Abstract
Simplified dichotomous schemata are described for the identification of anaerobic bacteria commonly encountered in clinical material. The procedures used are combinations of routine biochemical tests and techniques that are used to uniformly characterize these organisms. Over 200 anaerobic organisms were used in a three-stage evaluation in which data were compared with those obtained by conventional methods. When there was inconsistency between the biochemical tests described in the presumptive identification schemes and gas-liquid chromatography, additional biochemical tests or reference procedures were used to confirm identification. Strains from the American Type Culture Collection and the Center for Disease Control, as well as recent clinical isolates, were included in this evaluation. The results show the simplified procedures to be useful for the identification of anaerobic isolates from clinical material.
Full text
PDF


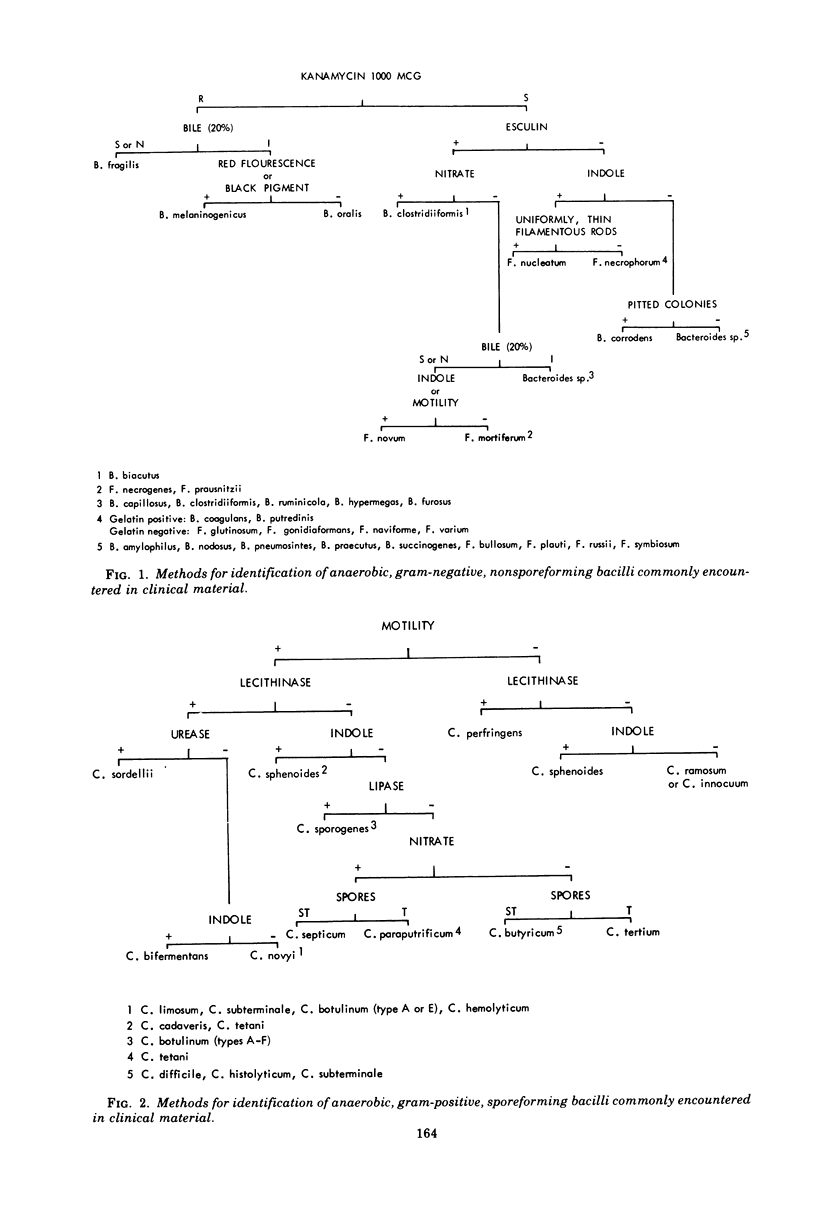
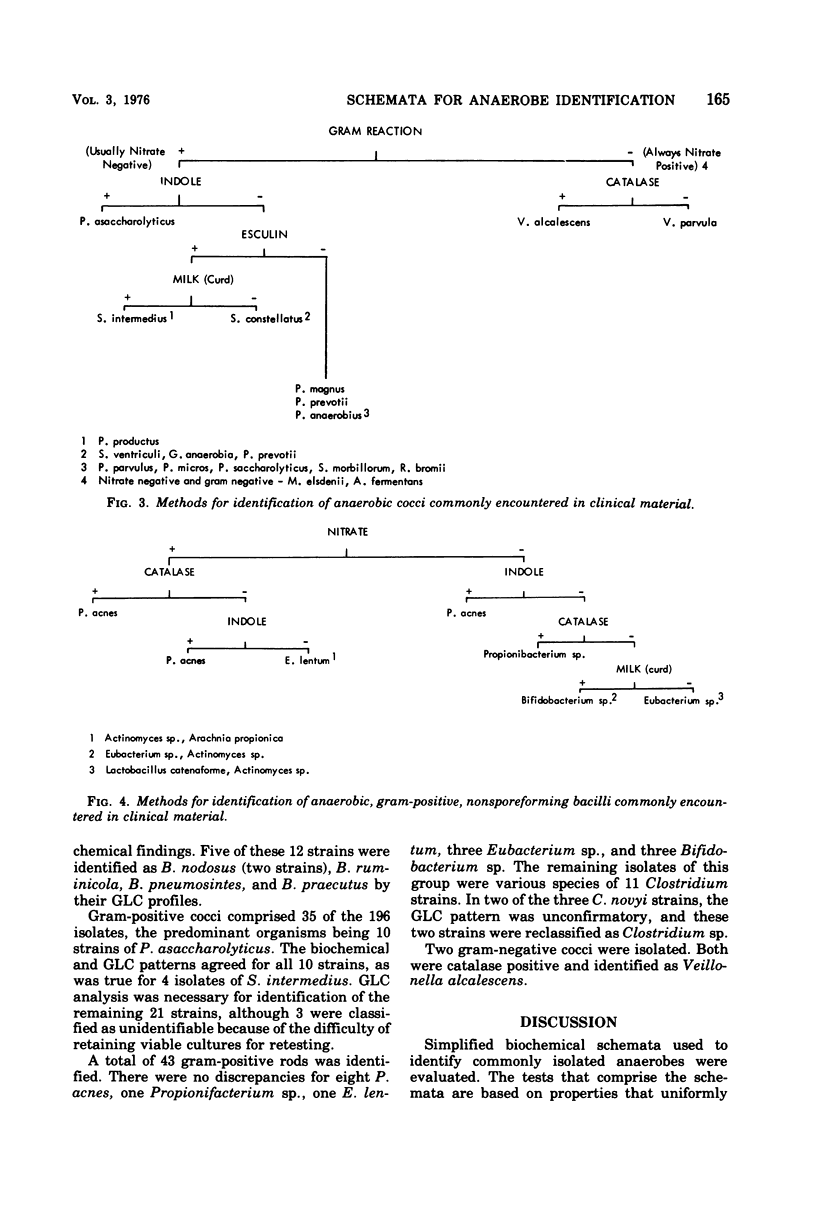
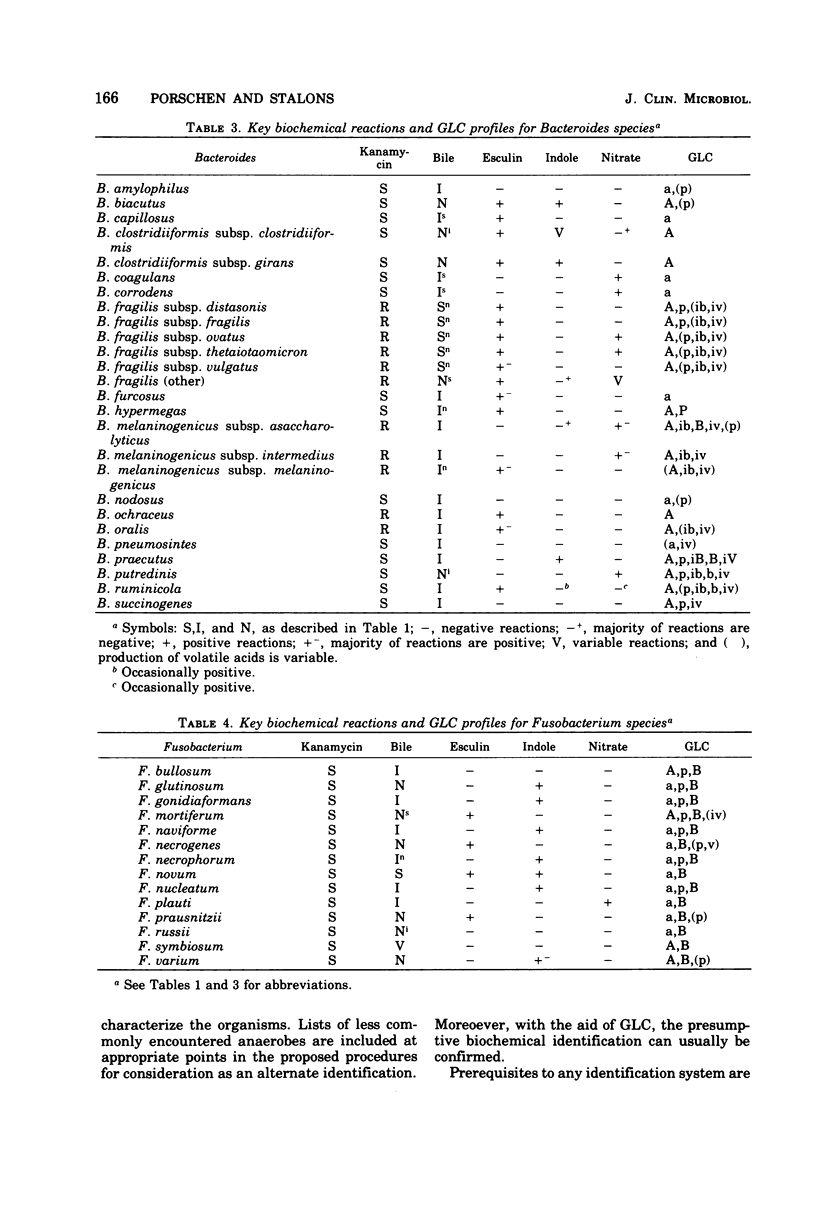
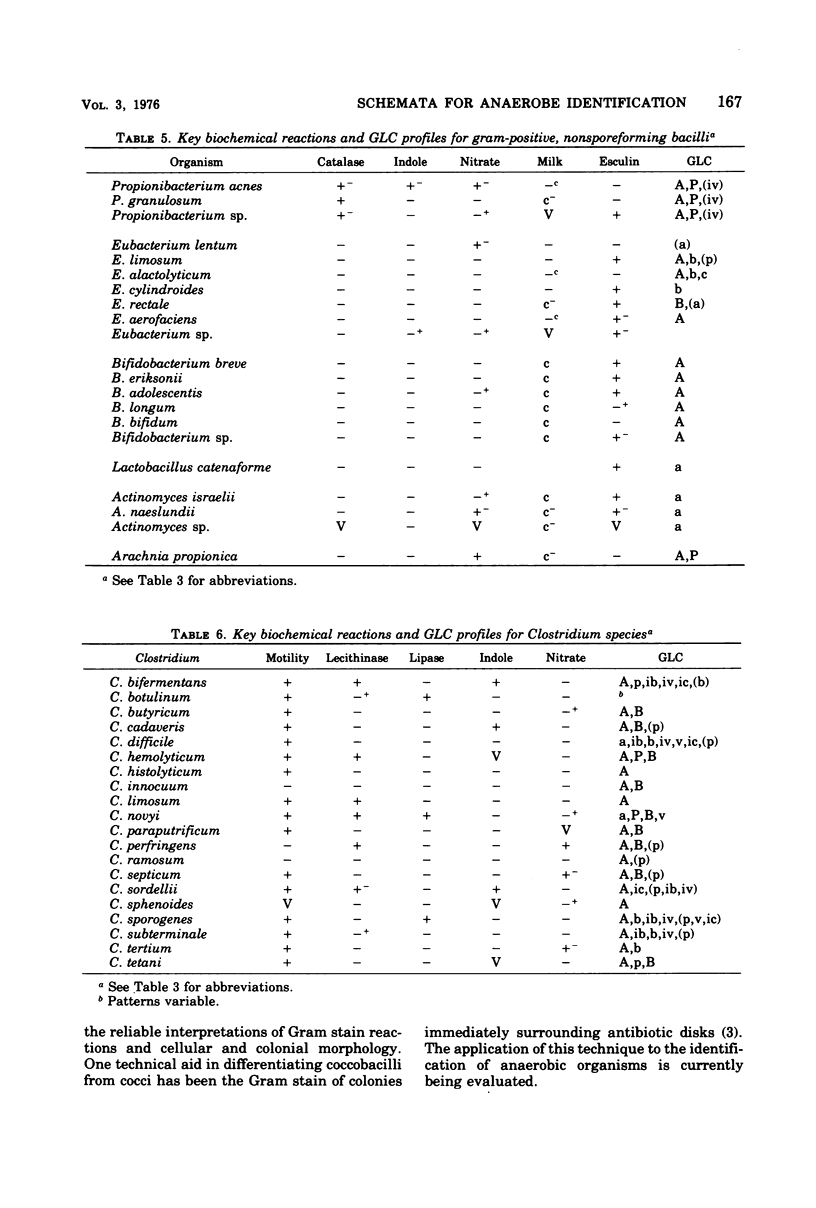



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BORNSTEIN D. L., WEINBERG N., SWARTZ M. N., KUNZ L. J. ANAEROBIC INFECTIONS--REVIEW OF CURRENT EXPERIENCE. Medicine (Baltimore) 1964 May;43:207–232. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196405000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catlin B. W. Cellular elongation under the influence of antibacterial agents: way to differentiate coccobacilli from cocci. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):102–105. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.102-105.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Bartlett J. G. Anaerobic infections. 1. N Engl J Med. 1974 May 23;290(21):1177–1184. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197405232902106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. J. Isolation and indentification of anaerobic bacteria in the clinical laboratory. A 2-year experience. Mayo Clin Proc. 1974 May;49(5):300–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. J. Practical method for isolation of anerobic bacteria in the clinical laboratory. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Dec;22(6):1168–1171. doi: 10.1128/am.22.6.1168-1171.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pien F. D., Thompson R. L., Martin W. J. Clinical and bacteriologic studies of anaerobic gram-positive cocci. Mayo Clin Proc. 1972 Apr;47(4):251–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Carter W. T. Evaluation of media and reagents for indole-spot tests in anaerobic bacteriology. Am J Clin Pathol. 1972 Sep;58(3):335–338. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/58.3.335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Antibiotic disc susceptibility tests for rapid presumptive identification of Gram-negative anaerobic bacilli. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Jan;21(1):13–20. doi: 10.1128/am.21.1.13-20.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vargo V., Korzeniowski M., Spaulding E. H. Tryptic soy bile-kanamycin test for the indentification of Bacteroides fragilis. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Mar;27(3):480–483. doi: 10.1128/am.27.3.480-483.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


