Abstract
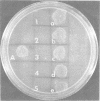
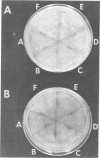
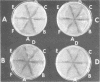
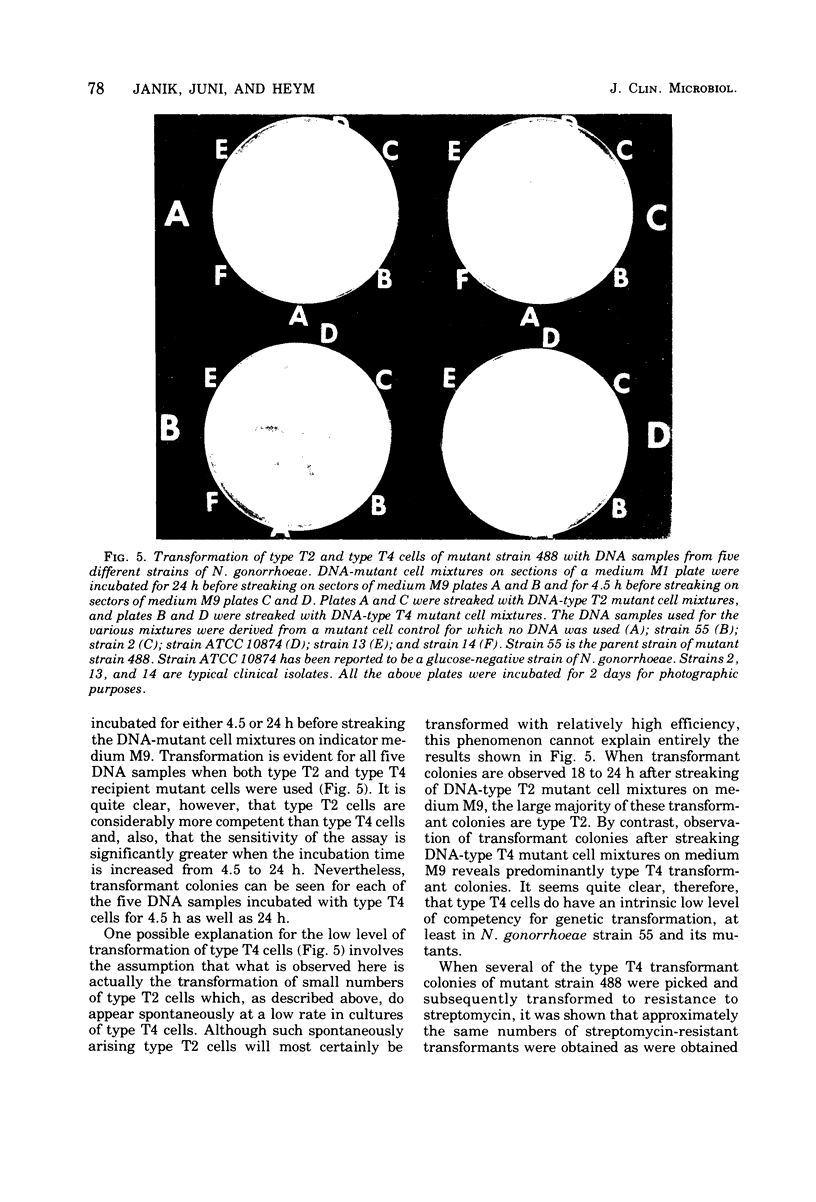
A rapid method for the detection of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, making use of the ability of deoxyribonucleic acid samples from clinically isolated strains of this organism to transform nutritional mutants of a particular strain of N. gonorrhoeae, has been described. In addition to using isolated cultures, transforming deoxyribonucleic acid can be obtained directly from the material that adheres to swabs of the cervix or the urethra. The time interval for transfer of swabs to the diagnostic laboratory is not a significant factor. It is not necessary to use pure cultures on primary isolation plates to obtain definitive results. Nongonorrhoeae neisserias, as well as a large variety of commonly encountered unrelated bacteria, do not react or interfere in the transformation assay when using one of the mutant strains under a standardized set of conditions. The entire assay can be completed in less than 24 h. It has also been shown that type T4 cells of the strain of N. gonorrhoeae employed in the present study are competent for genetic transformation, although type T4 cells are transformed at a significantly lower frequency than are type T2 cells of the same strain.
