Abstract
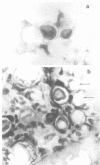
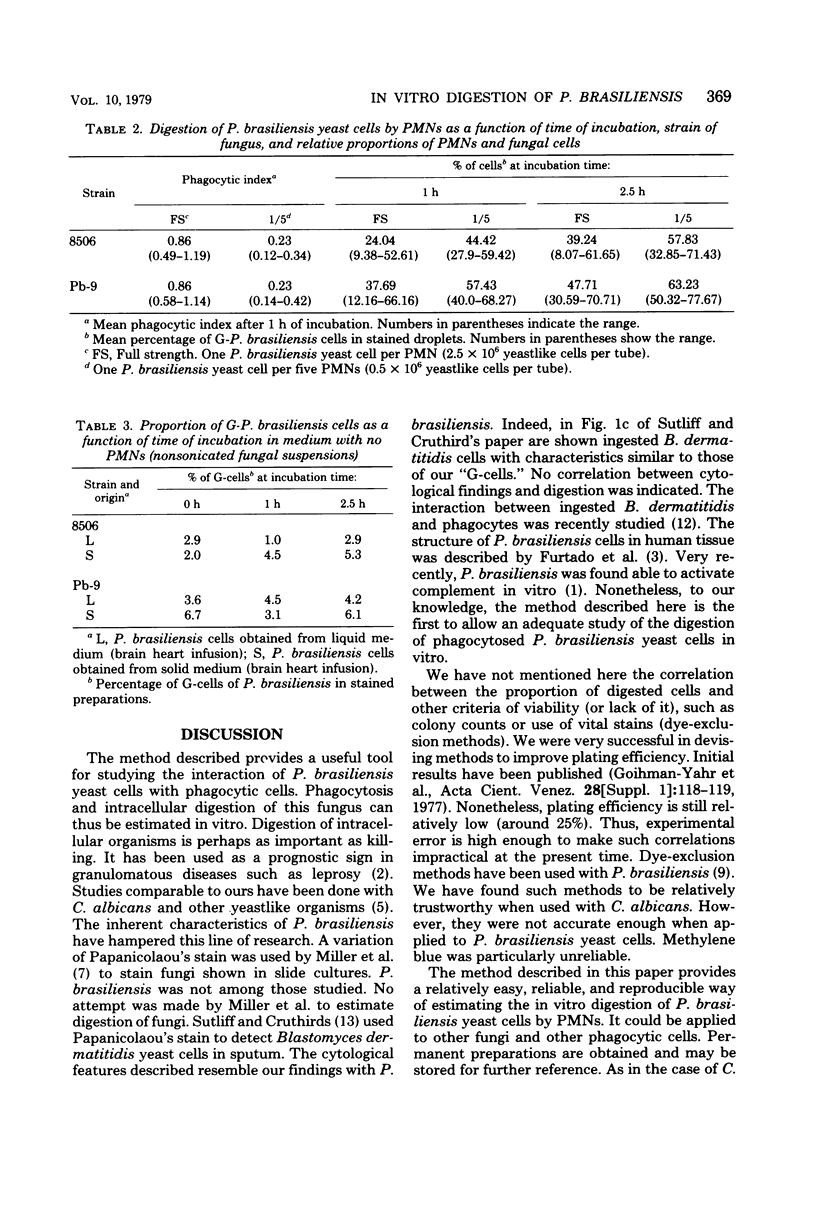
We describe a method by which phagocytosis and digestion of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis yeast cells by polymorphonuclear leukocytes or other phagocytic cells may be estimated. Suspensions of P. brasiliensis in its yeastlike phase were sonicated, counted, and incubated with known numbers of peripheral blood polymorphonuclear leukocytes. At given intervals, cytocentrifuge droplets were stained by a variation of Papanicolaou's method. Stained preparations were examined with phase-contrast optics. Digested organisms showed total or partial disappearance of protoplasm. Green-stained cell walls resisted digestion. The proportion of digested cells as a function of time was estimated.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Convit J., Avila J. L., Goihman M., Pinardi M. E. A test for the determination of competency in clearing bacilli in leprosy patients. Bull World Health Organ. 1972;46(6):821–826. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furtado J. S., de Brito T., Freymuller E. The structure and reproduction of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis in human tissue. Sabouraudia. 1967 Feb;5(3):226–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giraldo R., Restrepo A., Gutiérrez F., Robledo M., Londoño F., Hernández H., Sierra F., Calle G. Pathogenesis of paracoccidioidomycosis: a model based on the study of 46 patients. Mycopathologia. 1976 Jun 18;58(2):63–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00707174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Cline M. J. Interaction of Candida albicans with human leukocytes and serum. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):996–1004. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.996-1004.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I. Measurement of candidacidal activity of specific leukocyte types in mixed cell populations I. Normal, myeloperoxidase-deficient, and chronic granulomatous disease neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1970 Jul;2(1):42–47. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.1.42-47.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. L., Green D. S., Sodeman M. H., Sodeman T. M. Preparation of permanent microslides of fungi for reference and teaching. Am J Clin Pathol. 1973 Apr;59(4):601–604. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/59.4.601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS H. J., TERRYBERRY J. E. Counting actively metabolizing tissue cultured cells. Exp Cell Res. 1957 Oct;13(2):341–347. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(57)90013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Restrepo A., Vélez H. Efectos de la fagocitosis in vitro sobre el Paracoccidioides brasiliensis. Sabouraudia. 1975 Mar;13(Pt 1):10–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- San-Blas G., San-Blas F., Serrano L. E. Host-parasite relationships in the yeastlike form of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis strain IVIC Pb9. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):343–346. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.343-346.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- San-Blas G., Vernet D. Induction of the synthesis of cell wall alpha-1,3-glucan in the yeastlike form of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis strain IVIC Pb9 by fetal calf serum. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):897–902. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.897-902.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixbey J. W., Fields B. T., Sun C. N., Clark R. A., Nolan C. M. Interactions between human granulocytes and Blastomyces dermatitidis. Infect Immun. 1979 Jan;23(1):41–44. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.1.41-44.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutliff W. D., Cruthirds T. P. Blastomyces dermatitidis in cytologic preparations. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Jul;108(1):149–151. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.108.1.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]