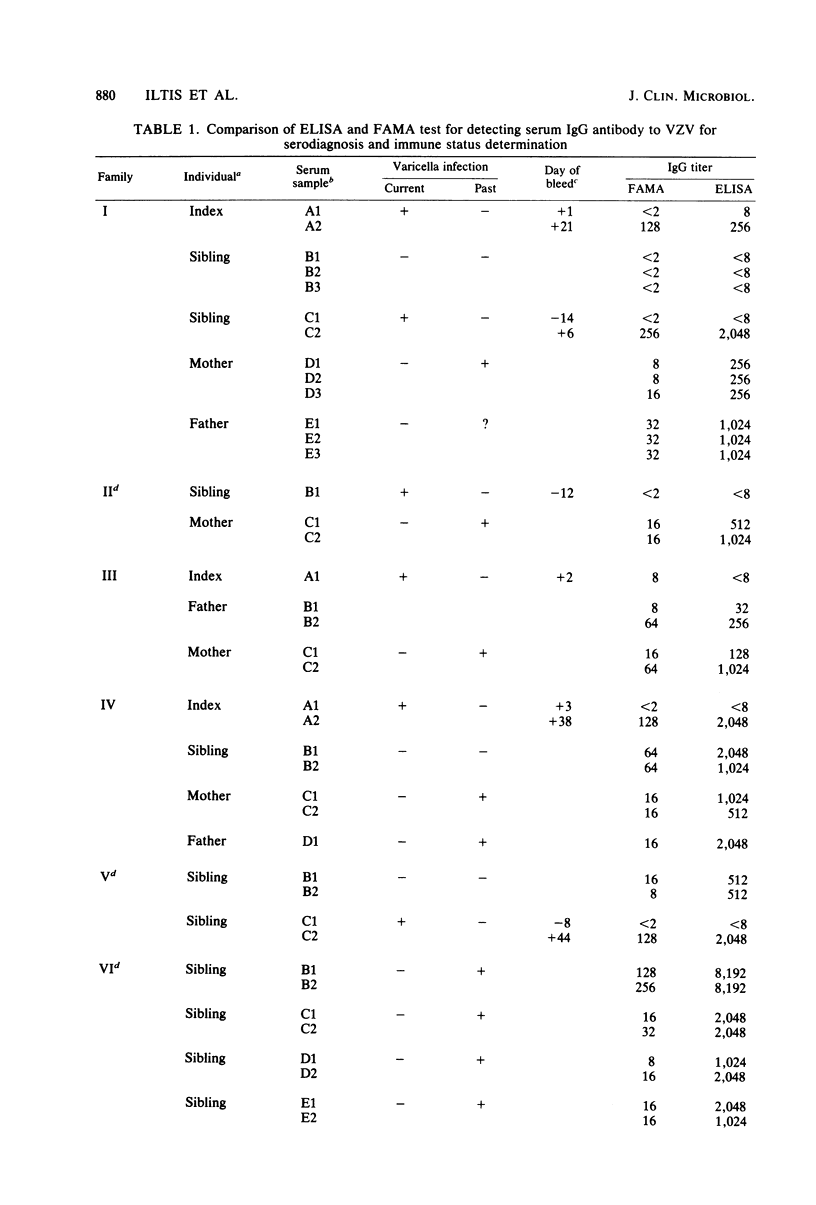
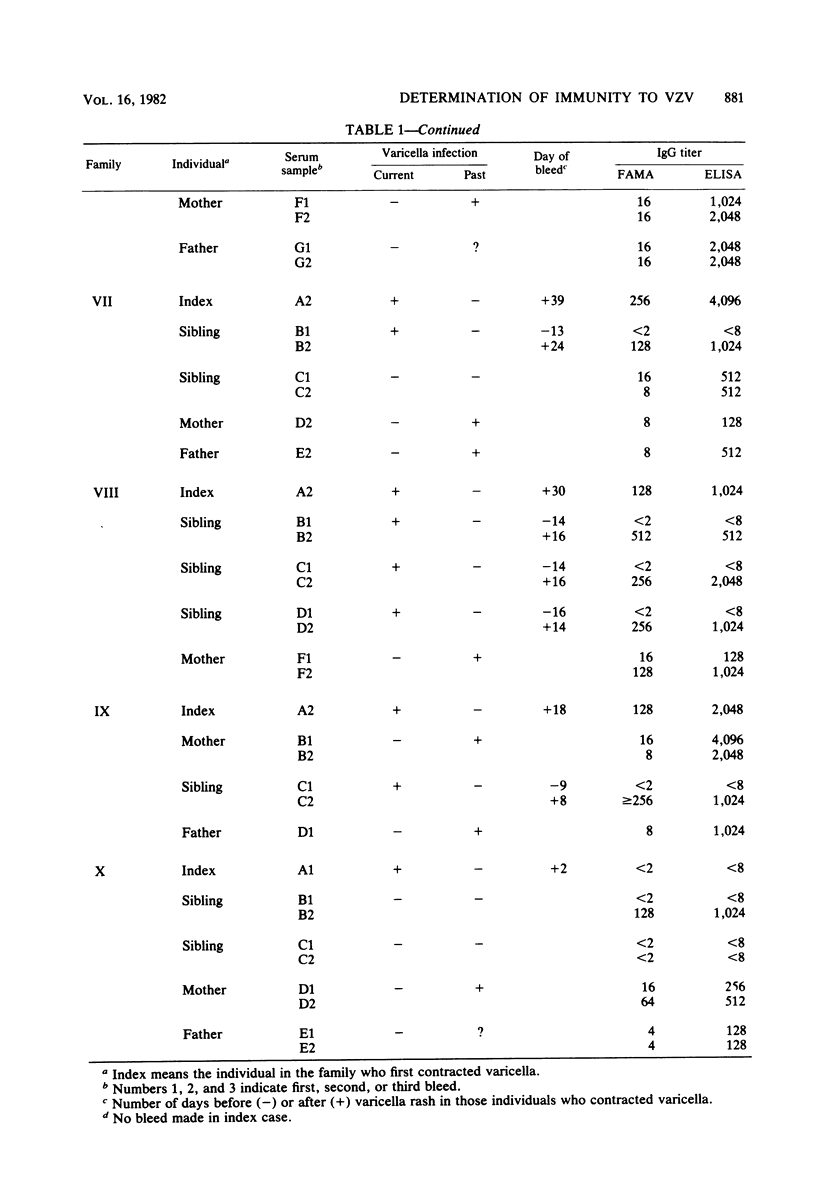
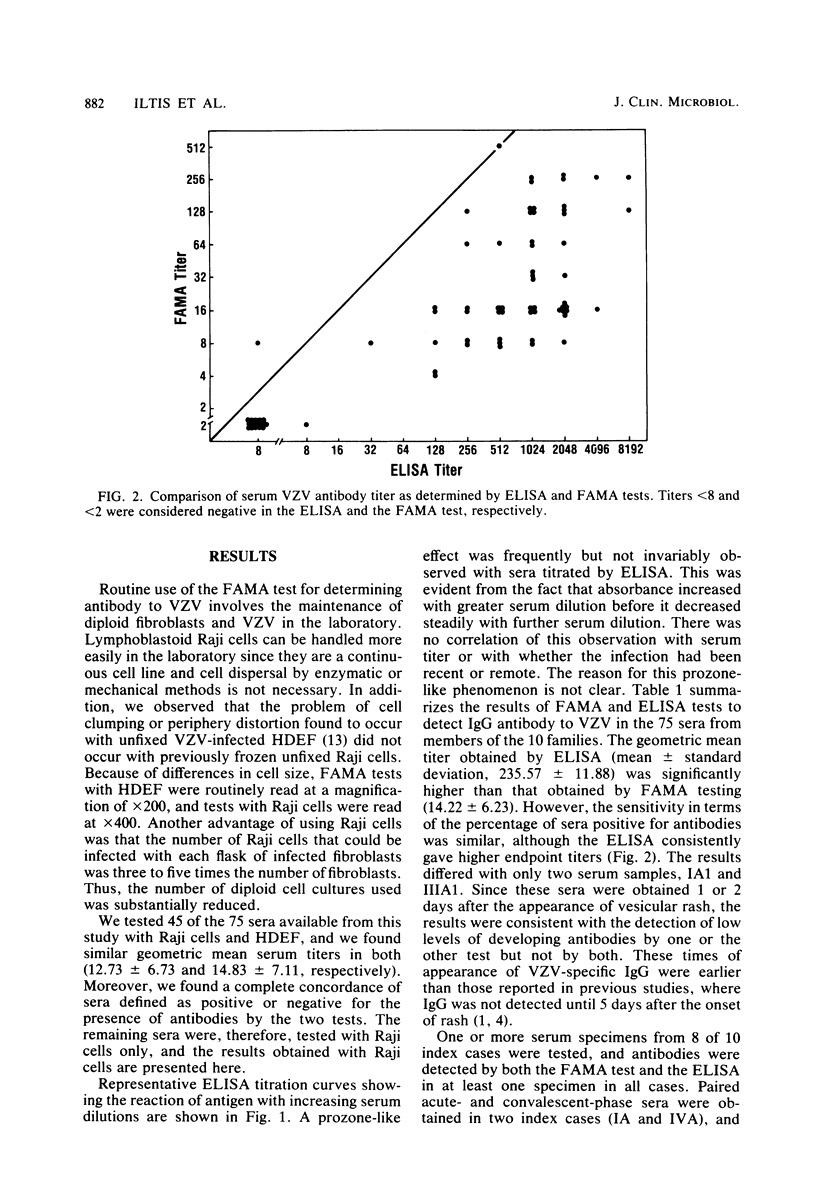
A prospective study was performed comparing the fluorescent antibody to membrane antigen (FAMA) test and the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for identifying susceptibility and seroconversion to varicella-zoster virus (VZV) infection. A total of 75 sera were collected from index cases and from sibling and parent contacts in 10 families. Varicella-zoster virus-infected human diploid embryonic fibroblasts and continuous lymphoblastoid cells (Raji cells) were compared as indicator cells in the FAMA test. Equivalent results were obtained with both types of cell. Results of the FAMA test and the ELISA were identical in two ways. (i) The same 11 individuals were initally defined as susceptible (seronegative), and 9 of them (82%) developed fourfold rises in antibody titers, clinical varicella, or both. (ii) Of 21 immune (seropositive) individuals, 4 developed fourfold antibody rises by FAMA tests, and 3 of these 4 responded by ELISA. Infection was asymptomatic in these individuals. The geometric mean titer by ELISA was significantly higher than by the FAMA test. The results indicated that the ELISA and the FAMA test have similar capacities to define susceptibility to varicella-zoster virus and that subclinical infection with varicella-zoster virus may be common.