Abstract
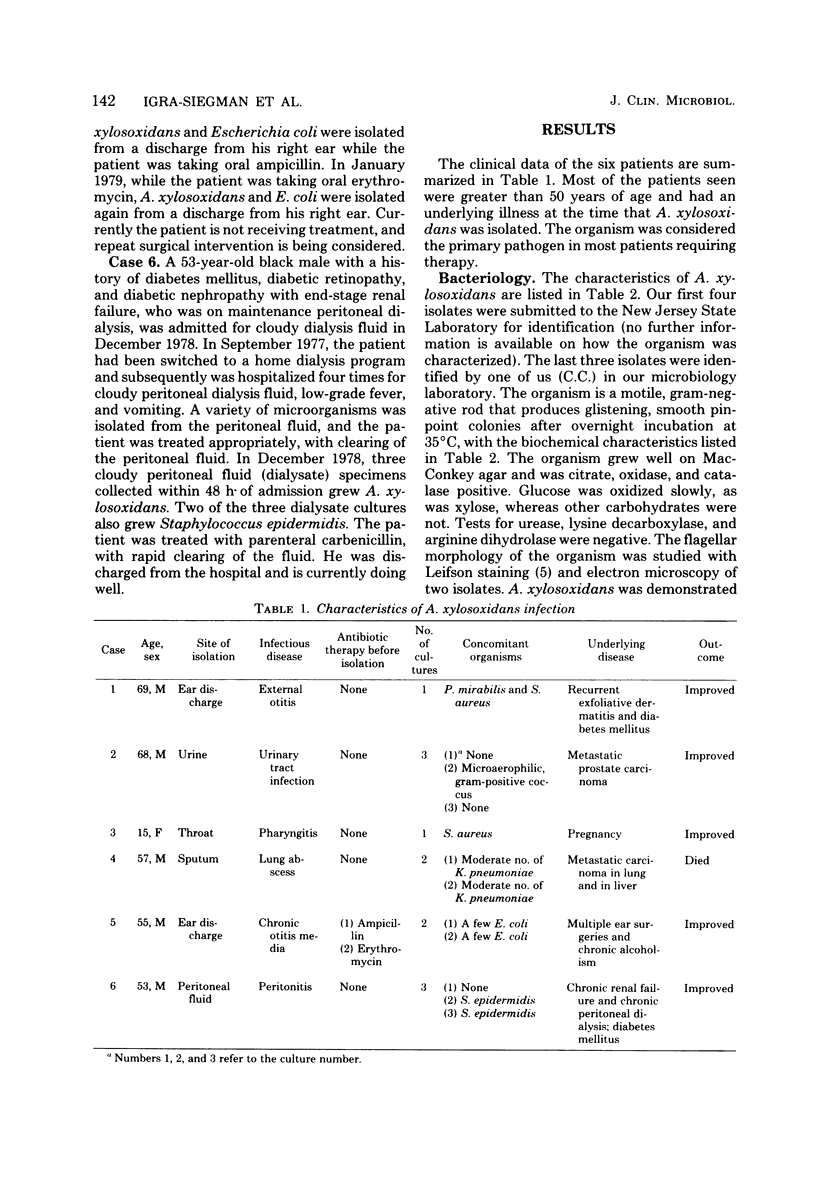
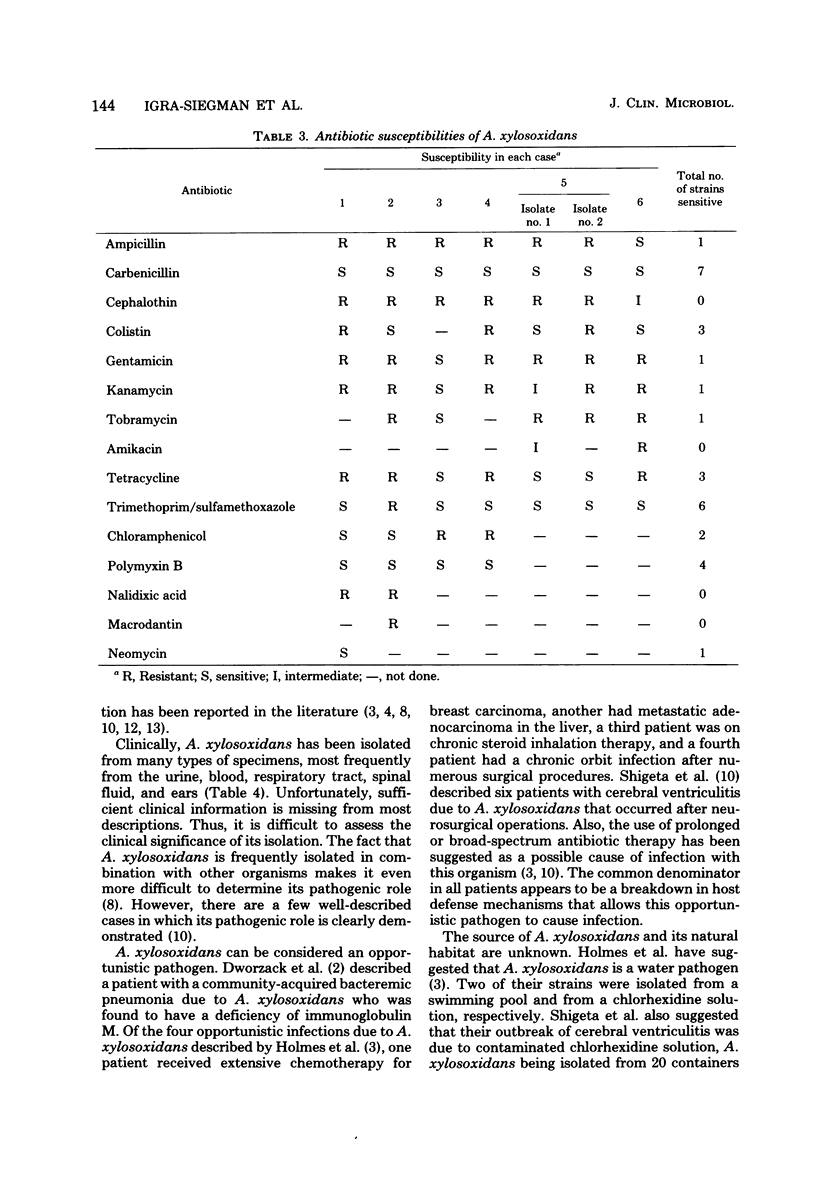
Achromobacter xylosoxidans was isolated from six patients. The organism causes opportunistic infections in patients who are compromised. A. xylosoxidans is a catalase- and oxidase-positive, motile, gram-negative rod that oxidizes xylose and glucose. The organism exists in a water environment and may be confused with Pseudomonas species. Unlike pseudomonas, achromobacter has peritrichous flagella. The clinical and laboratory characteristics of A. xylosoxidans are presented.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- De Ley J., Kersters K., Khan-Matsubara J., Shewan J. M. Comparative D-gluconate metabolism and DNA base composition in Achromobacter and Alcaligenes. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1970;36(2):193–207. doi: 10.1007/BF02069021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworzack D. L., Murray C. M., Hodges G. R., Barnes W. G. Community-acquired bacteremic Achromobacter xylosoxidans type IIIa pneumonia in a patient with idiopathic IgM deficiency. Am J Clin Pathol. 1978 Oct;70(4):712–717. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/70.4.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes B., Snell J. J., Lapage S. P. Strains of Achromobacter xylosoxidans from clinical material. J Clin Pathol. 1977 Jul;30(7):595–601. doi: 10.1136/jcp.30.7.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igari J., Kosakai N., Oguri T., Kakegawa H. [Clinical and bacteriological studies on infections due to Achromobacter xylosoxidans (author's transl)]. Jpn J Antibiot. 1978 Apr;31(4):211–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIFSON E. Staining, shape and arrangement of bacterial flagella. J Bacteriol. 1951 Oct;62(4):377–389. doi: 10.1128/jb.62.4.377-389.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE H. B., PICKETT M. J. Organisms resembling Alcaligenes faecalis. Can J Microbiol. 1960 Feb;6:43–52. doi: 10.1139/m60-007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pien F. D., Higa H. Y. Achromobacter xylosoxidans isolates in Hawaii. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Feb;7(2):239–241. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.2.239-241.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigeta S., Yasunaga Y., Honzumi K., Okamura H., Kumata R., Endo S. Cerebral ventriculitis associated with Achromobacter xylosoxidans. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Feb;31(2):156–161. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.2.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabuuchi E., Oyama A. Achromobacter xylosoxidans n. sp. from human ear discharge. Jpn J Microbiol. 1971 Sep;15(5):477–481. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1971.tb00607.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


