Abstract
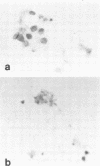
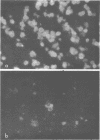
We compared histological and immunological techniques in the early diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in bronchial lavage fluid of steroid-treated rats. The rats were sacrificed weekly and lavage fluids were: (i) examined with cresyl echt violet and Giemsa stains; (ii) examined for P. carinii antigens by indirect fluorescent-antibody, counterimmunoelectrophoresis, and double-diffusion techniques, using high-titer spectific antisera to P. carinii raised in rabbits. P. carinii was detected in lavage fluid by cresyl echt violet at 2 weeks of steroids and persisted even with steroid tapering; the intensity of the infection in lavage fluid closely paralleled that in the lungs. P. carinii was not detected in lavage by Giemsa stain until 4 weeks and disappeared from the fluids with steroid tapering. P. carinii was detected by indirect fluorescent antibody as early as 1 week of steroids, and the results correlated well with those of cresyl echt violet. P. carinii antigens were not detected in lavage fluids or serum by counterimmunoelectrophoresis or double-diffusion techniques. Although precipitin lines sometimes occurred, they were nonspecific. In this model, cresyl echt violet and indirect fluorescent antibody were the preferred techniques for the early diagnosis of P. carinii infection in bronchial lavage fluid.
Full text
PDF


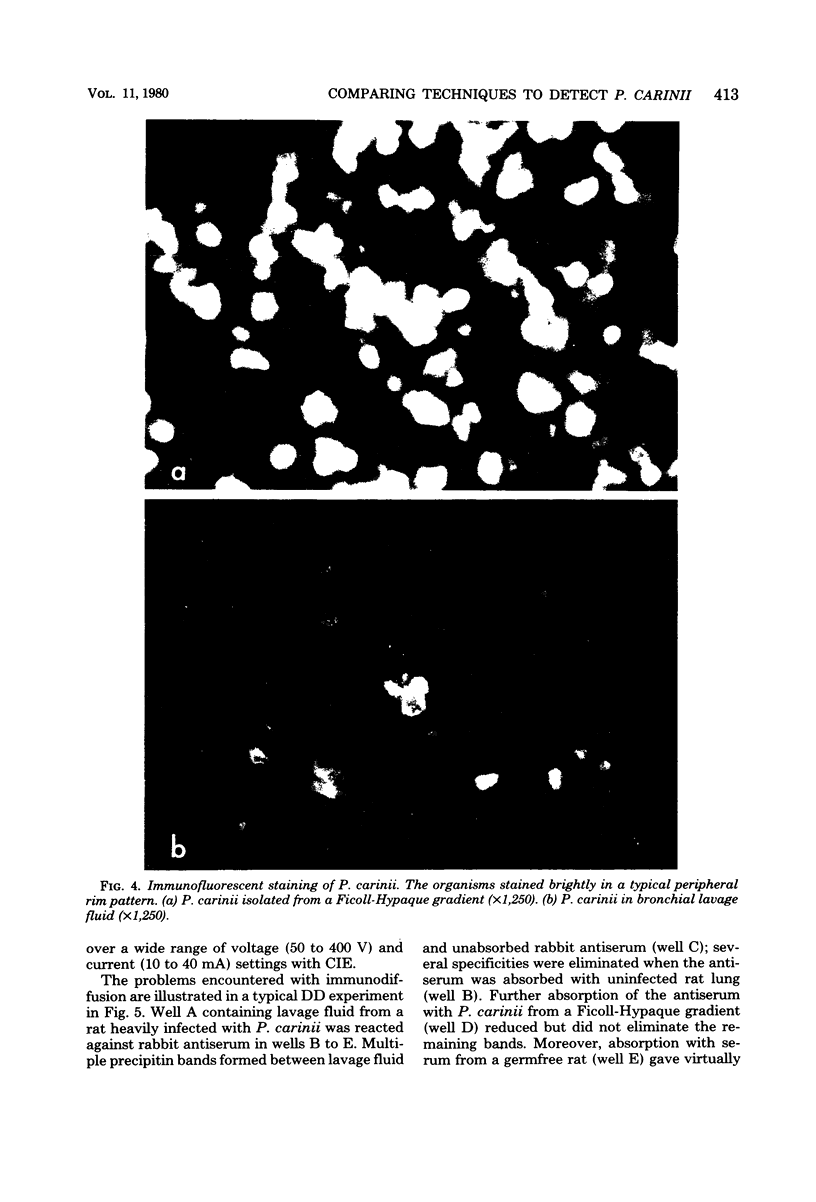
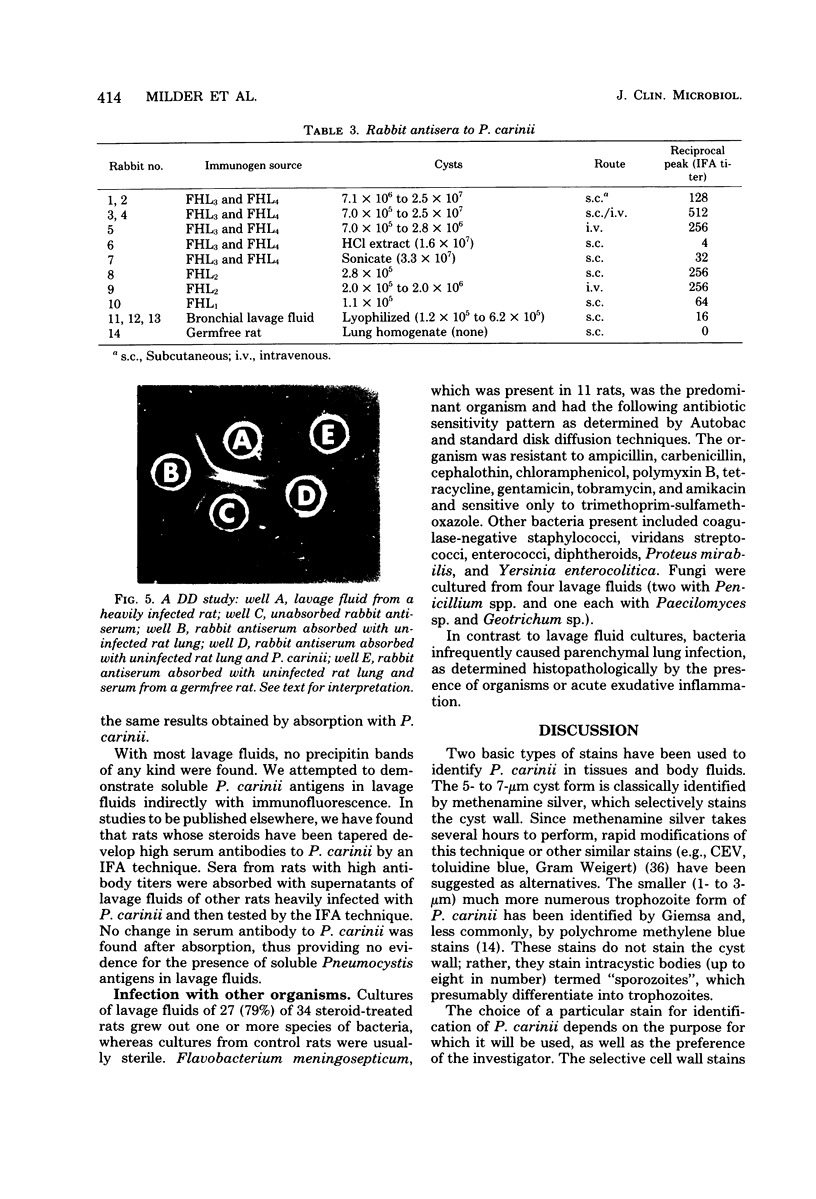



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowling M. C., Smith I. M., Wescott S. L. A rapid staining procedure for Pneumocystis carinii. Am J Med Technol. 1973 Jul;39(7):267–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzosko W. J., Krawczyński K., Madaliński K., Nowoslawski A. Immunopathologic aspects of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in infants as revealed by immunofluorescence and electron microscopy. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1976 Oct;43:163–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Weekly clinicopathological exercises. Case 33-1972. N Engl J Med. 1972 Aug 17;287(7):349–354. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197208172870711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caubarrere I., Sors H., Even P. Diagnosis of pneumocystis pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 30;298(13):741–741. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803302981312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan H., Pifer L., Hughes W. T., Feldman S., Pearson T. A., Woods D. Comparison of gastric contents to pulmonary aspirates for the cytologic diagnosis of Pneuomcystis carinii pneumonia. J Pediatr. 1977 Feb;90(2):243–244. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80638-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coonrod J. D., Drennan D. P. Pneumococcal pneumonia: capsular polysaccharide antigenemia and antibody responses. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Mar;84(3):254–260. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-84-3-254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew W. L., Finley T. N., Mintz L., Klein H. Z. Diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia by bronchopulmonary lavage. JAMA. 1974 Nov 4;230(5):713–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortuny I. E., Tempero K. F., Amsden T. W. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia diagnosed from sputum and successfully treated with pentamidine isethionate. Cancer. 1970 Oct;26(4):911–913. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197010)26:4<911::aid-cncr2820260426>3.0.co;2-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K., Good J. T., Shultz J. A. Latent Pneumocystis infection of rats, relapse, and chemotherapy. Lab Invest. 