Abstract
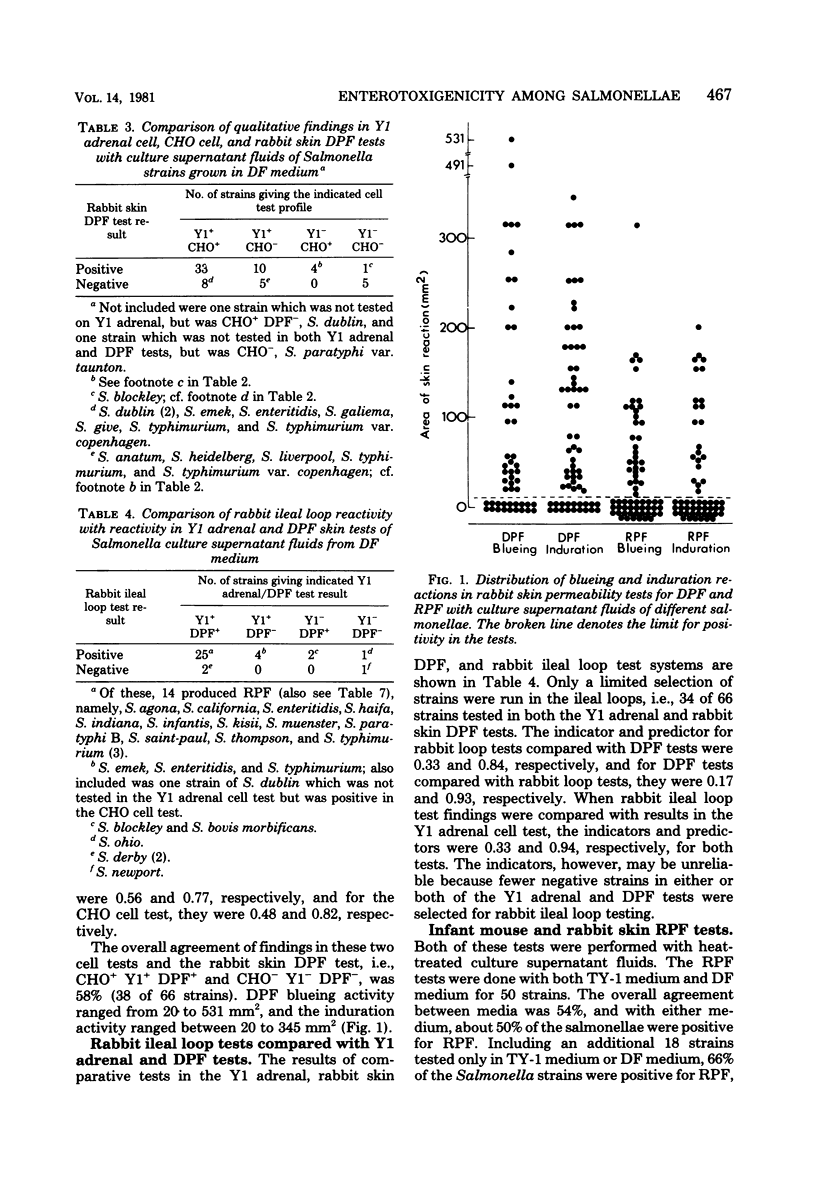
Sixty-eight Salmonella strains representing 39 serotypes were variously screened for enterotoxigenicity by using the Chinese hamster ovary (CHO), Y1 adrenal, and Vero cell tests, rabbit skin tests for delayed permeabiltity factor (DPF) and rapid permeability factor (RPF), the rabbit ileal loop test, and the infant mouse test. An iron-sufficient medium, YT-1, and a deferrated medium, DF, were compared. Of the culture supernatant fluids of strains grown in DF medium, 66% yielded positive reactions in the CHO cell test compared with only 10% with TY-1 medium. The corresponding performances with supernatant fluids of DF medium cultures in Y1 adrenal and Vero cell tests were 85 and 69% positive, respectively. The overall agreement between the Y1 adrenal or CHO cell test and the rabbit skin test for DPF, i.e., positive or negative in both tests, was about 70%. Positivity in DPF tests was a better predictor of positivity in either the Y1 adrenal or rabbit ileal loop test than vice versa. CHO cell, DPF, and rabbit ileal loop reactivities of unheated culture filtrates were each neutralized by anticholera antitoxin. Only four strains gave positive reactions in the infant mouse test, whereas up to 66% were positive for RPF in rabbit skin, based on positivity in Ty-1 or DR medium or both. DPF and RPF were produced by 35% of the strains. Of the 28 isolates from human stools, 82 and 92% and all of 11 strains tested were positive in the DPF, Y1 adrenal cell, and rabbit ileal loop tests, respectively. The corresponding data for 17 sewage isolates, representing 17 different serotypes rarely isolated from human stools in Sweden, were 63 and 69% and 8 of 8 tested. On the basis of this investigation, rabbit skin tests for both DPF and RPF provide the most reliable means of screening for enterotoxigenicity among salmonellae.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Annapurna E., Sanyal S. C. Enterotoxicity of Aeromonas hydrophila. J Med Microbiol. 1977 Aug;10(3):317–323. doi: 10.1099/00222615-10-3-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorn M. J., Iglewski B. H., Ives S. K., Sadoff J. C., Vasil M. L. Effect of iron on yields of exotoxin A in cultures of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA-103. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):785–791. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.785-791.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorn M. J., Sokol P. A., Iglewski B. H. Influence of iron on yields of extracellular products in Pseudomonas aeruginosa cultures. J Bacteriol. 1979 Apr;138(1):193–200. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.1.193-200.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess M. N., Bywater R. J., Cowley C. M., Mullan N. A., Newsome P. M. Biological evaluation of a methanol-soluble, heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin in infant mice, pigs, rabbits, and calves. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):526–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.526-531.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Smith D. M. Stimulation of steroidogenesis in tissue culture by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and its neutralization by specific antiserum. Infect Immun. 1974 Mar;9(3):500–505. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.3.500-505.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Gots R. E., Charney A. N., Greenough W. B., 3rd, Formal S. B. Pathogenesis of Salmonella-mediated intestinal fluid secretion. Activation of adenylate cyclase and inhibition by indomethacin. Gastroenterology. 1975 Dec;69(6):1238–1245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A. Importance of the intestinal inflammatory reaction in salmonella-mediated intestinal secretion. Infect Immun. 1979 Jan;23(1):140–145. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.1.140-145.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Rout W. R., Formal S. B., Collins H. Role of plasma filtration in the intestinal fluid secretion mediated by infection with Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1976 Feb;13(2):470–474. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.2.470-474.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A. Suckling mouse model for detection of heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin: characteristics of the model. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):95–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.95-99.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brunton L. L., Schnaitman T. C., Rebhun L. I., Gilman A. G. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate and alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology: a rapid, sensitive in vitro assay for the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):320–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.320-327.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L. Limitations of the infant mouse test for Escherichia coli heat stable enterotoxin. Can J Comp Med. 1979 Oct;43(4):371–379. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P., Sebag J. Decision-making in clinical practice and medical research: a theroretical analysis of predicators, indicators, and health index. Int J Biomed Comput. 1974 Oct;5(4):301–309. doi: 10.1016/0020-7101(74)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelterborn E. Uber die Häufigkeit des Vorkommens der Salmonella-Species. Eine Untersuchung an 1,5 Millionen Salmonella-Kulturen, die von 1934 bis 1975 in 109 Ländern isoliert worden waren. