Abstract
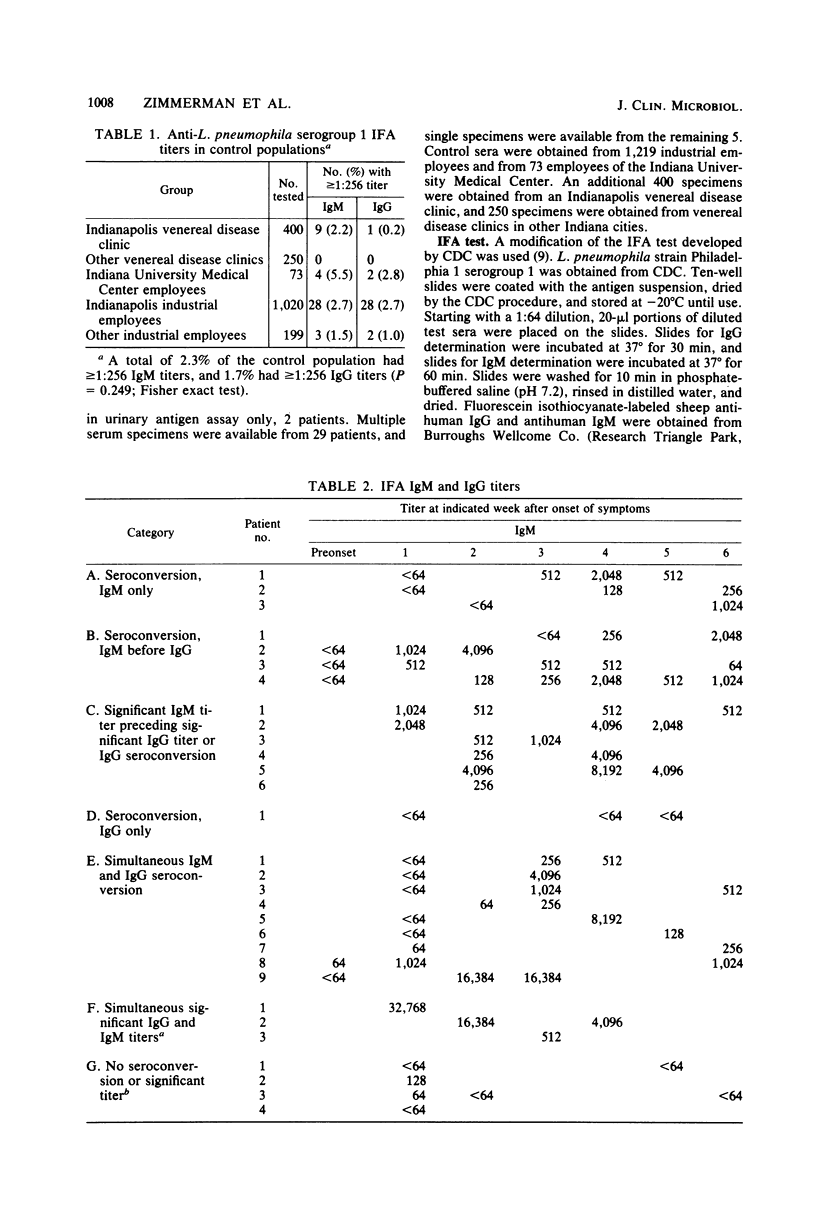
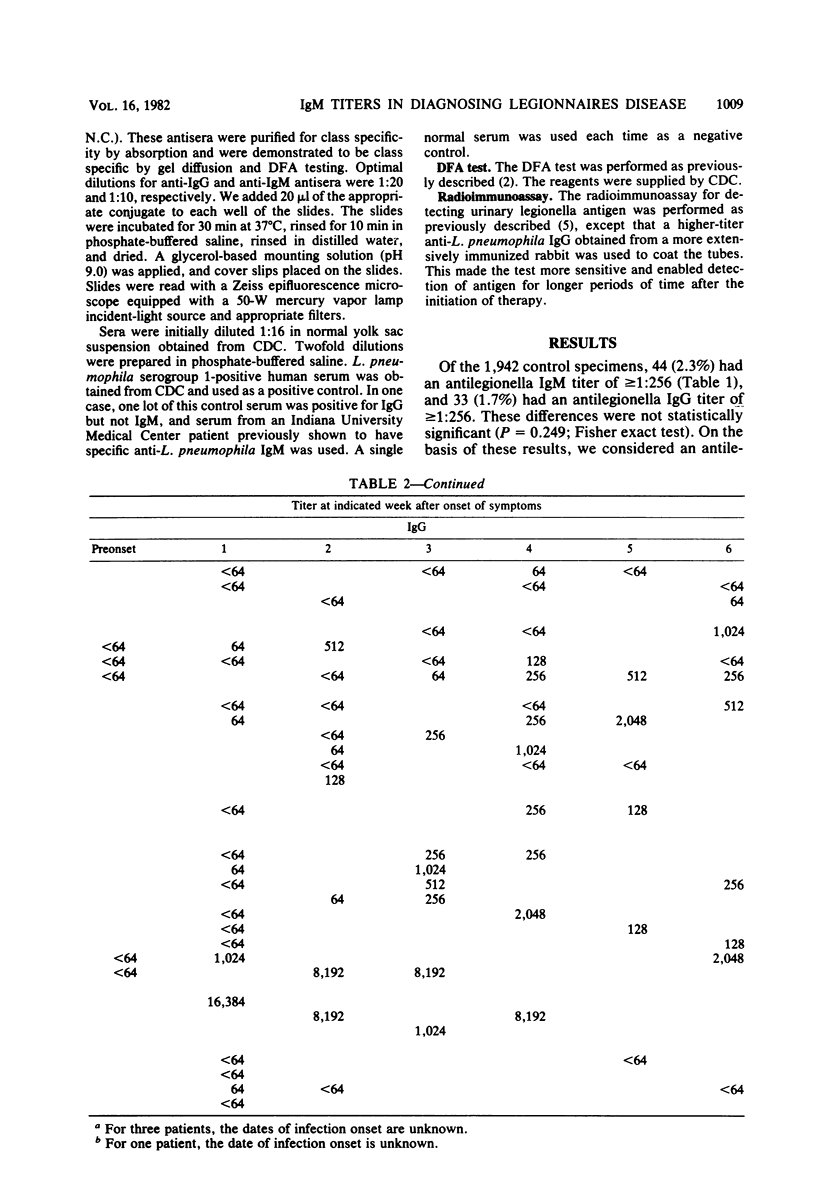
The purpose of this study was to determine whether measurement of immunoglobulin M (IgM) antibodies against Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 can aid in the diagnosis of Legionnaires disease. On the basis of measurements of antibody levels in 1,942 control sera, we used an IgM titer of 1:256, observed in 2.3% of the controls, as presumptive evidence of Legionnaires disease. Measurement of IgM titers permitted us to presumptively or definitively diagnose Legionnaires disease in 13 of 34 patients earlier than we would have if only IgG titers had been measured. Of the 13 patients, 5 were diagnosed serologically only by IgM antibody determination. IgM titers were presumptively diagnostic in week 1 of clinical symptoms in 4 of the 13 patients. We conclude that conjugates used for antilegionella indirect fluorescent-antibody tests should be capable of detecting IgM antibodies so that the value of serological results in diagnosing and managing Legionnaires disease will be maximized.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackmon J. A., Chandler F. W., Cherry W. B., England A. C., 3rd, Feeley J. C., Hicklin M. D., McKinney R. M., Wilkinson H. W. Legionellosis. Am J Pathol. 1981 Jun;103(3):429–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry W. B., Pittman B., Harris P. P., Hebert G. A., Thomason B. M., Thacker L., Weaver R. E. Detection of Legionnaires disease bacteria by direct immunofluorescent staining. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):329–338. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.329-338.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H., Meyer R. D., Finegold S. M. Laboratory diagnosis of Legionnaires' disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Feb;121(2):317–327. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.2.