1966 Oct;15(10):1559–1577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K., Piekarski G. The demonstration of Toxoplasma and other organisms by immunofluorescence: a pitfall. J Infect Dis. 1978 Aug;138(2):265–266. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.2.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodell B., Jacobs J. B., Powell R. D., DeVita V. T. Pneumocystis carinii: the spectrum of diffuse interstitial pneumonia in patients with neoplastic diseases. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Mar;72(3):337–340. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-72-3-337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg K., Nord C. E., Wadström T. Serological studies of actionomyces israelii by crossed immunoelectrophoresis: standard antigen-antibody system for A. israelii. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):387–397. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.387-397.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T. Current status of laboratory diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. CRC Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 1975 Sep;6(2):145–170. doi: 10.3109/10408367509151568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan I. G., Norman L. G. Serology of pneumocystosis. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1976 Oct;43:121–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley J., Landis J. N., Davis G. S., Trainer T. D., Jakab G. J., Green G. M. Diagnosis of pneumonia due to Pneumocystis by subsegmental pulmonary lavage via the fiberoptic bronchoscope. Chest. 1978 Jul;74(1):24–28. doi: 10.1378/chest.74.1.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. K., Hughes W. T. Comparison of methods for identification of Pneumocystis carinii in pulmonary aspirates. Am J Clin Pathol. 1973 Oct;60(4):462–466. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/60.4.462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. K., Hughes W. T., Feldman S. Studies of morphology and immunofluorescence of Pneumocystis carinii. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Oct;141(1):304–309. doi: 10.3181/00379727-141-36764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre C. R., Sulzer A. J., Norman L. G. Serial propagation of Pneumocystis carinii in cell line cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1204–1206. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1204-1206.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau W. K., Young L. S., Remington J. S. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Diagnosis by examination of pulmonary secretions. JAMA. 1976 Nov 22;236(21):2399–2402. doi: 10.1001/jama.236.21.2399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim S. K., Eveland W. C., Porter R. J. Development and evaluation of a direct fluorescent antibody method for the diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii infections in experimental animals. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Nov;26(5):666–671. doi: 10.1128/am.26.5.666-671.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim S. K., Eveland W. C., Porter R. J. Direct fluorescent-antibody method for the diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis from sputa or tracheal aspirates from humans. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jan;27(1):144–149. doi: 10.1128/am.27.1.144-149.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masur H., Jones T. C. The interaction in vitro of Pneumocystis carinii with macrophages and L-cells. J Exp Med. 1978 Jan 1;147(1):157–170. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuwissen J. H., Tauber I., Leeuwenberg A. D., Beckers P. J., Sieben M. Parasitologic and serologic observations of infection with Pneumocystis in humans. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jul;136(1):43–49. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. D., Pifer L. L., Sale G. E., Thomas E. D. The value of Pneumocystis carinii antibody and antigen detection for diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia after marrow transplantation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Dec;120(6):1283–1287. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.120.6.1283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minielly J. A., McDuffie F. C., Holley K. E. Immunofluorescent identification of Pneumocystis carinii. Arch Pathol. 1970 Dec;90(6):561–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., Prescott B., Neva F. A. The characteristics of a circulating antigen in schistosomiasis. J Immunol. 1974 Apr;112(4):1500–1507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman L., Kagan I. G. Some observations on the serology of Pneumocystis carinii infections in the United States. Infect Immun. 1973 Sep;8(3):317–321. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.3.317-321.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pifer L. L., Hughes W. T., Murphy M. J., Jr Propagation of Pneumocystis carinii in vitro. Pediatr Res. 1977 Apr;11(4):305–316. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197704000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pifer L. L., Hughes W. T., Stagno S., Woods D. Pneumocystis carinii infection: evidence for high prevalence in normal and immunosuppressed children. Pediatrics. 1978 Jan;61(1):35–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pifer L. L., Woods D., Hughes W. T. Propagation of Pneumocystis carinii in Vero cell culture. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):66–68. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.66-68.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer C., Armstrong D., Rosen P. P., Walzer P. D., Yu B. Diffuse pulmonary infiltrates in immunosuppressed patients. Prospective study of 80 cases. Am J Med. 1979 Jan;66(1):110–120. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90490-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Behren L. A., Pesanti E. L. Uptake and degradation of Pneumocystis carinii by macrophages in vitro. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Dec;118(6):1051–1059. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.118.6.1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Perl D. P., Krogstad D. J., Rawson P. G., Schultz M. G. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in the United States. Epidemiologic, diagnostic, and clinical features. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Jan;80(1):83–93. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-1-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D. Pneumocystis carinii infection. South Med J. 1977 Nov;70(11):1330–1337. doi: 10.1097/00007611-197711000-00027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Powell R. D., Jr, Yoneda K. Experimental Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in different strains of cortisonized mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):939–947. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.939-947.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Powell R. D., Jr, Yoneda K., Rutledge M. E., Milder J. E. Growth characteristics and pathogenesis of experimental Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Infect Immun. 1980 Mar;27(3):928–937. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.3.928-937.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Rutledge M. E., Yoneda K., Stahr B. J. Pneumocystis carinii: new separation method from lung tissue. Exp Parasitol. 1979 Jun;47(3):356–368. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(79)90088-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]