Abstract
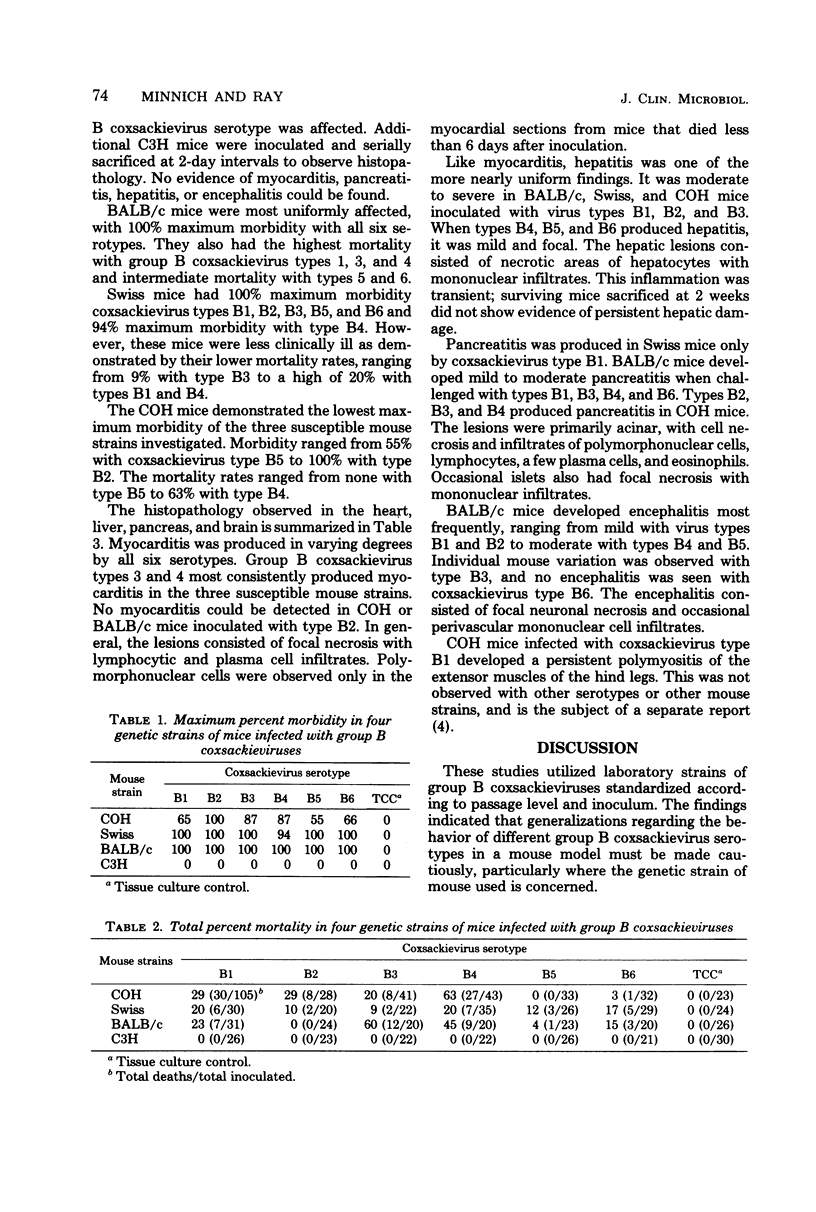
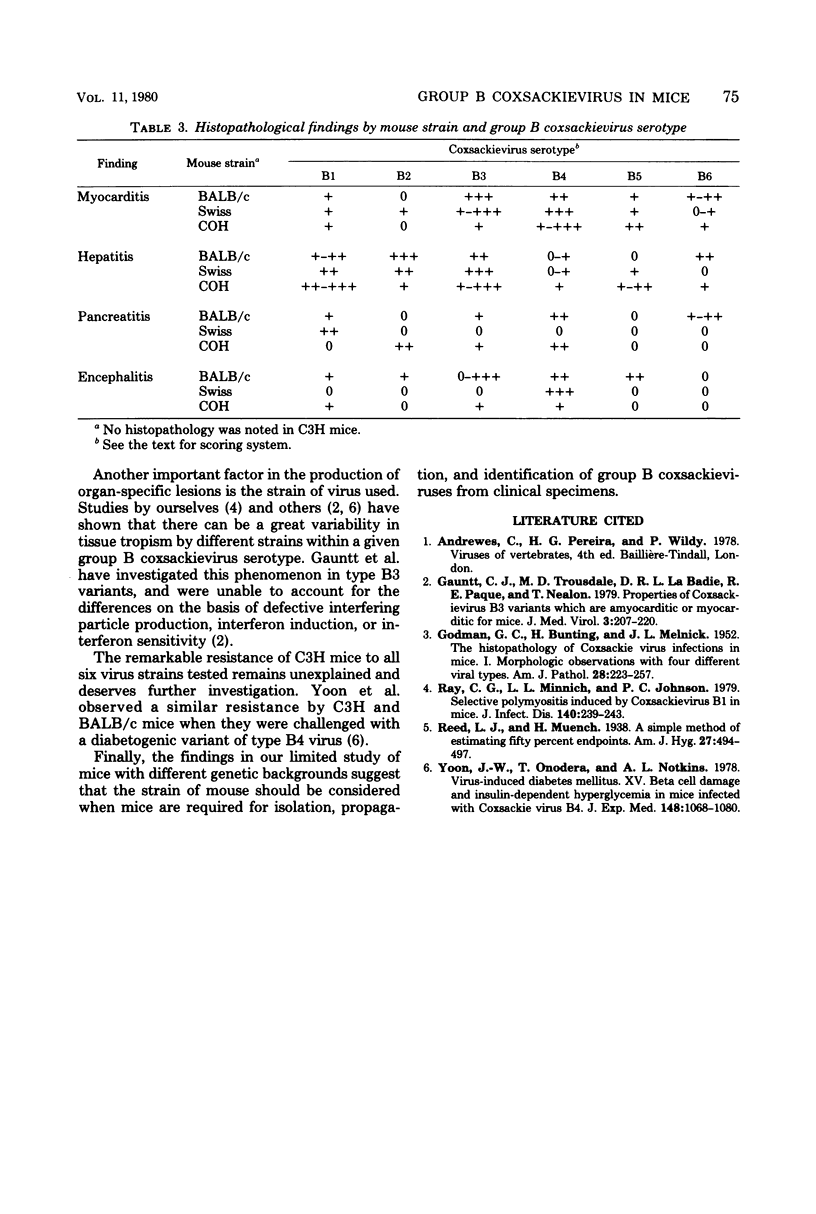
Laboratory strains of group B coxsackievirus serotypes 1 to 6 were inoculated intraperitoneally into newborn mice of differing genetic backgrouns. Of the four genetic strains investigated, C3H mice appeared to be resistant to all six serotypes, whereas BALB/c mice were most susceptible. Swiss mice and a random-bred Swiss strain (COH) were intermediate in susceptibility. The findings underscore the fact that clinical isolation attempts and experimental studies involving group B coxsackieviruses must take into account both the virus strain used and the genetic background of the host. For clinical isolation of these viruses, the BALB/c mouse may be the most suitable of th strains tested.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GODMAN G. C., BUNTING H., MELNICK J. L. The histopathology of Coxsackie virus infection in mice. I. Morphologic observations with four different viral types. Am J Pathol. 1952 Mar-Apr;28(2):223–257. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauntt C. J., Trousdale M. D., LaBadie D. R., Paque R. E., Nealon T. Properties of coxsackievirus B3 variants which are amyocarditic or myocarditic for mice. J Med Virol. 1979;3(3):207–220. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890030307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray C. G., Minnich L. L., Johnson P. C. Selective polymyositis inducted by coxsackievirus B1 in mice. J Infect Dis. 1979 Aug;140(2):239–243. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.2.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon J. W., Onodera T., Notkins A. L. Virus-induced diabetes mellitus. XV. Beta cell damage and insulin-dependent hyperglycemia in mice infected with coxsackie virus B4. J Exp Med. 1978 Oct 1;148(4):1068–1080. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.4.1068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


