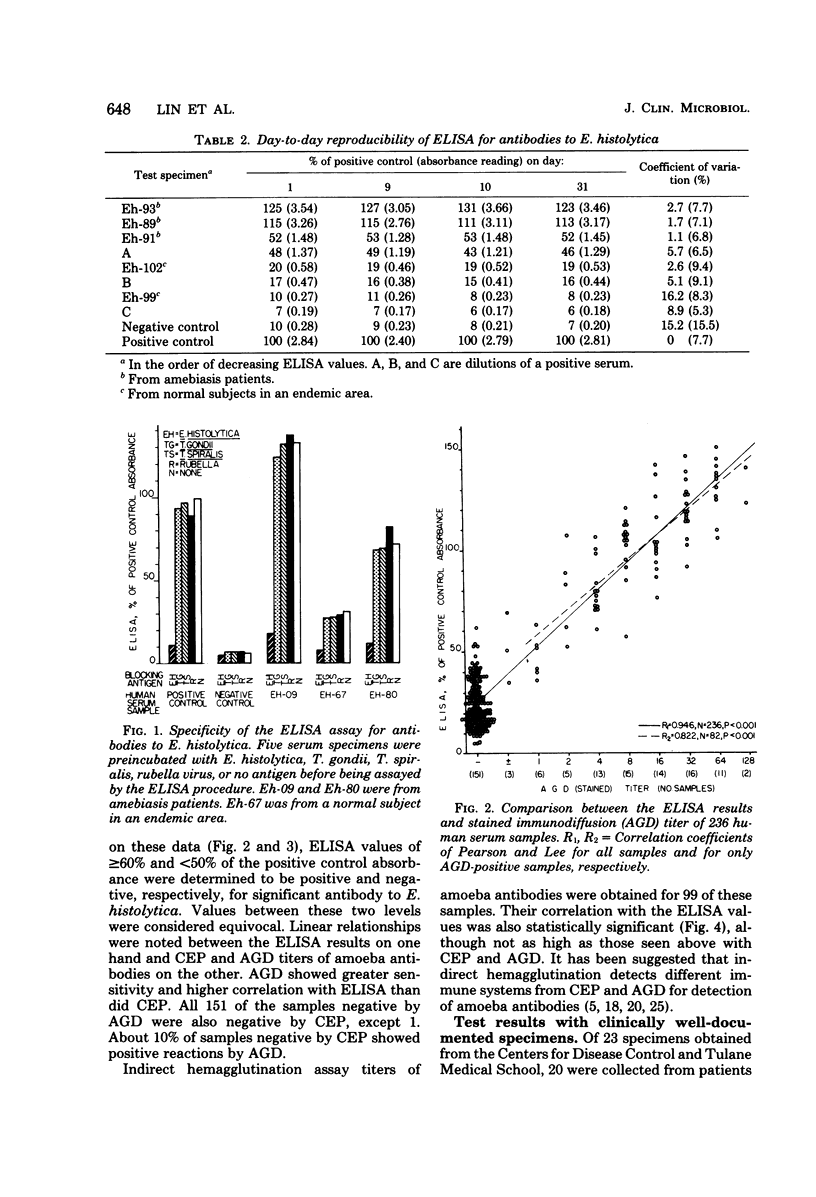
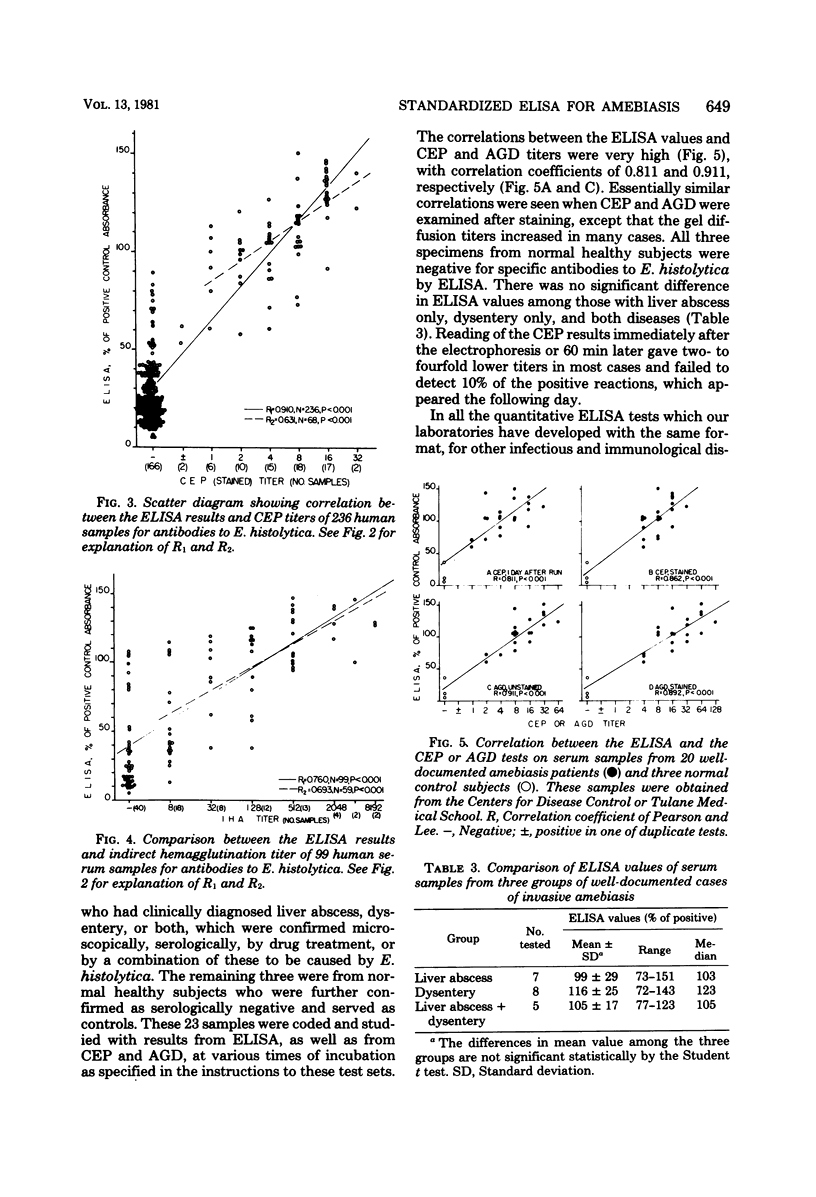
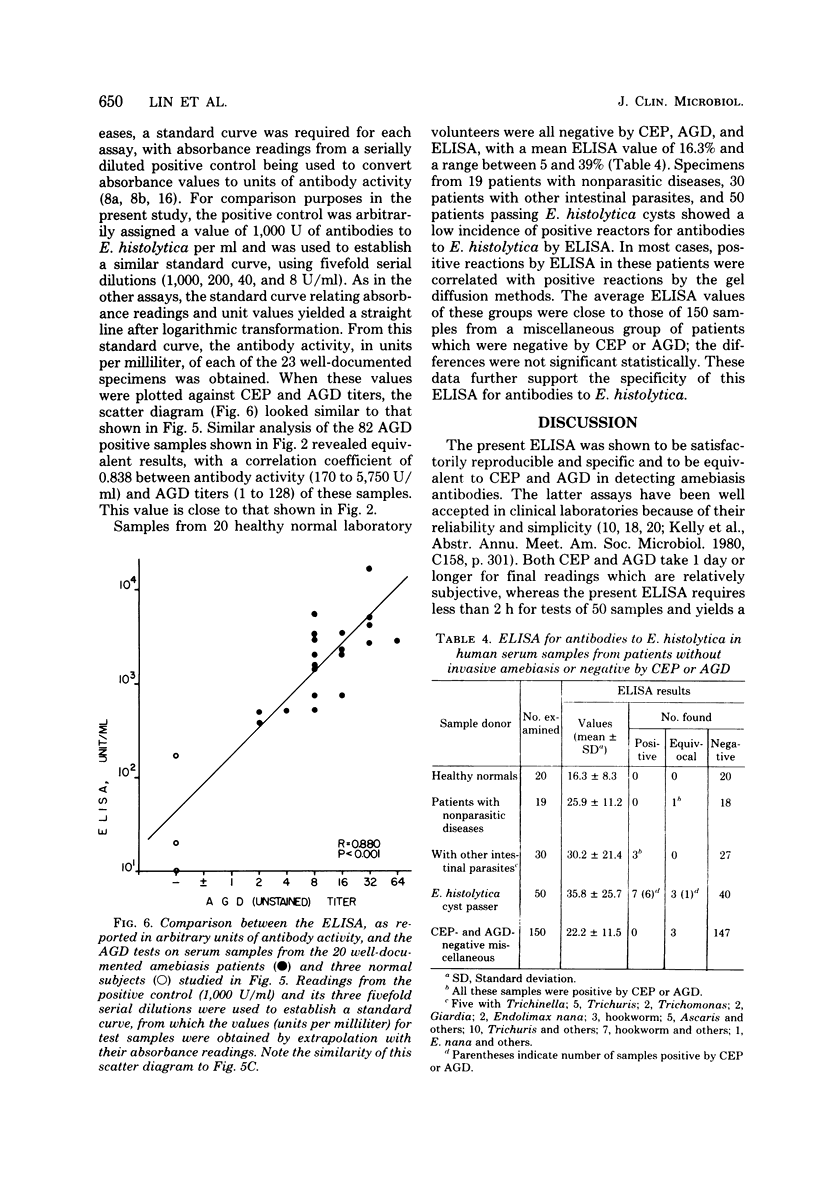
Abstract
A simple solid-phase enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay procedure for the detection of human antibodies to Entamoeba histolytica was developed which showed a high degree of correlation with the agar gel diffusion, counterelectrophoresis, and indirect hemagglutination methods, as well as with clinical data. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay is rapid (1 h 15 min, total incubation time), and the reported values are referenced to a positive control so that they correlate with levels of antibody sufficient to be detected by the gel diffusion methods. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay is highly reproducible, specific, and sensitive; it can be used qualitatively or quantitatively.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambroise-Thomas P., Desgeorges P. T., Monget D. Diagnostic immuno-enzymologique (ELISA) des maladies parasitaires par une microméthode modifiée. 2. Résultats pour la toxoplasmose, l'amibiase, la trichinose, l'hydatidose et l'aspergillose. Bull World Health Organ. 1978;56(5):797–804. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross J. H., Wheeling C., Banzon T., Basaca-Sevilla V., Sevilla J. Amoebiasis and intestinal parasitic infections in a population on Cebu Island, the Philippines. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1977 Dec;71(4):435–441. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1977.11687209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S. Techniques of axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica Schaudinn, 1903 and E. histolytica-like amebae. J Parasitol. 1968 Oct;54(5):1047–1056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldson-Dew R. The aetiology, diagnosis and treatment of amoebic disease. Arch Invest Med (Mex) 1974;5(Suppl 2):561–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farid Z., Hassan A., Trabolsi B., Higashi G. I., Mansour N. S., Miner W. F. Hepatic amebiasis: diagnostic counterimmunoelectrophoresis and metronidazole (flagyl) therapy. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 Jul;26(4):822–823. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1977.26.822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbert S. P., Anken M. Detection of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBS Ag) with use of alkaline phosphatase-labeled antibody to HBS Ag. J Infect Dis. 1977 Oct;136 (Suppl):S318–S323. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement_2.s318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbert S. P., Karsh J., Anken M. A quantitative enzyme immunoassay for IgM rheumatoid factor using human immunoglobulin G as substrate. Am J Clin Pathol. 1980 Dec;74(6):776–784. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/74.6.776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbert S. P., Karsh J., Anken M. Studies on autoantibodies to deoxyribonucleic acid and deoxyribonucleoprotein with enzyme-immunoassay (ELISA). J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Jan;97(1):97–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy G. R. Laboratory diagnosis of amebiasis. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1971 May;47(5):478–493. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy G. R., Visvesvara G. S., Kagan I. G. Observations on the persistence of antibodies to E. histolytica. Arch Invest Med (Mex) 1974;5(Suppl 2):495–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney M., Abrams H., Eveland L. K., Yermakov V. Amebiasis. Unusual location in lung. N Y State J Med. 1975 Aug;75(9):1542–1543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H., Finkelstein S. Serologic responses in amebiasis. Arch Invest Med (Mex) 1978;9 (Suppl 1):357–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogstad D. J., Spencer H. C., Jr, Healy G. R. Current concepts in parasitology. Amebiasis. N Engl J Med. 1978 Feb 2;298(5):262–265. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197802022980507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp I. M. Comparison of counterimmunoelectrophoresis with other serologic tests in the diagnosis of amebiasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1974 Jan;23(1):27–30. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1974.23.