Abstract
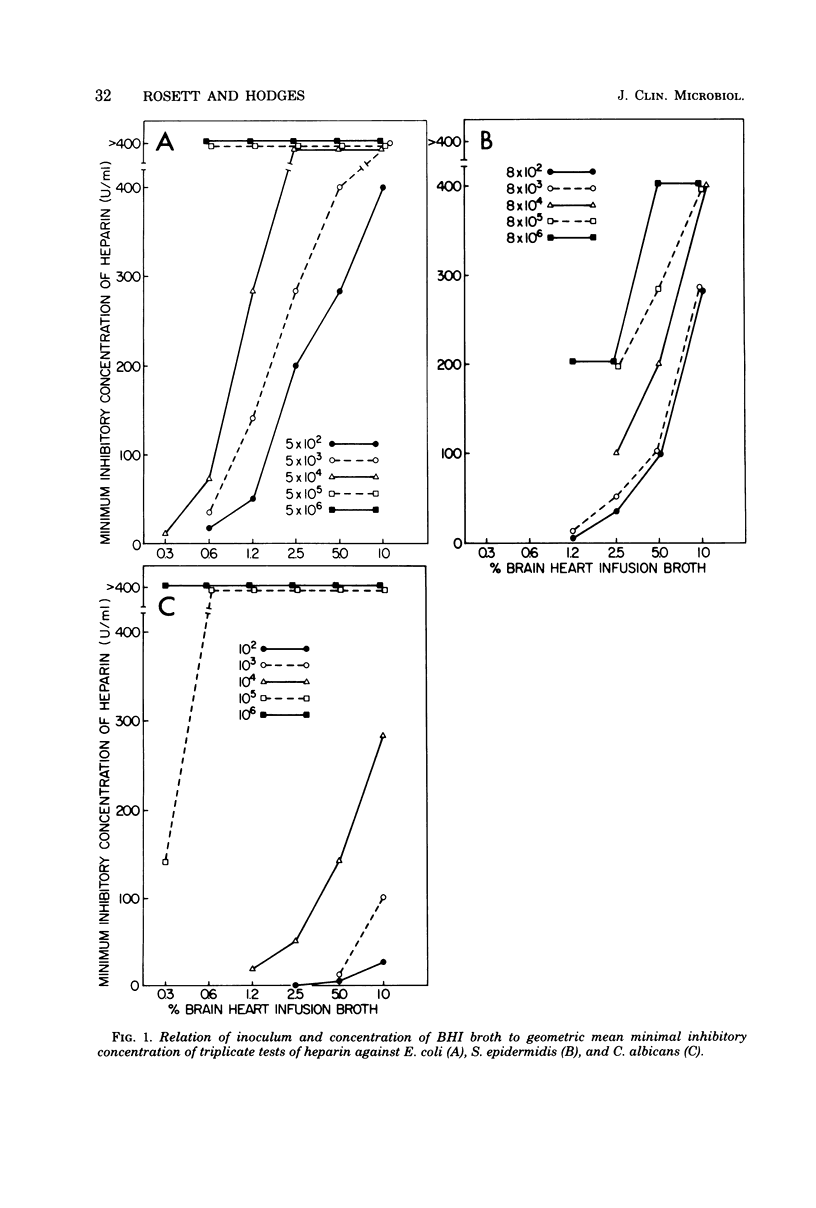
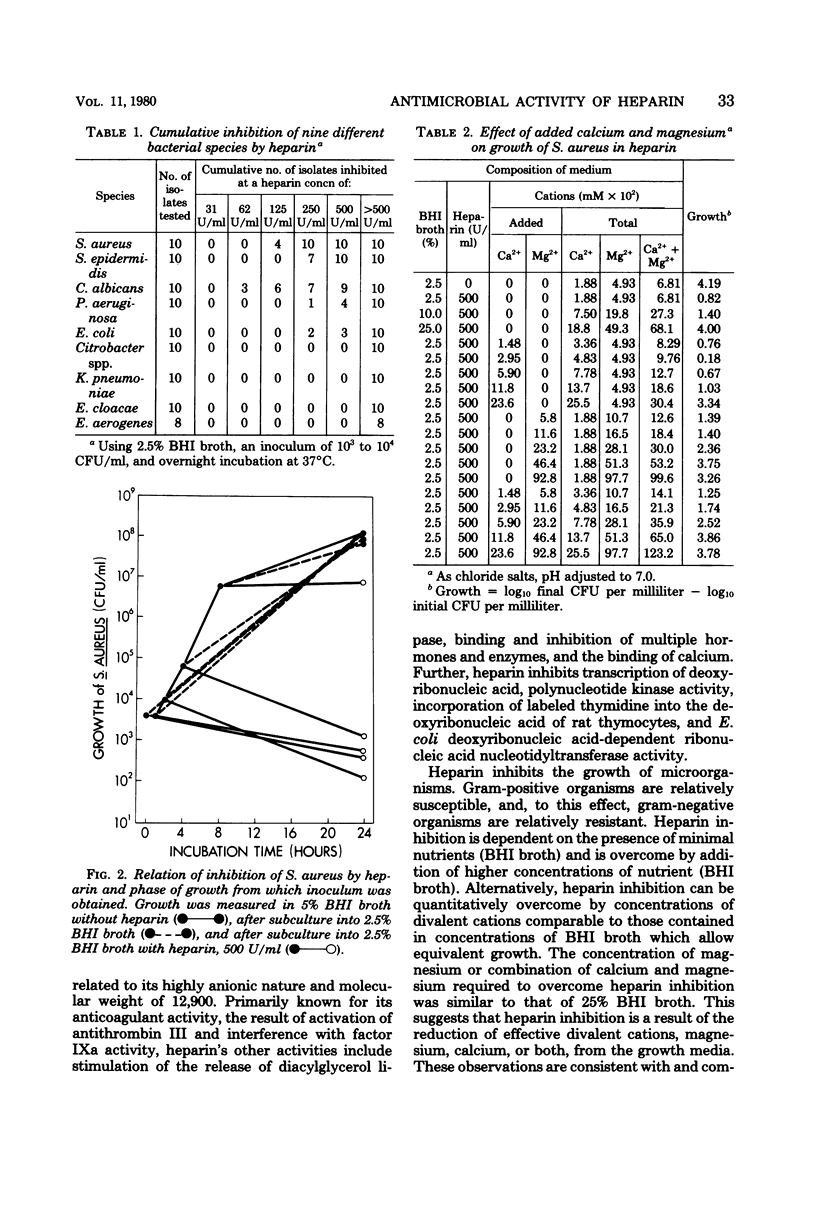
Single clinical isolates of eight species of microorganisms were incubated in solutions of heparin and brain heart infusion broth at various concentrations to determine the possible antibacterial effect of heparin. At heparin concentrations ranging from 12.5 to 400 U/ml, the effect on Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Candida albicans, Staphylococcus aureus, and S. epidermidis varied with brain heart infusion broth concentrations of 1.2 to 10% and inocula of 102 to 106 colony-forming units per ml; similar effects were not observed with Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter aerogenes, and Citrobacter spp. The minimal inhibitory concentrations of heparin for ten strains of each species were determined in 2.5% brain heart infusion broth with inocula of 104 colony-forming units per ml. All 10 isolates of S. aureus and all 10 of S. epidermidis were inhibited by heparin concentrations of 125 to 500 U/ml. Three E. coli, four P. aeruginosa, and nine C. albicans strains were inhibited by ≤500 U of heparin per ml. None of the K. pneumoniae, E. aerogenes, Enterobacter cloacae, and Citrobacter spp. was inhibited by heparin at ≤500 U/ml. Heparin inhibition of S. aureus in 2.5% brain heart infusion broth-500 U of heparin per ml could be quantitatively overcome by addition of magnesium, calcium, or magnesium and calcium. These data suggest that the growth of microorganisms from heparin-containing material may be suppressed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHRISTMAN J. F., DOHERTY D. G. The antimicrobial action of heparin. J Bacteriol. 1956 Oct;72(4):433–435. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.4.433-435.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich J., Stivala S. S. Chemistry and pharmacology of heparin. J Pharm Sci. 1973 Apr;62(4):517–544. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600620402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans G. L., Cekoric T., Jr, Searcy R. L. Comparative effects of anticoagulants on bacterial growth in experimental blood cultures. Am J Med Technol. 1968 Feb;34(2):103–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson R. L., Rosett W., Hodges G. R., Barnes W. G. Complications with heparin-lock needles. A prospective evaluation. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Nov;85(5):583–586. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-85-5-583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN J. R., GRAHAM F. The effect of heparin on the growth of bacteria and yeasts. J Bacteriol. 1950 Aug;60(2):171–174. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.2.171-174.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