Full text
PDF

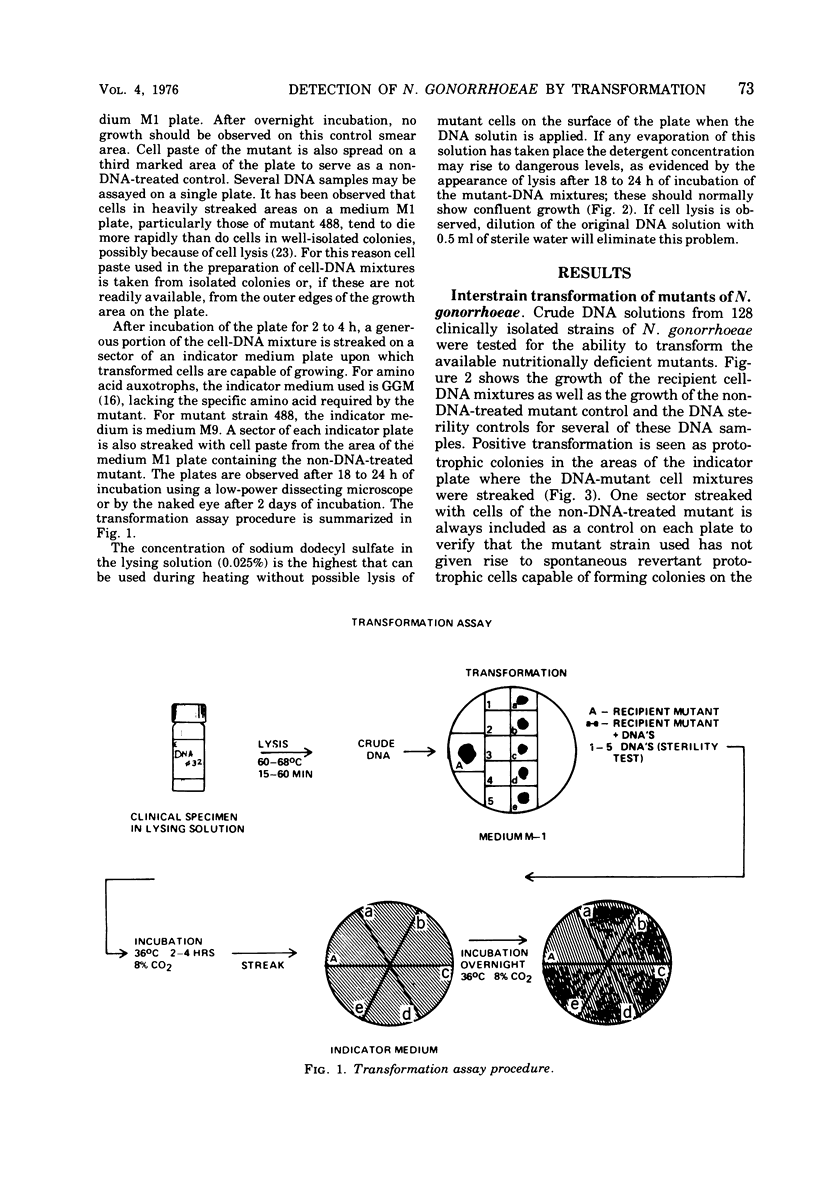
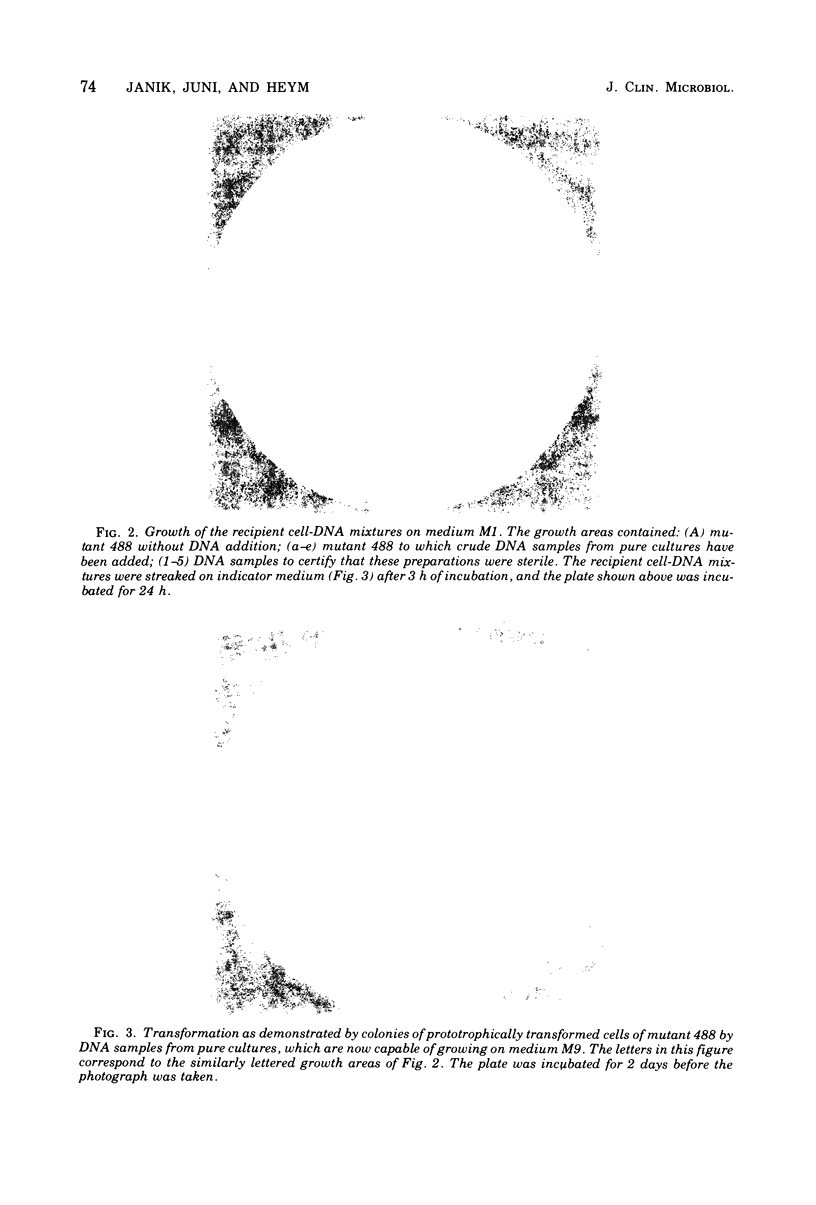
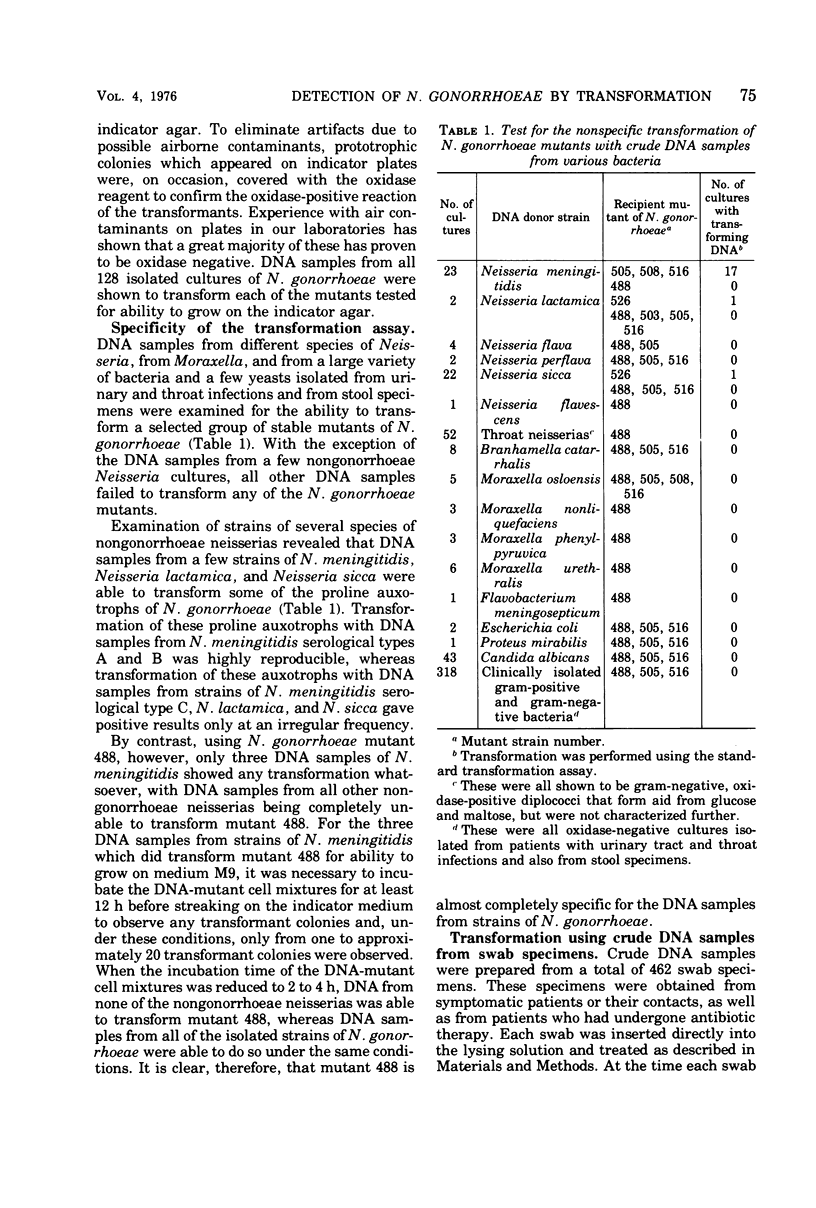

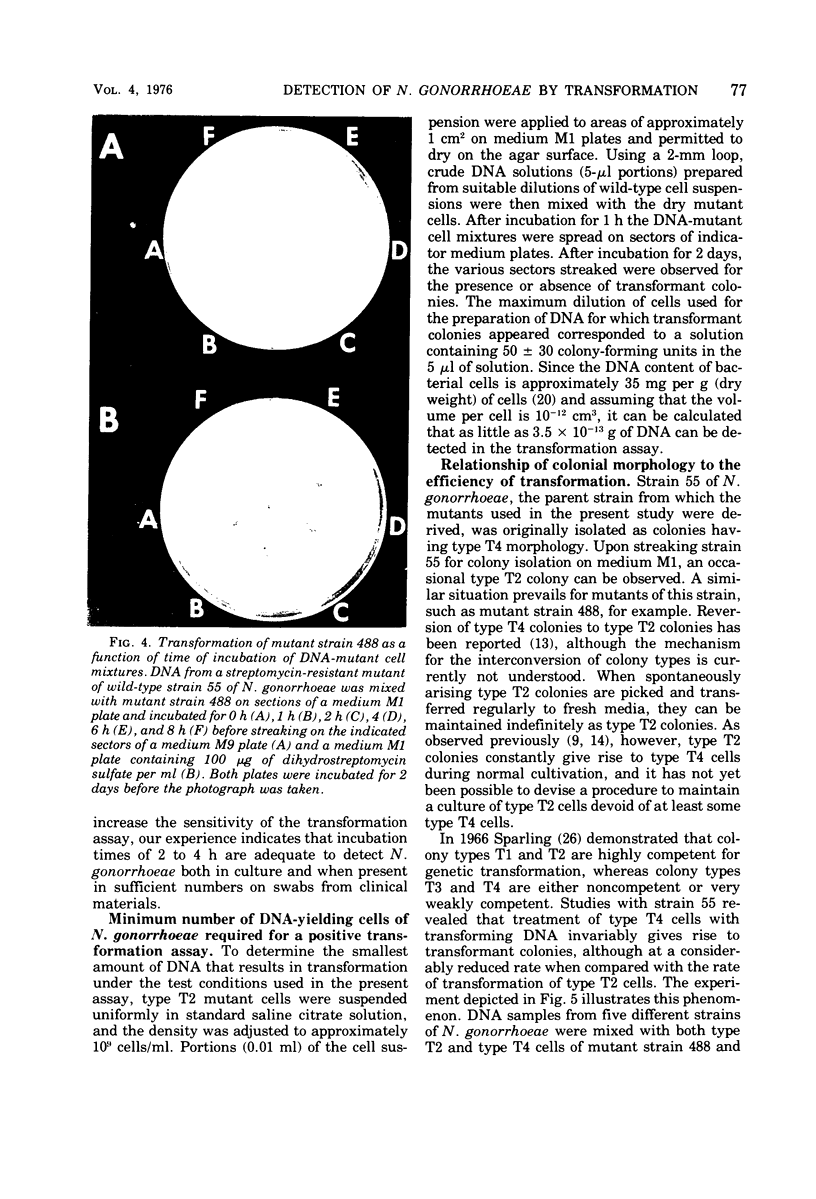



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bovre K., Fiandt M., Szybalski W. DNA base composition of Neisseria, Moraxella, and Acinetobacter, as determined by measurement of buoyant density in CsCl gradients. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Apr;15(4):335–338. doi: 10.1139/m69-062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. J., Kraus S. J. Gonococcal colony types. JAMA. 1974 May 13;228(7):862–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATLIN B. W., CUNNINGHAM L. S. Transforming activities and base contents of deoxyribonucleate preparations from various Neisseriae. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Oct;26:303–312. doi: 10.1099/00221287-26-2-303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carifo K., Catlin B. W. Neisseria gonorrhoeae auxotyping: differentiation of clinical isolates based on growth responses on chemically defined media. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Sep;26(3):223–230. doi: 10.1128/am.26.3.223-230.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catlin B. W. Genetic transformation of biosynthetically defective Neisseria gonorrhoeae clinical isolates. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):203–209. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.203-209.