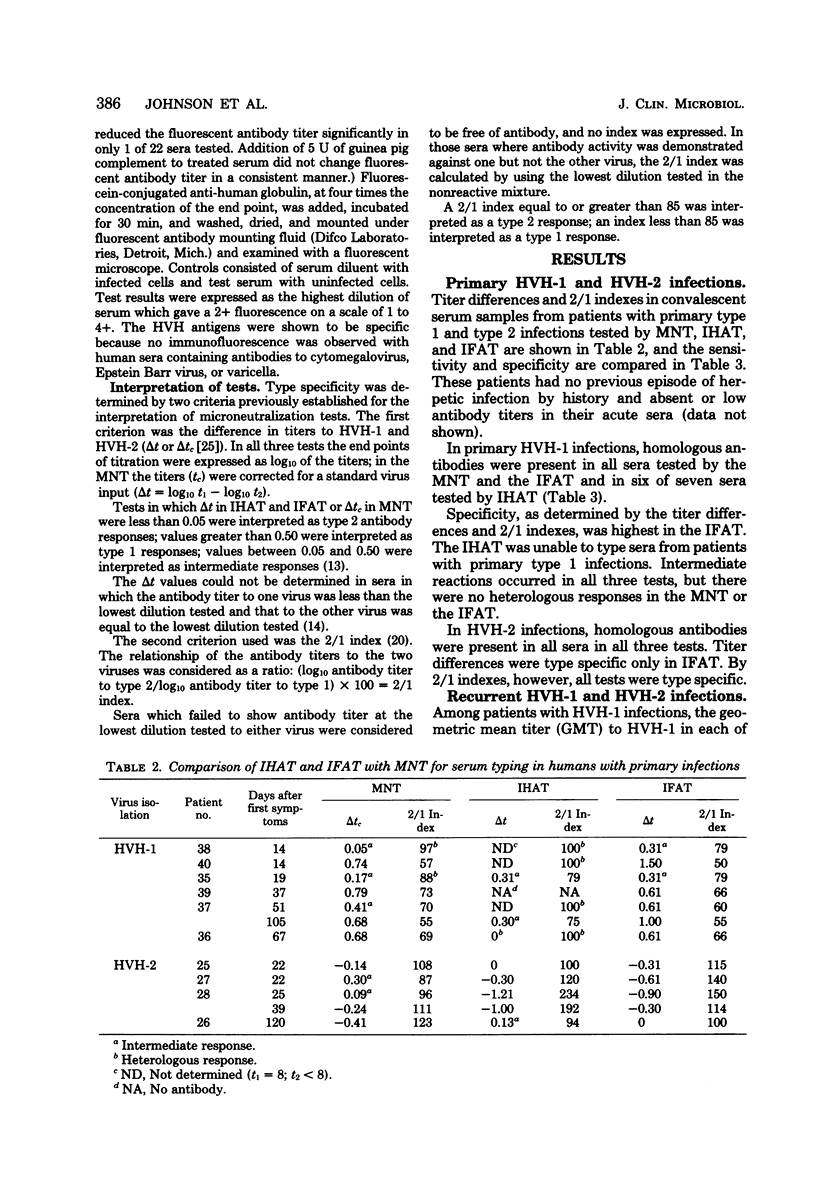
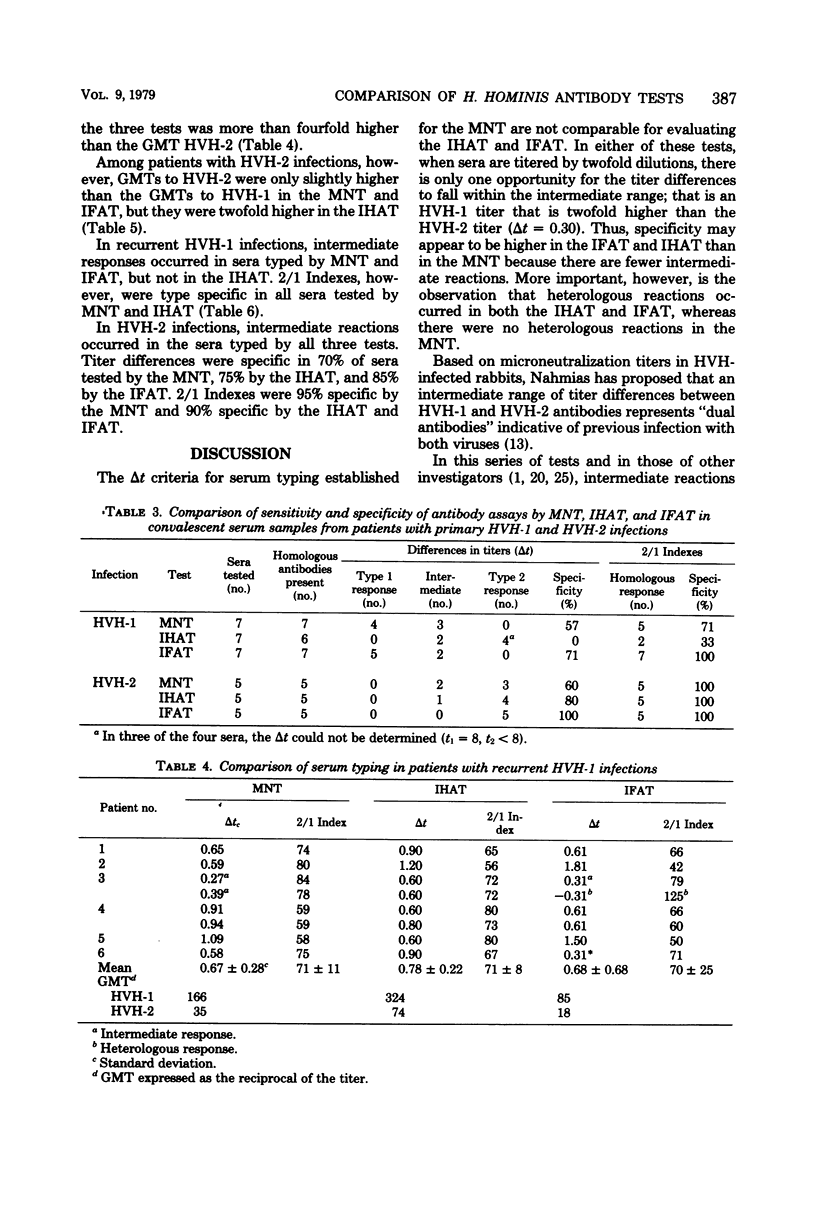
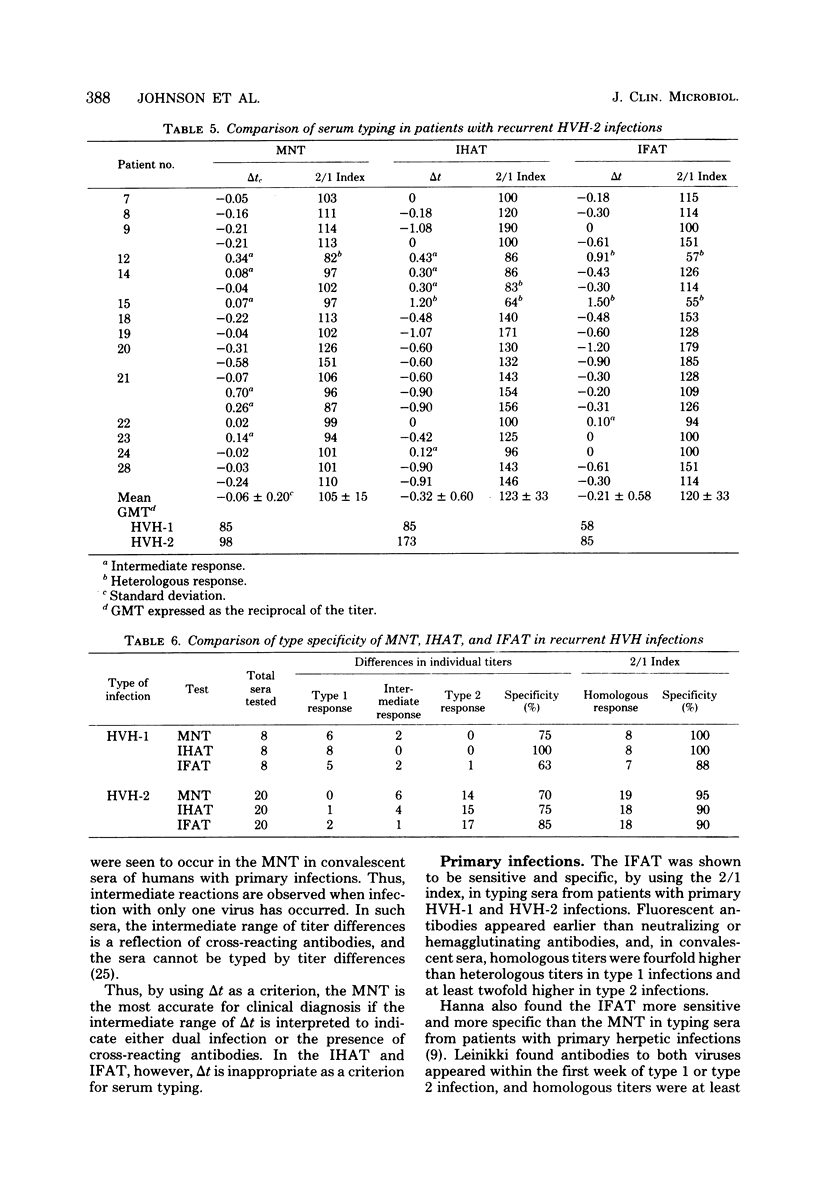
Abstract
Indirect hemagglutinating and immunofluorescent antibody responses to Herpesvirus hominis types 1 and 2 were compared to neutralizing antibody responses in infected humans from whom H. hominis type 1 or 2 was isolated. The indirect immunofluorescent antibody test was shown to be the most sensitive and specific for primary human infections. The sensitivity and specificity of the indirect hemagglutination and the immunofluorescent antibody tests were shown to be equal to that of the microneutralization test among patients who had primary or recurrent H. hominis type 2 infections. It is suggested that the indirect hemagglutination test is preferable for assaying large populations for previous infection with H. hominis type 2 because it is rapid, easier to perform, and more economical. The intermediate range of titer differences (deltat) between H. hominis types 1 and 2 previously reported to be due to infections with both viruses was shown to occur in all three tests among patients with primary infections with either virus.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Back A. F., Schmidt N. J. Indirect hemagglutinating antibody response to Herpesvirus hominis types 1 and 2 in immunized laboratory animals and in natural infections of man. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Sep;28(3):392–399. doi: 10.1128/am.28.3.392-399.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Back A. F., Schmidt N. J. Typing Herpesvirus hominis antibodies and isolates by inhibition of the indirect hemagglutination reaction. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Sep;28(3):400–405. doi: 10.1128/am.28.3.400-405.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein M. T., Stewart J. A. Method for typing antisera to Herpesvirus hominis by indirect hemagglutination inhibition. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Apr;21(4):680–684. doi: 10.1128/am.21.4.680-684.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catalano L. W., Jr, Johnson L. D. Herpesvirus antibody and carcinoma in situ of the cervix. JAMA. 1971 Jul 26;217(4):447–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho C. T., Feng K. K., Brahmacupta N., Liu C. Immunofluorescent staining for the measurement of antibodies to Herpesvirus hominis. J Infect Dis. 1975 Sep;132(3):311–315. