Abstract
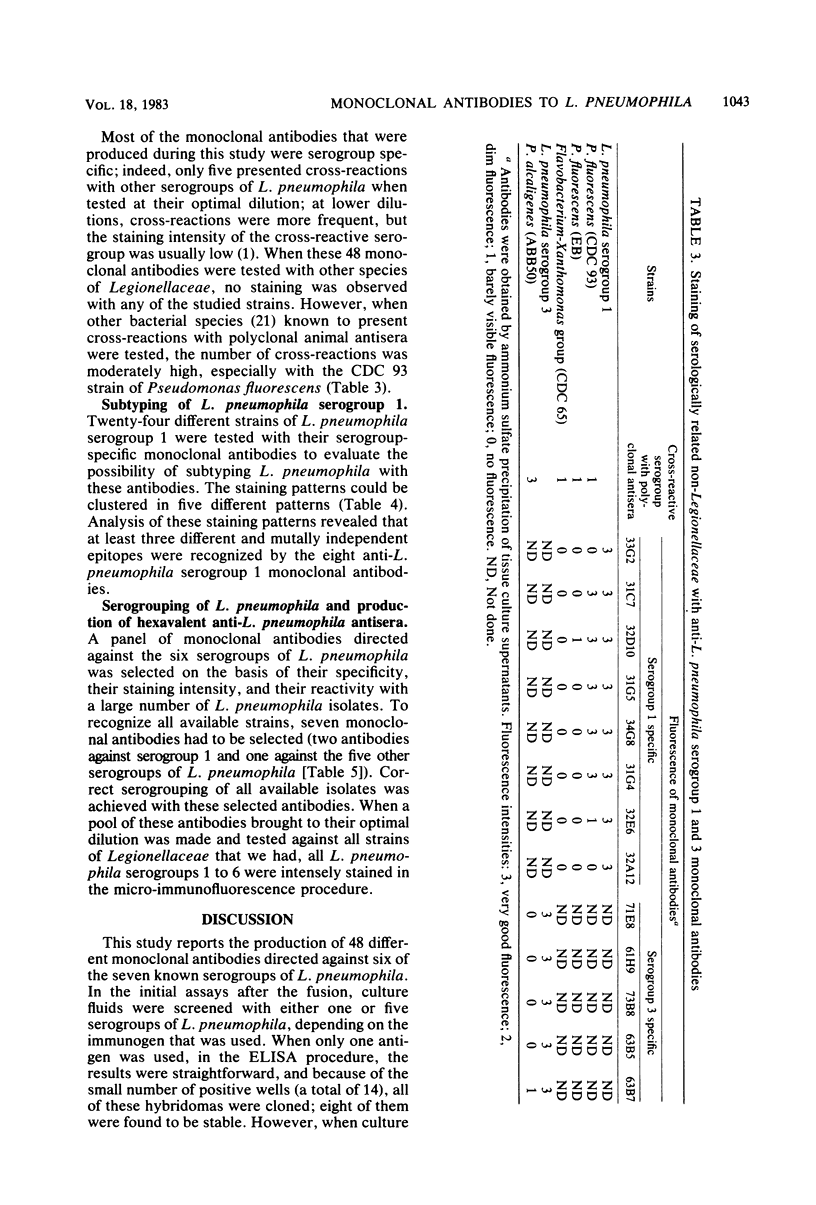
Monoclonal antibodies directed against Legionella pneumophila serogroups 1 to 6 were produced by fusing splenocytes of BALB/c mice with the Sp 2/0-Ag14 or the NSO mouse myeloma cell lines. Specificity of these antibodies was determined by indirect fluorescent-antibody staining: 8 reacted with L. pneumophila serogroup 1 and, respectively, 13, 6, 6, 5, and 10 reacted with serogroups 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6; all except 5 were serogroup specific, and none presented cross-reactions with six other species of Legionellaceae. Serogroup determination of 35 isolates of L. pneumophila with seven selected monoclonal antibodies resulted in correct serogrouping in all instances; a pool of the same seven monoclonal antibodies stained intensely all strains of L. pneumophila without any staining of the other species of Legionellaceae. When 24 serogroup 1 isolates of L. pneumophila were stained with eight serogroup 1-specific monoclonal antibodies, the staining patterns could be clustered in five distinct groups. These hybridomas thus represent an unlimited source of standard reagent that could be used in the detection and serogrouping of L. pneumophila; differences in staining patterns could be used as epidemiological markers for these bacteria.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg R. A., Yolken R. H., Rennard S. I., Dolin R., Murphy B. R., Straus S. E. New enzyme immunoassays for measurement of influenza A/Victoria/3/75 virus in nasal washes. Lancet. 1980 Apr 19;1(8173):851–853. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91356-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb W. F., Arnow P. M., Dellinger D. L., Perryman S. R. Isolation and characterization of a seventh serogroup of Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Feb;17(2):346–348. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.2.346-348.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A., Vickers R. M., Elder E. M., Lema M., Garrity G. M. Plasmid and surface antigen markers of endemic and epidemic Legionella pneumophila strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Aug;16(2):230–235. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.2.230-235.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry W. B., Pittman B., Harris P. P., Hebert G. A., Thomason B. M., Thacker L., Weaver R. E. Detection of Legionnaires disease bacteria by direct immunofluorescent staining. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):329–338. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.329-338.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. T., Cho S. N., Høiby N., Espersen F., Baek L., Reif J. S. Crossed immunoelectrophoretic analysis of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 antigens. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1428–1440. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1428-1440.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. T., Espersen F., Høiby N., Cho S. N., Friis-Møller A., Reif J. S. Cross-reactions between Legionella pneumophila (serogroup 1) and twenty-eight other bacterial species, including other members of the family Legionellaceae. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1441–1456. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1441-1456.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H. Improved semiselective medium for isolation of Legionella pneumophila from contaminated clinical and environmental specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):298–303. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.298-303.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England A. C., 3rd, Fraser D. W., Plikaytis B. D., Tsai T. F., Storch G., Broome C. V. Sporadic legionellosis in the United States: the first thousand cases. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Feb;94(2):164–170. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-2-164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliermans C. B., Cherry W. B., Orrison L. H., Smith S. J., Tison D. L., Pope D. H. Ecological distribution of Legionella pneumophila. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):9–16. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.9-16.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser D. W., Tsai T. R., Orenstein W., Parkin W. E., Beecham H. J., Sharrar R. G., Harris J., Mallison G. F., Martin S. M., McDade J. E. Legionnaires' disease: description of an epidemic of pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 1977 Dec 1;297(22):1189–1197. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197712012972201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfrè G., Milstein C. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies: strategies and procedures. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):3–46. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrity G. M., Elder E. M., Davis B., Vickers R. M., Brown A. Serological and genotypic diversity among serogroup 5- reacting environmental Legionella isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Apr;15(4):646–653. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.4.646-653.