Abstract
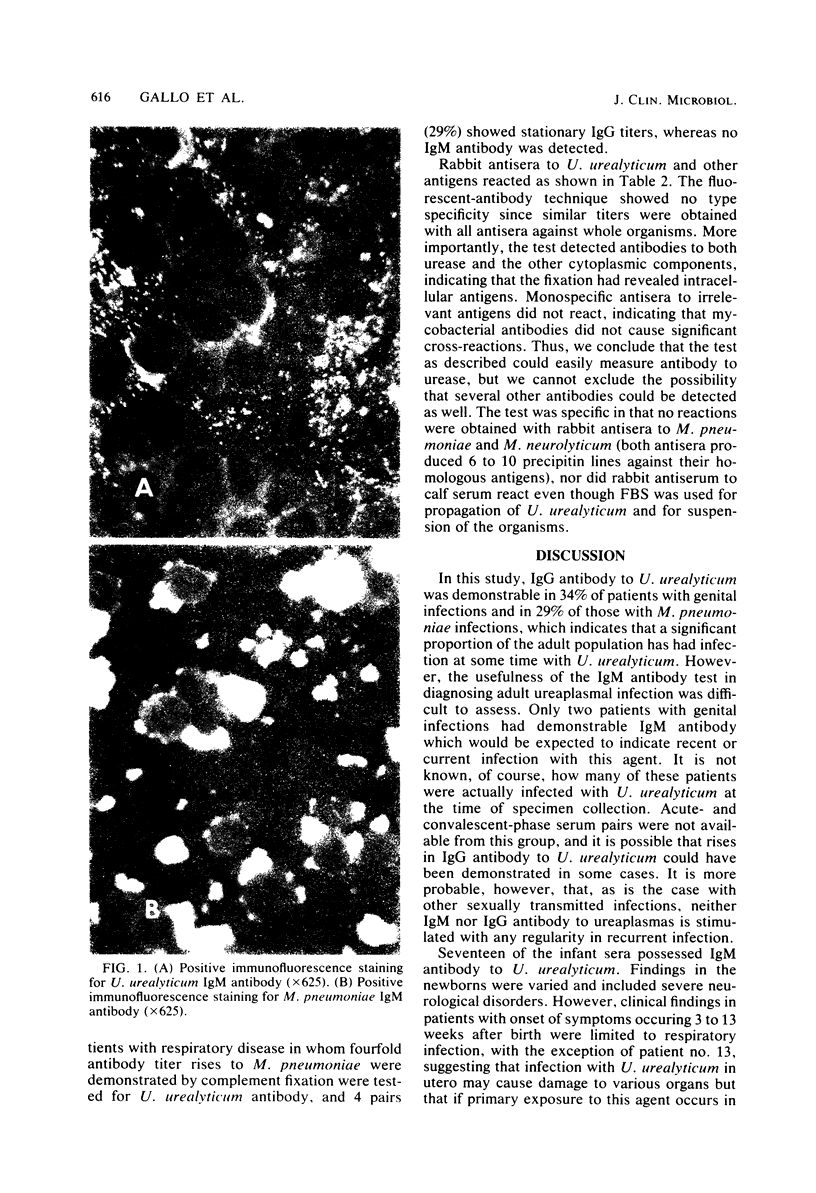
The indirect immunofluorescence test was used to measure immunoglobulin M (IgM) and IgG antibodies to acetone-fixed Ureaplasma urealyticum organisms in sera from 128 adults with genital infections and from 713 symptomatic newborns and babies 1 day to 18 months old. Thirty-four percent of the adults had demonstrable IgG antibody to ureaplasma. IgM antibody was detected in 2 of the adult sera and in 17 of the infant sera. These babies were divided into two distinct groups. Ten of the infants presented at birth with various physical findings, whereas the onset of symptoms for the other 7 occurred 3 to 13 weeks after birth, and the major clinical finding in 6 of the 7 was respiratory distress. The results of this study suggested that U. urealyticum infection may be associated with fetal damage and infant pneumonia, and if this is substantiated, the indirect immunofluorescence test employing acetone-fixed antigen to measure IgM antibody to U. urealyticum may be an important diagnostic tool.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander A. G., Kenny G. E. Characterization of membrane and cytoplasmic antigens of Mycoplasma arginini by two-dimensional (crossed) immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):313–321. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.313-321.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black F. T. Modifications of the growth inhibition test and its application to human T-mycoplasmas. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Apr;25(4):528–533. doi: 10.1128/am.25.4.528-533.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Embree J. E., Krause V. W., Embil J. A., MacDonald S. Placental infection with Mycoplasma homonis and Ureaplasma urealyticum: clinical correlation. Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Oct;56(4):475–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foy H. M., Kenny G. E., Levinsohn E. M., Grayston J. T. Acquisition of mycoplasmata and T-strains during infancy. J Infect Dis. 1970 Jun;121(6):579–587. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.6.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo D., Riggs J. L., Schachter J., Emmons R. W. Multiple-antigen slide test for detection of immunoglobulin M antibodies in newborn and infant sera by immunofluorescence. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Apr;13(4):631–636. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.4.631-636.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E., Cartwright F. D. Effect of urea concentration on growth of Ureaplasma urealyticum (T-strain mycoplasma). J Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;132(1):144–150. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.1.144-150.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E. Immunogenicity of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):510–515. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.510-515.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kundsin R. B., Driscoll S. G., Pelletier P. A. Ureaplasma urealyticum incriminated in perinatal morbidity and mortality. Science. 1981 Jul 24;213(4506):474–475. doi: 10.1126/science.7244646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinikki P. O., Panzar P., Tykkä H. Immunoglobulin M antibody response against Mycoplasma pneumoniae lipid antigen in patients with acute pancreatitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Aug;8(2):113–118. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.2.113-118.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinikki P., Pantzar P., Tykkä H. Antibody response in patients with acute pancreatitis to mycoplasma pneumoniae. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1973;8(7):631–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. S., Kendrick M. I., Kass E. H. Serologic typing of human genital T-mycoplasmas by a complement-dependent mycoplasmacidal test. J Infect Dis. 1972 Dec;126(6):658–663. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.6.658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H., Taylor-Robinson D., Wong D., Chanock R. M. Color test for the measurement of antibody to T-strain mycoplasmas. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):6–12. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.1.6-12.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendal S., Black F. T. Direct and indirect immunofluorescence of unfixed and fixed Mycoplasma colonies. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(4):615–622. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00186.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard M. C., Lunceford C. D. Serological typing of Ureaplasma urealyticum isolates from urethritis patients by an agar growth inhibition method. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Nov;8(5):566–574. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.5.566-574.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stagno S., Brasfield D. M., Brown M. B., Cassell G. H., Pifer L. L., Whitley R. J., Tiller R. E. Infant pneumonitis associated with cytomegalovirus, Chlamydia, Pneumocystis, and Ureaplasma: a prospective study. Pediatrics. 1981 Sep;68(3):322–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stemke G. W., Robertson J. A. Modified colony indirect epifluorescence test for serotyping Ureaplasma urealyticum and an adaptation to detect common antigenic specificity. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Nov;14(5):582–584. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.5.582-584.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Csonka G. W., Prentice M. J. Human intra-urethral inoculation of ureplasmas. Q J Med. 1977 Jul;46(183):309–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., McCormack W. M. The genital mycoplasmas (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1980 May 1;302(18):1003–1010. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198005013021805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]