Abstract
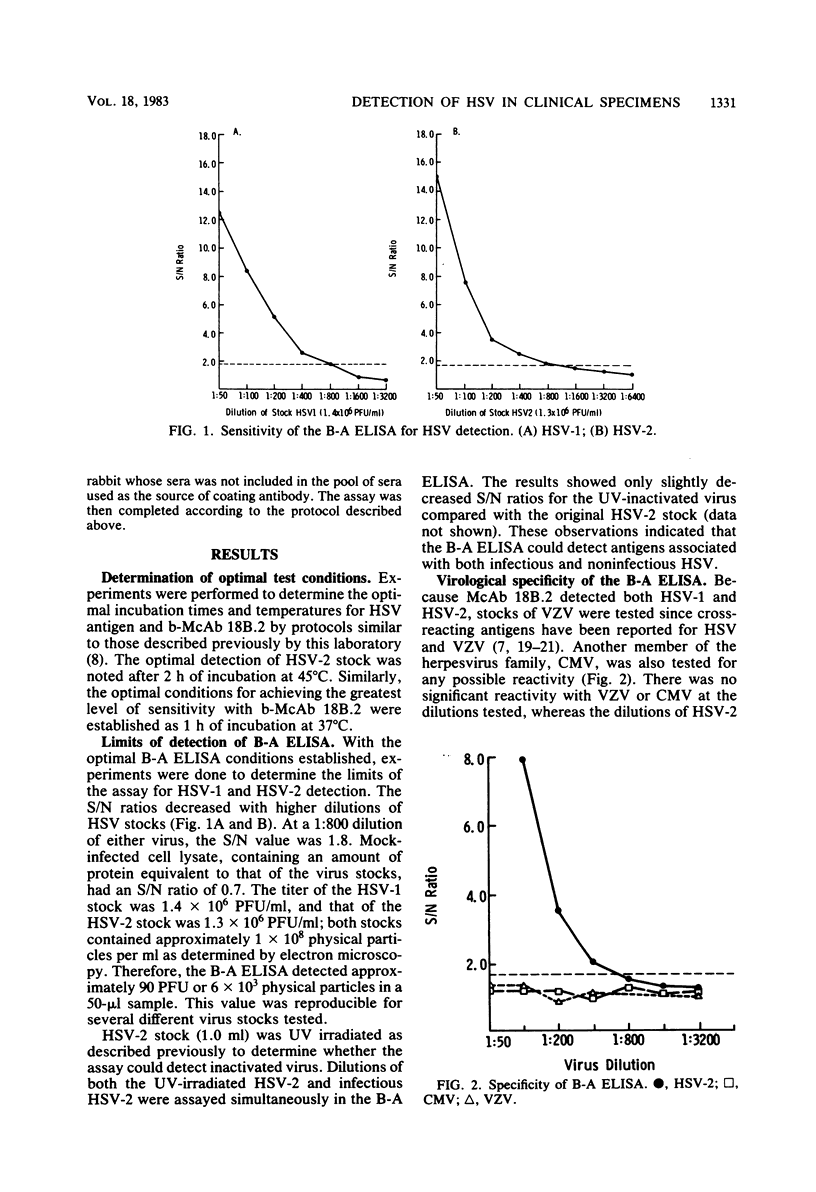
A biotin-avidin-amplified enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (B-A ELISA) has been developed to detect herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) and HSV-2 antigens in clinical specimens. The test was designed as a solid-phase, double-antibody, sandwich assay in which plates were coated with a polyclonal rabbit immunoglobulin G anti-HSV reagent, and the sandwich antibody was a biotin-labeled mouse immunoglobulin M monoclonal antibody that reacts with a common antigen associated with HSV-1 and HSV-2. The test can be completed in 4 h if antibody-coated plates are available. The detection limit of the B-A ELISA, determined by titration of virus stocks, was found to be approximately 90 PFU or 6 X 10(3) physical particles of either HSV-1 or HSV-2 per 50 microliter of virus stock. The following results were obtained in a study in which swabs were taken from a variety of lesions and assayed for infectivity in tissue culture and by B-A ELISA. Of 421 suspected HSV lesions tested, 69 were positive by both tests and 159 were negative by both tests. A total of 122 were positive by B-A ELISA but negative for infectivity. Seventy-one were negative by B-A ELISA but contained infectious virus. The HSV specificity of the assay was substantiated by partial blocking of reactivity with rabbit immunoglobulin G anti-HSV and by the absence of reactivity with a nonspecific biotin-labeled mouse immunoglobulin M monoclonal antibody.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam E., Dreesman G. E., Kaufman R. H., Melnick J. L. Asymptomatic virus shedding after herpes genitalis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Aug 1;137(7):827–830. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(80)90893-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balachandran N., Frame B., Chernesky M., Kraiselburd E., Kouri Y., Garcia D., Lavery C., Rawls W. E. Identification and typing of herpes simplex viruses with monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jul;16(1):205–208. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.1.205-208.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreesman G. R., Benyesh-Melnick M. Spectrum of human cytomegalovirus complement-fixing antigens. J Immunol. 1967 Dec;99(6):1106–1114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M. Avidin. Adv Protein Chem. 1975;29:85–133. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60411-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guesdon J. L., Ternynck T., Avrameas S. The use of avidin-biotin interaction in immunoenzymatic techniques. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979 Aug;27(8):1131–1139. doi: 10.1177/27.8.90074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPSENBERG J. G. POSSIBLE ANTIGENIC RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN VARICELLA ZOSTER VIRUS AND HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1964 Sep 9;15:67–73. doi: 10.1007/BF01241422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall C., Ionescu-Matiu I., Dreesman G. R. Utilization of the biotin/avidin system to amplify the sensitivity of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). J Immunol Methods. 1983 Feb 11;56(3):329–339. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(83)80022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy R. C., Adler-Storthz K., Henkel R. D., Dreesman G. R. Characteristics of a shared idiotype by two IgM anti-herpes simplex virus monoclonal antibodies that recognize different determinants. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1943–1946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCombs R. M., Melnick M. B., Brunschwig J. P. Biophysical studies of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):803–812. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.803-812.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerurkar L. S., Jacob A. J., Madden D. L., Sever J. L. Detection of genital herpes simplex infections by a tissue culture-fluorescent-antibody technique with biotin-avidin. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jan;17(1):149–154. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.1.149-154.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilheden E., Jeansson S., Vahlne A. Typing of herpes simplex virus by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;17(4):677–680. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.4.677-680.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Dondero D. V., Gallo D., Devlin V., Woodie J. D. Serological analysis of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 with monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):363–367. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.363-367.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson E., Schmidt O. W., Goldstein L. C., Nowinski R. C., Corey L. Typing of clinical herpes simplex virus isolates with mouse monoclonal antibodies to herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2: comparison with type-specific rabbit antisera and restriction endonuclease analysis of viral DNA. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jan;17(1):92–96. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.1.92-96.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pronovost A. D., Baumgarten A., Andiman W. A. Chemiluminescent immunoenzymatic assay for rapid diagnosis of viral infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Aug;16(2):345–349. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.2.345-349.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pronovost A. D., Baumgarten A., Hsiung G. D. Sensitive chemiluminescent enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for quantification of human immunoglobulin G and detection of herpes simplex virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jan;13(1):97–101. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.1.97-101.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D., Cleveland P. H., Oxman M. N. A rapid enzyme immunofiltration technique using monoclonal antibodies to serotype herpes simplex virus. J Med Virol. 1982;9(4):299–305. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890090408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J. Further evidence for common antigens in herpes simplex and varicella-zoster viruses. J Med Virol. 1982;9(1):27–36. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890090105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H., Magoffin R. L. Immunological relationship between herpes simplex and varicella-zoster viruses demonstrated by complement-fixation, neutralization and fluorescent antibody tests. J Gen Virol. 1969 Apr;4(3):321–328. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-4-3-321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiraki K., Okuno T., Yamanishi K., Takahashi M. Polypeptides of varicella-zoster virus (VZV) and immunological relationship of VZV and herpes simplex virus (HSV). J Gen Virol. 1982 Aug;61(Pt 2):255–269. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-61-2-255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wands J. R., Bruns R. R., Carlson R. I., Ware A., Menitove J. E., Isselbacher K. J. Monoclonal IgM radioimmunoassay for hepatitis B surface antigen: high binding activity in serum that is unreactive with conventional antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1277–1281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wands J. R., Carlson R. I., Schoemaker H., Isselbacher K. J., Zurawski V. R., Jr Immunodiagnosis of hepatitis B with high-affinity IgM monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1214–1218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H. Enzyme immunoassays for the detection of infectious antigens in body fluids: current limitations and future prospects. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Jan-Feb;4(1):35–68. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Leister F. J., Whitcomb L. S., Santosham M. Enzyme immunoassays for the detection of bacterial antigens utilizing biotin-labeled antibody and peroxidase biotin--avidin complex. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Feb 11;56(3):319–327. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(83)80021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Stopa P. J. Enzyme-linked fluorescence assay: Ultrasensitive solid-phase assay for detection of human rotavirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Sep;10(3):317–321. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.3.317-321.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