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby B. D., Snyder K. M., Meyer R. D., Finegold S. M. Legionnaires' disease: report of sixty-five nosocomially acquired cases of review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1980 May;59(3):188–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler R. B., Zimmerman S. E., Wilson E., Allen S. D., Edelstein P. H., Wheat L. J., White A. Rapid radioimmunoassay diagnosis of Legionnaires' disease: detection and partial characterization of urinary antigen. Ann Intern Med. 1981 May;94(5):601–605. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-5-601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagington J., Wreghitt T. G., Tobin J. O., Macrae A. D. The antibody response in Legionnaires' disease. J Hyg (Lond) 1979 Oct;83(2):377–381. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400026176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sathapatayavongs B., Kohler R. B., Wheat L. J., White A., Winn W. C., Jr, Girod J. C., Edelstein P. H. Rapid diagnosis of Legionnaires' disease by urinary antigen detection. Comparison of ELISA and radioimmunoassay. Am J Med. 1982 Apr;72(4):576–582. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90451-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Cruce D. D., Broome C. V. Validation of Legionella pneumophila indirect immunofluorescence assay with epidemic sera. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jan;13(1):139–146. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.1.139-146.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Farshy C. E., Fikes B. J., Cruce D. D., Yealy L. P. Measure of immunoglobulin G-, M-, and A-specific titers against Legionella pneumophila and inhibition of titers against nonspecific, gram-negative bacterial antigens in the indirect immunofluorescence test for legionellosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Nov;10(5):685–689. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.5.685-689.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


