Abstract
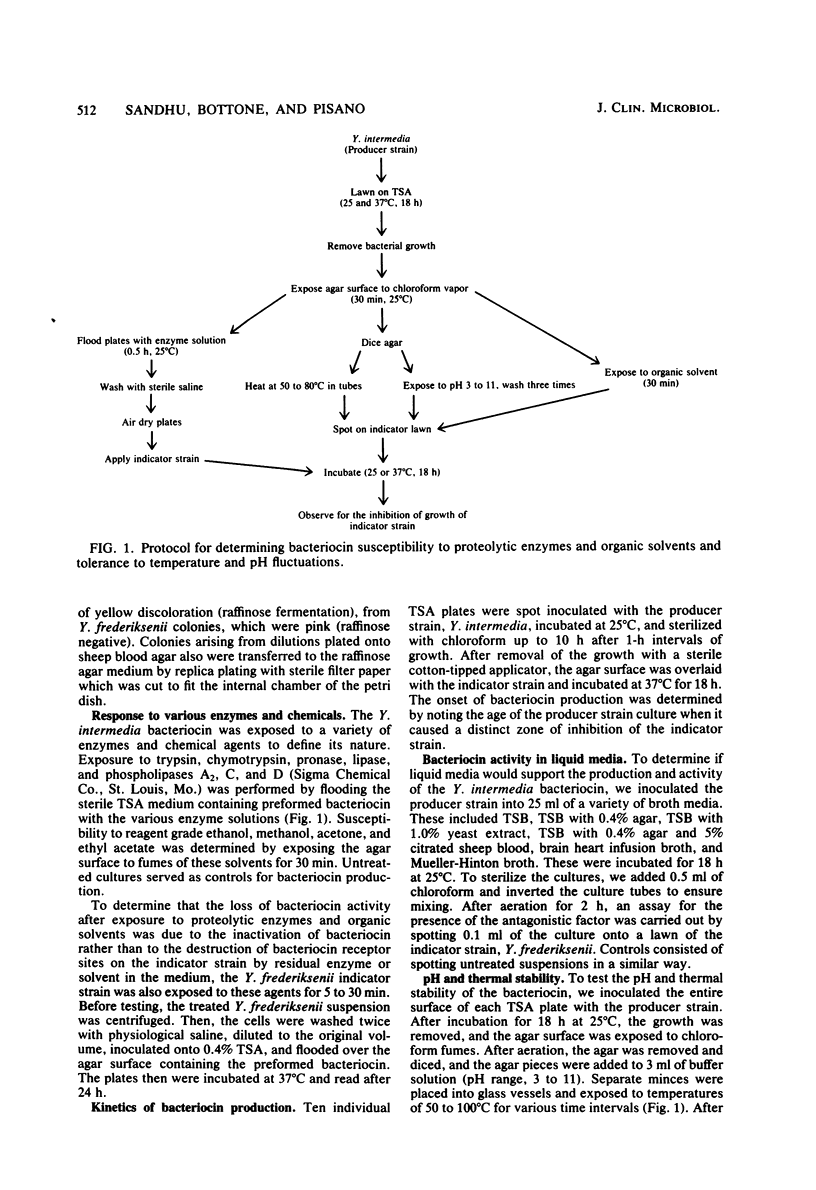
Yersinia intermedia produces a temperature-dependent (25 degrees C) bactericidal substance that is active against other Yersinia species. Crude preparations of the inhibitory substance were inactivated by chymotrypsin, trypsin, pronase, and heating but were not affected by lipolytic enzymes, chloroform, or other organic solvents. These data suggest that the active molecule is a bacteriocin of a proteinaceous nature. The molecular weight of the bacteriocin was estimated to be greater than 14,000. Exposure of agar fragments containing the active component to a pH range of 3 to 11 did not affect bactericidal activity. Bactericidal activity against the Y. frederiksenii indicator strain was shown by simultaneous and deferred antagonism and by the associative culture technique. The liquor from cell-free macerated agar fragments and broth cultures, however, were devoid of antibacterial activity.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEN-GURION R., HERTMAN I. Bacteriocin-like material produced by Pasteurella pestis. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Oct;19(2):289–297. doi: 10.1099/00221287-19-2-289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUBAKER R. R., SURGALLA M. J. Pesticins. I. Pesticinbacterium interrelationships, and environmental factors influencing activity. J Bacteriol. 1961 Dec;82:940–949. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.6.940-949.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottone E. J., Sandhu K. K., Pisano M. A. Yersinia intermedia: temperature-dependent bacteriocin production. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):433–436. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.433-436.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDERICQ P. Colicins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1957;11:7–22. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.11.100157.000255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy K. G. Colicinogeny and related phenomena. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Dec;39(4):464–515. doi: 10.1128/br.39.4.464-515.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagg J. R., Dajani A. S., Wannamaker L. W. Bacteriocins of gram-positive bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Sep;40(3):722–756. doi: 10.1128/br.40.3.722-756.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


