Abstract
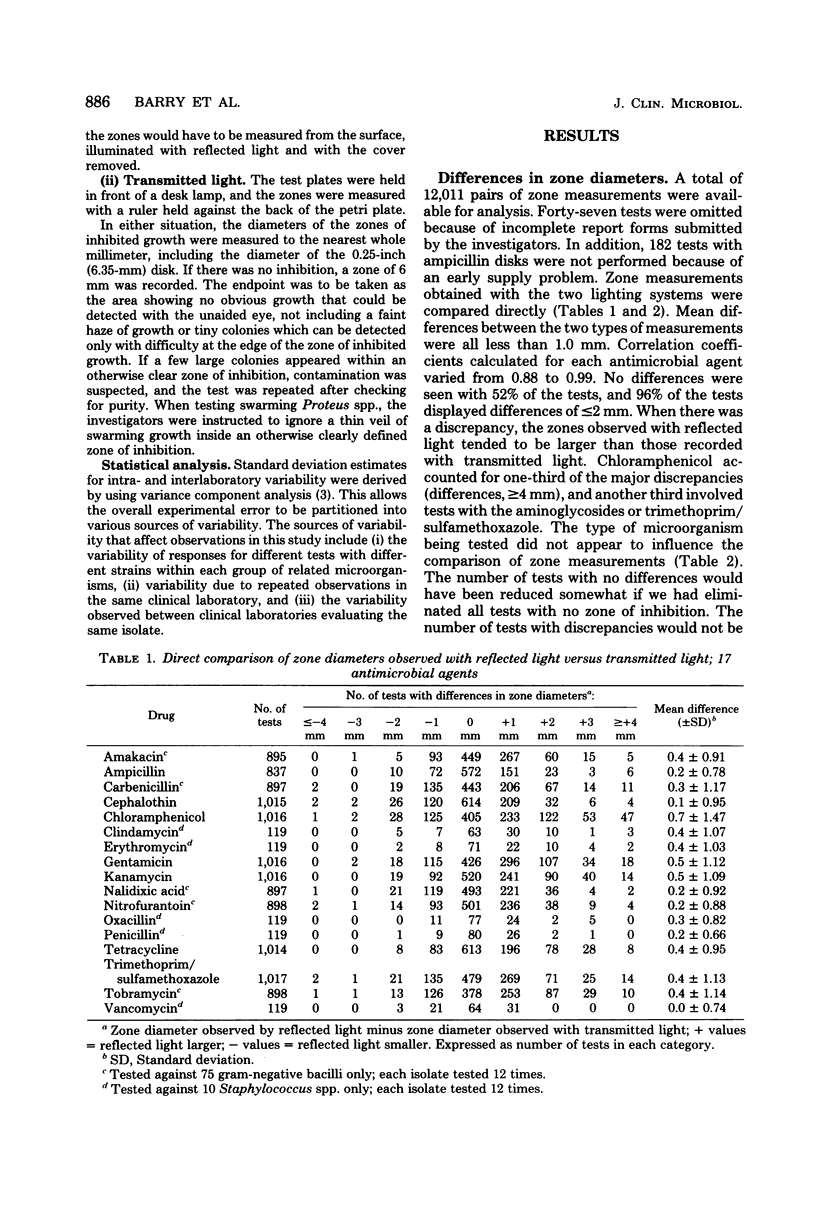
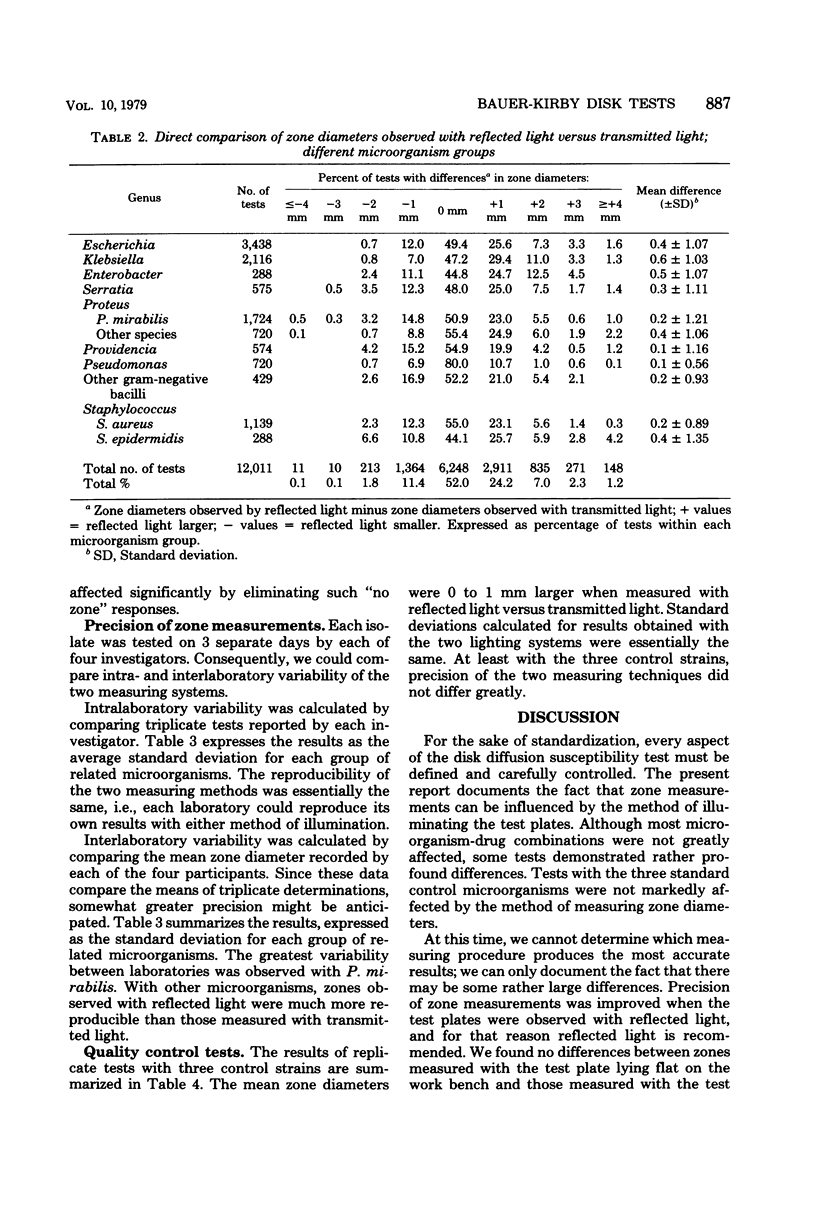
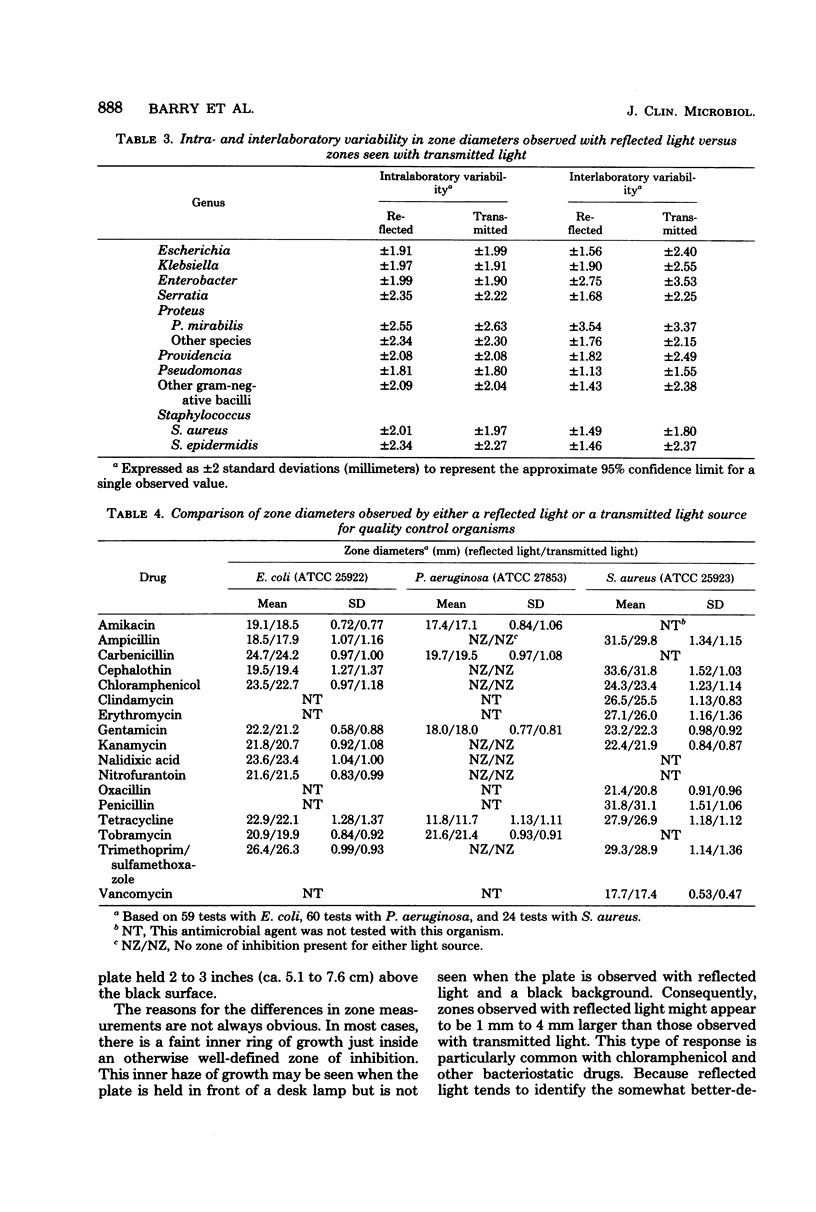
Standard Bauer-Kirby disk tests were performed with 85 selected isolates, each tested in triplicate by four different investigators. Each disk test was observed, and zone diameters were measured, under two lighting conditions (transmitted light and reflected light). The two lighting systems produced similar zone measurements (+/-2 mm) with 96% of the tests. When there were greater differences, zones appeared to be larger when observed with reflected light. Interlaboratory reproducibility was much greater when using reflected light rather than transmitted light. We concluded that zone diameters should be measured from the back of the plate while it is resting on, or held 2 to 3 inches [ca. 5.1 to 7.6 cm] above, a black, nonreflecting, flat surface, illuminated by a reflected light source.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


