Abstract
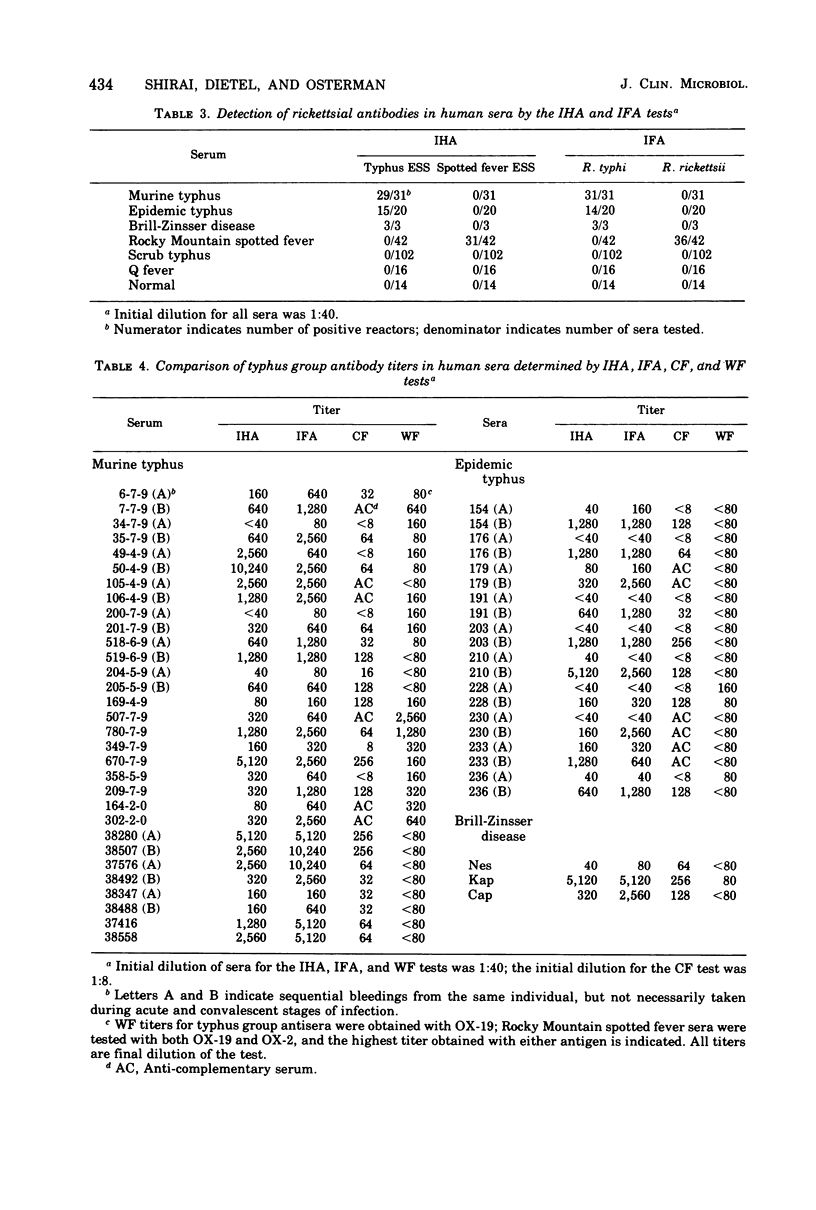
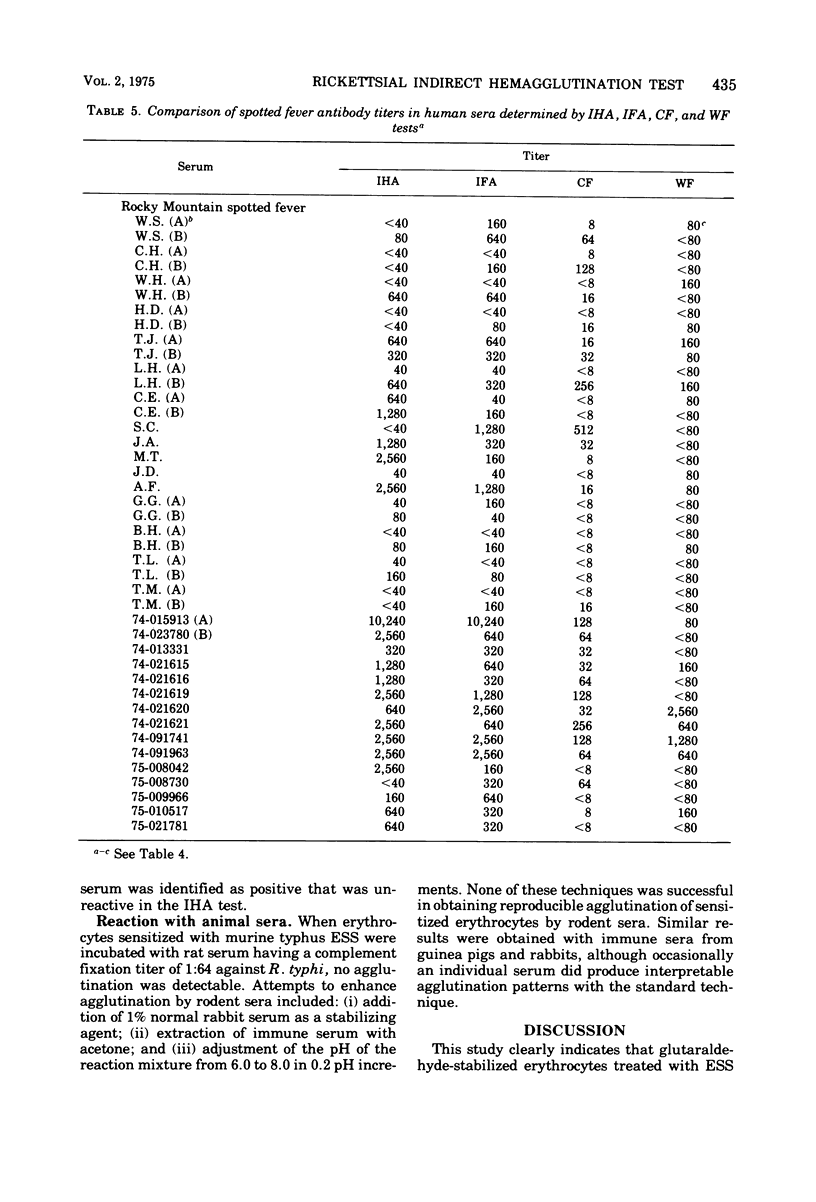
An indirect hemagglutination (IHA) test is described that uses glutaraldehyde-stabilized erythrocytes treated with a rickettsial erythrocyte-sensitizing substance obtained from Rickettsia typhi or Rickettsia rickettsii. The serological reagent was stable for at least 3 months at room temperature and 6 months at 4 C. It exhibited group specificity and no group cross-reactivity. At a minimum dilution of 1:40, acute and early convalescent epidemic and murine typhus antisera showed 86% positive reactors, whereas similar spotted fever antisera had 74% positive reactors. In comparison with the indirect fluorescent antibody test, the IHA procedure gave lower titers but showed comparable detection of seroconversion with most paired sera. The IHA test demonstrated significantly higher titers than the complement fixation test and was more sensitive than either the complement fixation or Weil-Felix test in identifying seroconversion. No agglutination was observed when sensitized erythrocytes were tested with rodent sera known to contain rickettsial antibodies.