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.3.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser C. E., Meléndez L. V., Daniel M. D., Barahona H. H. Fluorescent antibody studies on herpesviruses from new-world primates. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Jul;49(1):291–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuccillo D. A., Moder F. L., Catalano L. W., Jr, Vincent M. M., Sever J. L. Herpesvirus hominis types I and II: a specific microindirect hemagglutination test. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Mar;133(3):735–739. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geder L., Skinner G. R. Differentiation between type 1 and type 2 strains of herpes simplex virus by an indirect immunofluorescent technique. J Gen Virol. 1971 Aug;12(2):179–182. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-12-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna L., Keshishyan H., Jawetz E., Coleman V. R. Diagnosis of Herpesvirus hominis infections in a general hospital laboratory. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Mar;1(3):318–323. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.3.318-323.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahmias A. J., DelBuono I., Schneweis K. E., Gordon D. S., Thies D. Type-specific surface antigens of cells infected with herpes simplex virus (1 and 2). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Oct;138(1):21–27. doi: 10.3181/00379727-138-35824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahmias A. J., Dowdle W. R., Kramer J. H., Luce C. F., Mansour S. C. Antibodies to Herpesvirus hominis types 1 and 2 in the rabbit. J Immunol. 1969 Apr;102(4):956–962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahmias A. J., Josey W. E., Naib Z. M., Luce C. F., Duffey A. Antibodies to Herpesvirus hominis types 1 and 2 in humans. I. Patients with genital herpetic infections. Am J Epidemiol. 1970 Jun;91(6):539–546. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacsa A. S., Kummerländer L., Pejtsik B., Pali K. Herpesvirus antibodies and antigens in patients with cervical anaplasia and in controls. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Oct;55(4):775–781. doi: 10.1093/jnci/55.4.