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly J. R., Kenny G. E. Antigenic analysis of Legionella pneumophila and Tatlockia micdadei (Legionella micdadei) by two-dimensional (crossed) immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):721–729. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.721-729.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E., Dunsmoor C. L. Principles, problems, and strategies in the use of antigenic mixtures for the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;17(4):655–665. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.4.655-665.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane J. T., Finch R. G., Ward M. J., Macrae A. D. Hospital study of adult community-acquired pneumonia. Lancet. 1982 Jul 31;2(8292):255–258. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90334-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney R. M., Thacker L., Harris P. P., Lewallen K. R., Hebert G. A., Edelstein P. H., Thomason B. M. Four serogroups of Legionnaires' disease bacteria defined by direct immunofluorescence. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):621–624. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney R. M., Wilkinson H. W., Sommers H. M., Fikes B. J., Sasseville K. R., Yungbluth M. M., Wolf J. S. Legionella pneumophila serogroup six: isolation from cases of legionellosis, identification by immunofluorescence staining, and immunological response to infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):395–401. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.395-401.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orrison L. H., Bibb W. F., Cherry W. B., Thacker L. Determination of antigenic relationships among legionellae and non-legionellae by direct fluorescent-antibody and immunodiffusion tests. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Feb;17(2):332–337. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.2.332-337.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasculle A. W., Feeley J. C., Gibson R. J., Cordes L. G., Myerowitz R. L., Patton C. M., Gorman G. W., Carmack C. L., Ezzell J. W., Dowling J. N. Pittsburgh pneumonia agent: direct isolation from human lung tissue. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jun;141(6):727–732. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.6.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine L., George J. R., Reeves M. W., Harrell W. K. Development of a chemically defined liquid medium for growth of Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 May;9(5):615–626. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.5.615-626.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman M., Wilde C. D., Köhler G. A better cell line for making hybridomas secreting specific antibodies. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):269–270. doi: 10.1038/276269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. P., Grayston J. T. Immunologic relationship between genital TRIC, lymphogranuloma venereum, and related organisms in a new microtiter indirect immunofluorescence test. Am J Ophthalmol. 1970 Sep;70(3):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(70)90096-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Farshy C. E., Fikes B. J., Cruce D. D., Yealy L. P. Measure of immunoglobulin G-, M-, and A-specific titers against Legionella pneumophila and inhibition of titers against nonspecific, gram-negative bacterial antigens in the indirect immunofluorescence test for legionellosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Nov;10(5):685–689. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.5.685-689.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Fikes B. J., Cruce D. D. Indirect immunofluorescence test for serodiagnosis of Legionnaires disease: evidence for serogroup diversity of Legionnaires disease bacterial antigens and for multiple specificity of human antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Mar;9(3):379–383. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.3.379-383.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Reingold A. L., Brake B. J., McGiboney D. L., Gorman G. W., Broome C. V. Reactivity of serum from patients with suspected legionellosis against 29 antigens of legionellaceae and Legionella-like organisms by indirect immunofluorescence assay. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jan;147(1):23–31. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. H., Schalla W. O., Arko R. J., Bullard J. C., Feeley J. C. Immunochemical, serologic, and immunologic properties of major antigens isolated from the Legionnaires' disease bacterium. Observations bearing on the feasibility of a vaccine. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):634–638. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. L., Kroboth F. J., Shonnard J., Brown A., McDearman S., Magnussen M. Legionnaires' disease: new clinical perspective from a prospective pneumonia study. Am J Med. 1982 Sep;73(3):357–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de StGroth S. F., Scheidegger D. Production of monoclonal antibodies: strategy and tactics. J Immunol Methods. 1980;35(1-2):1–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