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould R. G., Kane L. W., Mueller J. H. On the Growth Requirements of Neisseria Gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1944 Mar;47(3):287–292. doi: 10.1128/jb.47.3.287-292.1944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jephcott A. E., Reyn A., Birch-Andersen A. Neisseria gonorrhoeae 3. Demonstration of presumed appendages to cells from different colony types. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(3):437–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1971.tb00086.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jephcott A. E., Reyn A. Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Colony variation I. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(5):609–614. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1971.tb00088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juni E. Interspecies transformation of Acinetobacter: genetic evidence for a ubiquitous genus. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):917–931. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.917-931.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juni E. Simple genetic transformation assay for rapid diagnosis of Moraxella osloensis. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jan;27(1):16–24. doi: 10.1128/am.27.1.16-24.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. S., Jr, Cohen I. R., Norins L. C., Schroeter A. L., Reising G. Neisseria gonorrhoeae. II. Colonial variation and pathogenicity during 35 months in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):596–605. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.596-605.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. S., Jr, Turner E. M. Rapid fermentation confirmation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Apr;25(4):550–552. doi: 10.1128/am.25.4.550-552.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDERBERG J. Streptomycin resistance; a genetically recessive mutation. J Bacteriol. 1951 May;61(5):549–550. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.5.549-550.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Scolea L. J., Jr, Young F. E. Development of a defined minimal medium for the growth of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jul;28(1):70–76. doi: 10.1128/am.28.1.70-76.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. F., Alexander J. J. Isolation of Neisseria meningitidis from the vagina and cervix. Am J Clin Pathol. 1974 Feb;61(2):216–217. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/61.2.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ley H. L., Jr, Mueller J. H. On the Isolation from Agar of an Inhibitor for Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1946 Oct;52(4):453–460. doi: 10.1128/jb.52.4.453-460.1946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. A., Bartenstein L. Factors affecting autolysis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Apr;145(4):1418–1421. doi: 10.3181/00379727-145-38025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punsalang A. P., Jr, Sawyer W. D. Role of pili in the virulence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):255–263. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.255-263.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYN A. LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS OF GONOCOCCAL INFECTIONS. Bull World Health Organ. 1965;32:449–469. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparling P. F. Genetic transformation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to streptomycin resistance. J Bacteriol. 1966 Nov;92(5):1364–1371. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.5.1364-1371.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spizizen J., Reilly B. E., Evans A. H. Microbial transformation and transfection. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1966;20:371–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.20.100166.002103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Kraus S. J., Gotschlich E. C. Studies on gonococcus infection. I. Pili and zones of adhesion: their relation to gonococcal growth patterns. J Exp Med. 1971 Oct 1;134(4):886–906. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.4.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer J. D., Martin J. E., Jr Improved medium selective for cultivation of N. gonorrhoeae and N. meningitidis. Public Health Rep. 1966 Jun;81(6):559–562. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]