Abstract
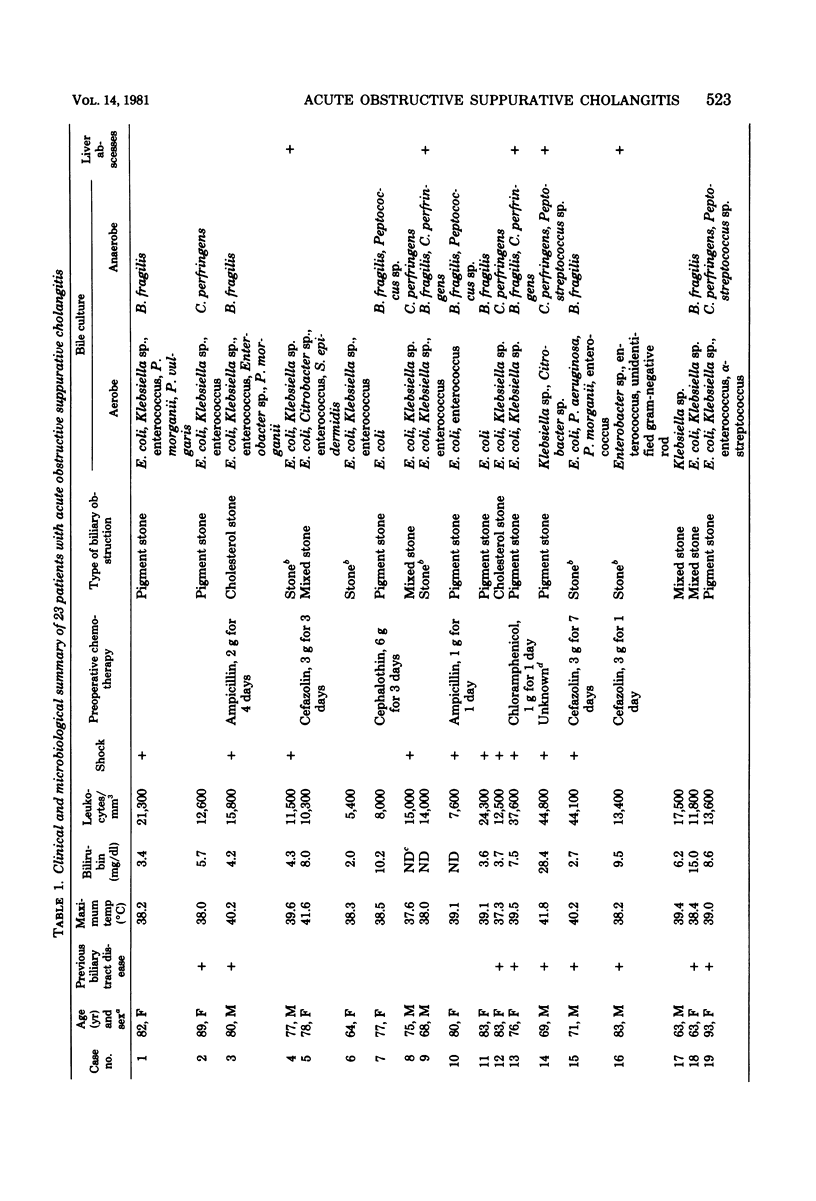
Bacteriological examination was performed on bile from 23 patients with acute obstructive suppurative cholangitis. Of 23 bile cultures, 15 yielded aerobic and anaerobic bacteria and 8 yielded aerobic bacteria only. No specimen grew anaerobic bacteria only. A total of 20 cultures yielded a polymicrobial flora, and 3 cultures grew one single aerobic bacterium. Escherichia coli, Klebsiella sp., enterococci, Bacteroids fragilis, and Clostridium perfringens were the predominant bacterial flora in bile of these patients. Bacteremia was documented in 10 of the 12 patients cultured. All bacteremias involved aerobic bacteria and were polymicrobial in three patients. The frequent presence of anaerobes in bile of patients with acute obstructive suppurative cholangitis suggests that antimicrobial therapy should provide adequate coverage for anaerobic bacteria and enteric organisms.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bourgault A. M., England D. M., Rosenblatt J. E., Forgacs P., Bieger R. C. Clinical characteristics of anaerobic bactibilia. Arch Intern Med. 1979 Dec;139(12):1346–1349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Murray G. F., Maddrey W. C. Aeromonas septicemia from hepatobiliary disease. Am J Dig Dis. 1973 Apr;18(4):323–331. doi: 10.1007/BF01070994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDLUND Y. A., MOLLSTEDT B. O., OUCHTERLONY O. Bacteriological investigation of the biliary system and liver in biliary tract disease correlated to clinical data and microstructure of the gallbladder and liver. Acta Chir Scand. 1959 May 15;116(5-6):461–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England D. M., Rosenblatt J. E. Anaerobes in human biliary tracts. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Nov;6(5):494–498. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.5.494-498.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lykkegaard Nielsen M., Asnaes S., Justesen T. Susceptibility of the liver and biliary tract to anaerobic infection in extrahepatic biliary tract obstruction. III. Possible synergistic effect between anaerobic and aerobic bacteria. An experimental study in rabbits. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1976;11(3):263–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen M. L., Justesen T. Anaerobic and aerobic bacteriological studies in biliary tract disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1976;11(5):437–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen M. L., Justesen T. Route of infection in extrahepatic biliary tract disease. II: Bacterial recovery from gallbladder bile and gallbladder wall in human biliary tract disease. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1976;37:17–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onderdonk A. B., Weinstein W. M., Sullivan N. M., Bartlett J. G., Gorbach S. L. Experimental intra-abdominal abscesses in rats: quantitative bacteriology of infected animals. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1256–1259. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1256-1259.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saik R. P., Greenburg A. G., Farris J. M., Peskin G. W. Spectrum of cholangitis. Am J Surg. 1975 Aug;130(2):143–150. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(75)90362-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Graevenitz A., Mensch A. H. The genus aeromonas in human bacteriology report of 30 cases and review of the literature. N Engl J Med. 1968 Feb 1;278(5):245–249. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196802012780504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein W. M., Onderdonk A. B., Bartlett J. G., Gorbach S. L. Experimental intra-abdominal abscesses in rats: development of an experimental model. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1250–1255. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1250-1255.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Graevenitz A., Simon G. Potentially pathogenic, nonfermentative, H2S-producing gram-negative rod (1 b). Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jan;19(1):176–176. doi: 10.1128/am.19.1.176-176.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