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer G. A review of the identification and titration of antibodies to herpes simplex viruses type 1 and type 2 in human sera. Cancer Res. 1973 Jun;33(6):1469–1476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer G., Masterson J. G. Herpes simplex virus and cancer of the cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1971 Sep;111(1):81–84. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(71)90929-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawls W. E., Gardner H. L., Kaufman R. L. Antibodies to genital herpesvirus in patients with carcinoma of the cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1970 Jul 1;107(5):710–716. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)33989-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawls W. E., Garfield C. H., Seth P., Adam E. Serological and epidemiological considerations of the role of herpes simplex virus type 2 in cervical cancer. Cancer Res. 1976 Feb;36(2 Pt 2):829–835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawls W. E., Iwamoto K., Adam E., Melnick J. L. Measurement of antibodies to herpesvirus types 1 and 2 in human sera. J Immunol. 1970 Mar;104(3):599–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawls W. E., Tompkins W. A., Melnick J. L. The association of herpesvirus type 2 and carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Am J Epidemiol. 1969 May;89(5):547–554. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royston I., Aurelian L. The association of genital herpesvirus with cervical atypia and carcinoma in situ. Am J Epidemiol. 1970 Jun;91(6):531–538. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner G. R., Thouless M. E., Jordan J. A. Antibodies to type 1 and type 2 herpes virus in women with abnormal cervical cytology. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw. 1971 Nov;78(11):1031–1038. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1971.tb00221.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W., Adam E., Melnick J. L., Rawls W. E. Use of the 51 Cr release test to demonstrate patterns of antibody response in humans to herpesvirus types 1 and 2. J Immunol. 1972 Sep;109(3):554–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalder H., Oxman M. N., Herrmann K. L. Herpes simplex virus microneutralization: a simplification of the test. J Infect Dis. 1975 Apr;131(4):423–430. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.4.423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