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brunell P. A., Gershon A. A., Uduman S. A., Steinberg S. Varicella-Zoster Immunoglobulins during Varicella, Latency, and Zoster. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jul;132(1):49–54. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forghani B., Schmidt N. J., Dennis J. Antibody assays for varicella-zoster virus: comparison of enzyme immunoassay with neutralization, immune adherence hemagglutination, and complement fixation. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Nov;8(5):545–552. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.5.545-552.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerna G., Cereda P. M., Cattaneo E., Achilli G., Gerna M. T. Antibody to early antigens of varicella-zoster virus during varicella and zoster. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jul;140(1):33–41. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon A., Steinberg S., Greenberg S., Taber L. Varicella-zoster-associated encephalitis: detection of specific antibody in cerebrospinal fluid. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Dec;12(6):764–767. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.6.764-767.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leventon-Kriss S., Gotlieb-Stematsky T., Vonsover A., Smetana Z. Infection and persistence of varicella-zoster virus in lymphoblastoid Raji cell line. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1979;167(4):275–283. doi: 10.1007/BF02120813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanley J., Myers M., Edmond B., Steele R. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibody to varicella-zoster virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):208–211. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.208-211.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E., Bartlett A. Enzyme immunoassays in diagnostic medicine. Theory and practice. Bull World Health Organ. 1976;53(1):55–65. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams V., Gershon A., Brunell P. A. Serologic response to varicella-zoster membrane antigens measured by direct immunofluorescence. J Infect Dis. 1974 Dec;130(6):669–672. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.6.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada A., Ogino S., Asano Y., Otsuka T., Takahashi M., Baba K., Yabuuchi H. Comparison of 4 serological tests--complement fixation, neutralization, fluorescent antibody to membrane antigen and immune adherence hemagglutination--for assay of antibody to varicella-zoster (V-Z) virus. Biken J. 1979 Jun;22(2):55–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaia J. A., Oxman M. N. Antibody to varicella-zoster virus-induced membrane antigen: immunofluorescence assay using monodisperse glutaraldehyde-fixed target cells. J Infect Dis. 1977 Oct;136(4):519–530. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.4.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