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1979 Apr;243(2-3):289–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Guerrant R. L., Wells J. G., Short H. B., Engert R. F. Comparison of assay of coliform enterotoxins by conventional techniques versus in vivo intestinal perfusion. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):146–152. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.146-152.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn H., Tschäpe H., Rische H. Enterotoxigenicity among salmonellae--a prospective analysis for a surveillance programme. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1978 Apr;240(2):171–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. Exotoxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. I. Factors that influence the production of exotoxin A. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(4):506–513. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.4.506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson E., Söderlind O. Comparison of different assays for definition of heat-stable enterotoxigenicity of Escherichia coli porcine strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jan;11(1):6–15. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.1.6-15.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. W. Salmonella toxin. Pharmacol Ther. 1980;11(3):719–724. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(80)90046-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. W., Sandefur P. D. Evidence of a role for permeability factors in the pathogenesis of salmonellosis. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Jan;32(1):197–209. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.1.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prost E., Riemann H. Food-borne salmonellosis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1967;21:495–528. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.21.100167.002431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rout W. R., Formal S. B., Dammin G. J., Giannella R. A. Pathophysiology of Salmonella diarrhea in the Rhesus monkey: Intestinal transport, morphological and bacteriological studies. Gastroenterology. 1974 Jul;67(1):59–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakazaki R., Tamura K., Nakamura A., Kurata T. Enteropathogenic and enterotoxigenic activities on ligated gut loops in rabbits of Salmonella and some other enterobacteria isolated from human patients with diarrhea. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1974 Feb;27(1):45–48. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.27.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandefur P. D., Peterson J. W. Isolation of skin permeability factors from culture filtrates of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):671–679. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.671-679.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandefur P. D., Peterson J. W. Neutralization of Salmonella toxin-induced elongation of Chinese hamster ovary cells by cholera antitoxin. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):988–992. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.988-992.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandstedt K., Gunnarsson A., Hurvell B., Nordblom B., Rutqvist L., Söderlind O. Salmonella isolated from animals and feed stuffs in Sweden during 1973-1977. Nord Vet Med. 1980 Feb;32(2):57–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedlock D. M., Deibel R. H. Detection of Salmonella enterotoxin using rabbit ileal loops. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Mar;24(3):268–273. doi: 10.1139/m78-046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedlock D. M., Koupal L. R., Deibel R. H. Production and partial purification of Salmonella enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):375–380. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.375-380.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speirs J. I., Stavric S., Konowalchuk J. Assay of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin with vero cells. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):617–622. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.617-622.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Takeda T., Yano T., Yamamoto K., Miwatani T. Purification and partial characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):978–985. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.978-985.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull P. C. Food poisoning with special reference to Salmonella -- its epidemiology, pathogenesis and control. Clin Gastroenterol. 1979 Sep;8(3):663–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull P. C., Richmond J. E. A model of salmonella enteritis: the behaviour of Salmonella enteritidis in chick intestine studies by light and electron microscopy. Br J Exp Pathol. 1978 Feb;59(1):64–75. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wensink J., Gankema H., Jansen W. H., Guinée P. A., Witholt B. Isolation of the membranes of an enterotoxigenic strain of Escherichia coli and distribution of enterotoxin activity in different subcellular fractions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 4;514(1):128–136. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90082-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


