Abstract
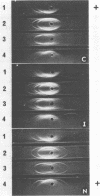
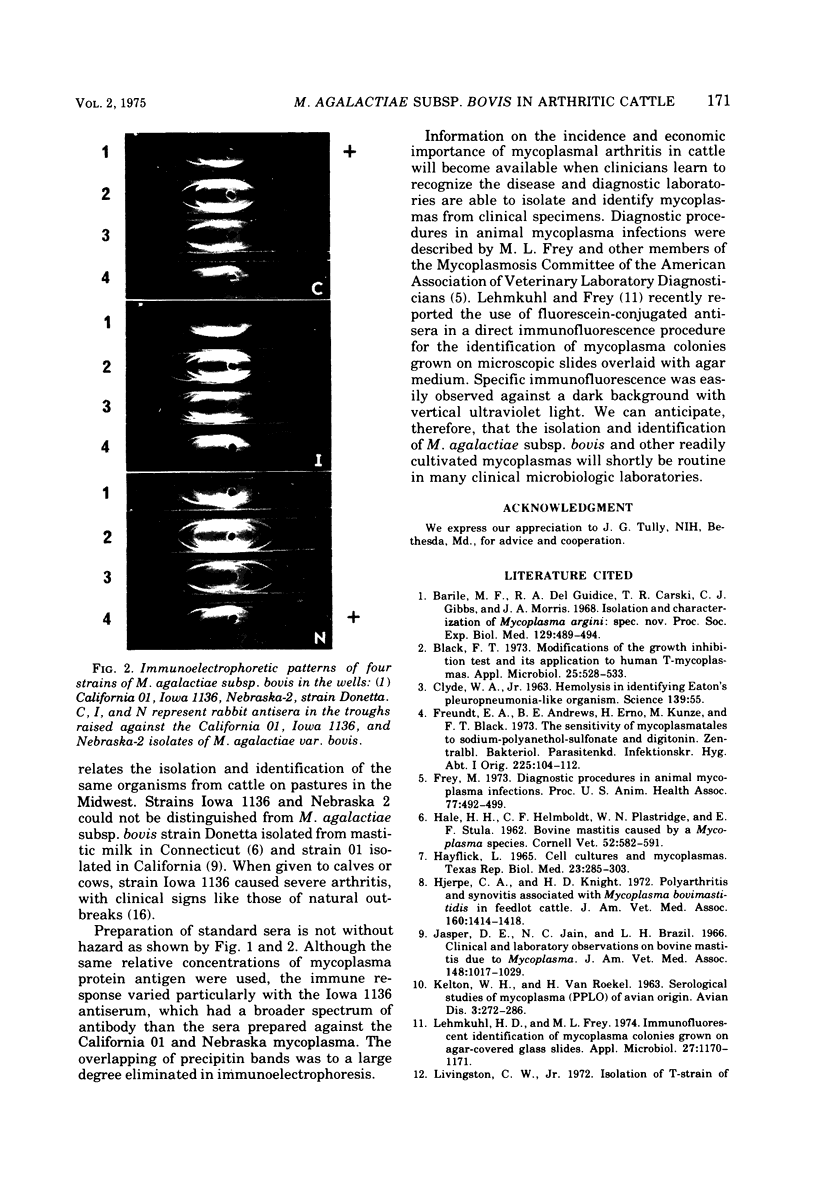
Two strains of Mycoplasma were isolated from synovial fluids of arthritic feeder cattle and were identified as Mycoplasma agalactiae subsp. bovis by growth inhibition and fluorescent antibody tests. The strains (Iowa 1136 and Nebraska 2) could not be distinguished from known strains (Donetta and California 01) by immunoelectrophoresis or by agar gel precipitation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barile M. F., DelGiudice R. A., Carski T. R., Gibbs C. J., Morris J. A. Isolation and characterization of Mycoplasma arginini: spec. nov. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Nov;129(2):489–494. doi: 10.3181/00379727-129-33351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black F. T. Modifications of the growth inhibition test and its application to human T-mycoplasmas. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Apr;25(4):528–533. doi: 10.1128/am.25.4.528-533.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLYDE W. A., Jr Hemolysis in identifying Eaton's pleuro-pneumonia-like organism. Science. 1963 Jan 4;139(3549):55–55. doi: 10.1126/science.139.3549.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freundt E. A., Andrews B. E., Erno H., Kunze M., Black F. T. The sensitivity of mycoplasmatales to sodium-polyanethol-sulfonate and digitonin. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1973 Oct;225(1):104–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey M. L. Diagnostic precedures in animal mycoplasma infections. Proc Annu Meet U S Anim Health Assoc. 1973;(77):492–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALE H. H., HELMBOLDT C. F., PLASTRIDGE W. N., STULA E. F. Bovine mastitis caused by a Mycoplasma species. Cornell Vet. 1962 Oct;52:582–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayflick L. Tissue cultures and mycoplasmas. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1965 Jun;23(Suppl):285+–285+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjerpe C. A., Knight H. D. Polyarthritis and synovitis associated with Mycoplasma bovimastitidis in feedlot cattle. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1972 May 15;160(10):1414–1418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasper D. E., Jain N. C., Brazil L. H. Clinical and laboratory observations on bovine mastitis due to Mycoplasma. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1966 May 1;148(9):1017–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelton W. H., Van Roekel H. Serological studies of mycoplasma (PPLO) of avian origin. Avian Dis. 1963 Aug;7(3):272–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmkuhl H. D., Frey M. L. Immunofluorescent identification of mycoplasma colonies grown on agar-covered glass slides. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jun;27(6):1170–1171. doi: 10.1128/am.27.6.1170-1171.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston C. W., Jr Isolation of T-strain of mycoplasma from Texas feedlot cattle. Am J Vet Res. 1972 Oct;33(10):1925–1929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh U. M., Doig P. A., Ruhnke H. L. Mycoplasma arthritis in calves. Can Vet J. 1971 Sep;12(9):183–185. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobeslavsky O., Prescott B., Chanock R. M. Adsorption of Mycoplasma pneumoniae to neuraminic acid receptors of various cells and possible role in virulence. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):695–705. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.695-705.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalheim O. H., Hubbert W. T., Foley J. W. Infectivity of two mycoplasmas of bovine origin in pregnant heifers. Am J Vet Res. 1974 Jan;35(1):63–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone S. S., Shifrine M. Comparative studies of antigens from Mycoplasma mycoides and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1254–1259. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1254-1259.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone S. S., Tessler J. Fluorescent labeling of antibody for identifying mycoplasma colonies by incident ultraviolet light. Am J Vet Res. 1974 Jan;35(1):107–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Manchee R. J. Spermadsorption and spermagglutination by mycoplasmas. Nature. 1967 Jul 29;215(5100):484–487. doi: 10.1038/215484a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully J. G., Barile M. F., Del Giudice R. A., Carski T. R., Armstrong D., Razin S. Proposal for classifying strain PG-24 and related canine mycoplasmas as Mycoplasma edwardii sp. n. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):346–349. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.346-349.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]