Full text
PDF

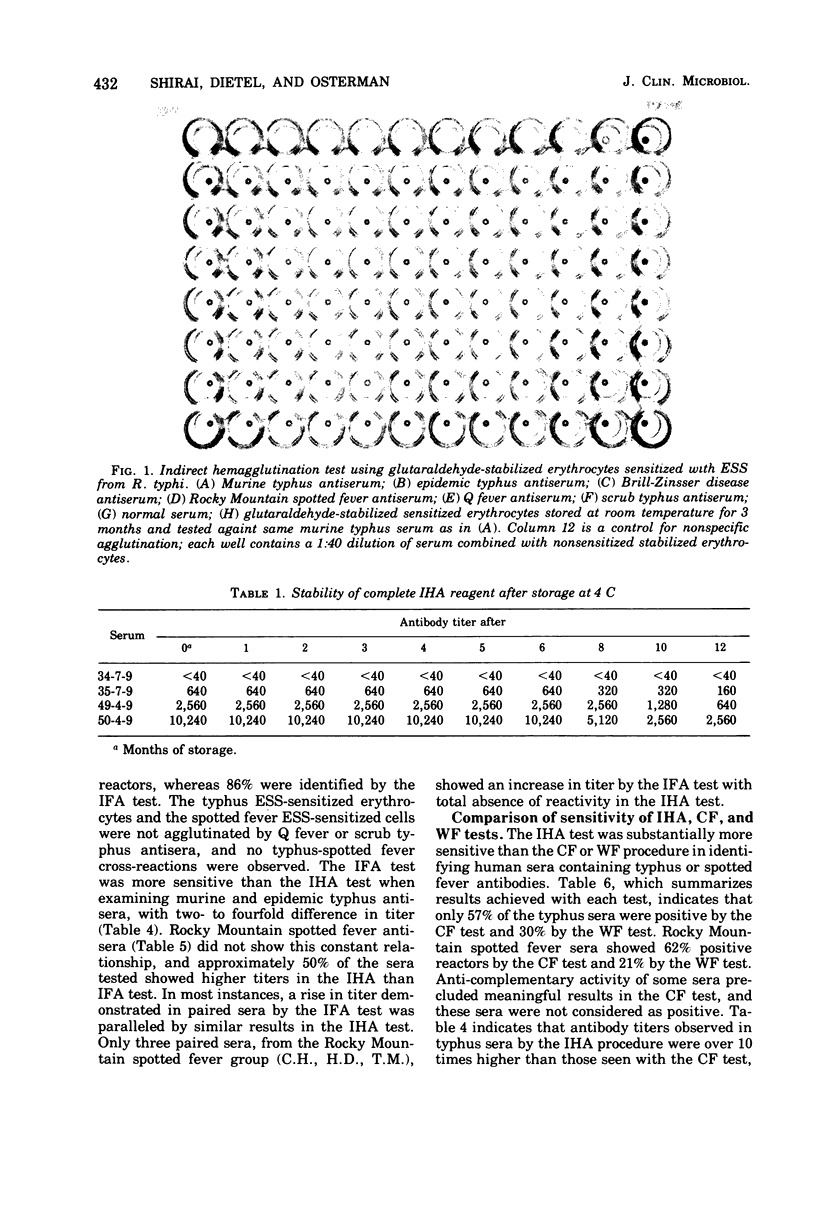
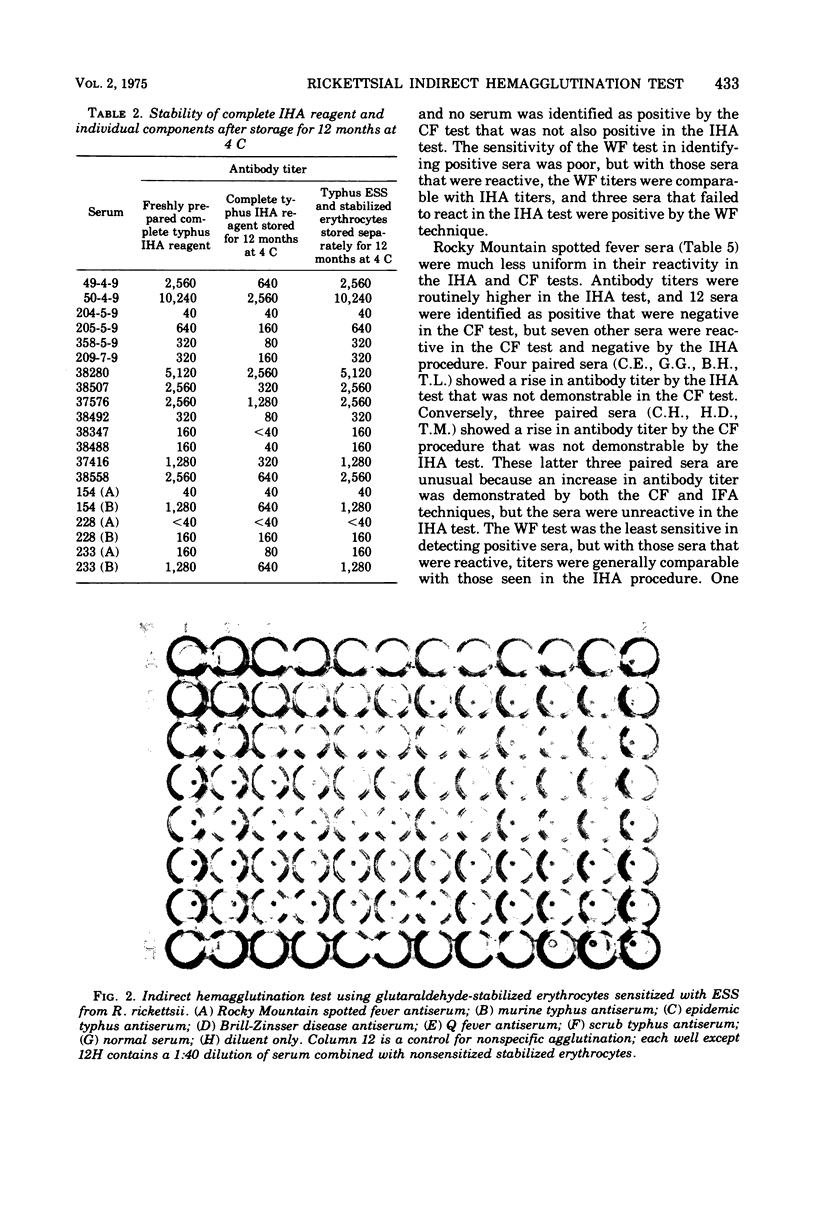


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOZEMAN F. M., ELISBERG B. L. Serological diagnosis of scrub typhus by indirect immunofluorescence. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Mar;112:568–573. doi: 10.3181/00379727-112-28107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakemeier R. F. A study of phase variation in Coxiella burneti employing hemagglutination tests. J Immunol. 1965 Nov;95(5):880–886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANG R. S., MURRAY E. S., SNYDER J. C. Erythrocyte-sensitizing substances from Rickettsiae of the Rocky Mountain spotted fever group. J Immunol. 1954 Jul;73(1):8–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANG S. M. A serologically-active erythrocyte-sensitizing substance from typhus rickettsiae. I. Isolation and titration. J Immunol. 1953 Mar;70(3):212–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANG S. M., SNYDER J. C., MURRAY E. S. A serologically active erythrocyte sensitizing substance from typhus rickettsiae. II. Serological properties. J Immunol. 1953 Mar;70(3):215–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOWNS C. M., FEVURLY J., MEYER M. M. Studies on hemagglutination inhibition phenomena. I. The presence of inhibiting antigen in typhus-infected animals. J Immunol. 1955 Jul;75(1):35–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAN E. S. Hemagglutination test for epidemic and murine typhus fever using sheep erythrocytes sensitized with Proteus OX 19 extracts. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1951 Mar;31(2):243–251. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1951.s1-31.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERSEY D. F., COLVIN M. C., SHEPARD C. C. Studies on the serologic diagnosis of murine typhus and Rocky Mountain spotted fever. II. Human infections. J Immunol. 1957 Nov;79(5):409–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENT J. F., FIFE E. H., Jr Precise standardization of reagents for complement fixation. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1963 Jan;12:103–116. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1963.12.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]