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp I. M., Powell S. J. Antibody response to invasive amebiasis in Durban, South Africa. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1971 May;20(3):414–420. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1971.20.414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin T. M., Halbert S. P., O'Connor G. R. Standardized quantitative enzyme-linked immunoassay for antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jun;11(6):675–681. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.6.675-681.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson M., Healy G. R., Shabot J. M. Serologic testing for amoebiasis. Gastroenterology. 1980 Jan;78(1):136–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman F. E., el-Hashimi W. K., Pittman J. C. Studies of human amebiasis. I. Clinical and laboratory findings in eight cases of acute amebic colitis. Gastroenterology. 1973 Oct;65(4):581–587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan D. J., Bottone E. J., Pavletich K., Heath M. C. Entamoeba histolytica: efficacy of microscopic, cultural, and serological techniques for laboratory diagnosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Aug;10(2):128–133. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.2.128-133.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speiser F. Anwendung einer Enzym-Immunmethode (ELISA) für die Serologie der Amöbiase. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1980 Mar 15;110(11):404–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E., Bartlett A., Edwards R. A comparison of isotopic and enzyme-immunoassays for tropical parasitic diseases. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1977;71(5):431–437. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(77)90046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Kennedy M. T. Evaluation of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the serodiagnosis of amebiasis. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Dec;10(6):778–785. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.6.778-785.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


