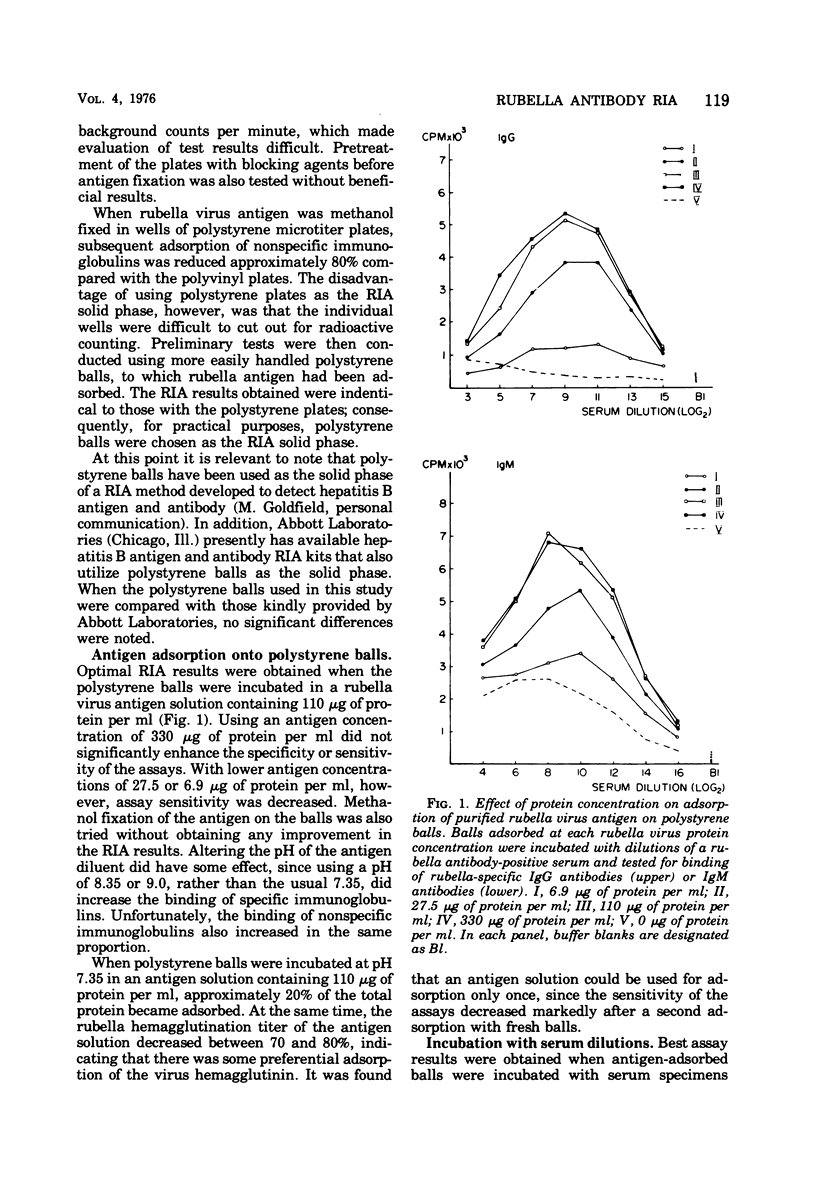
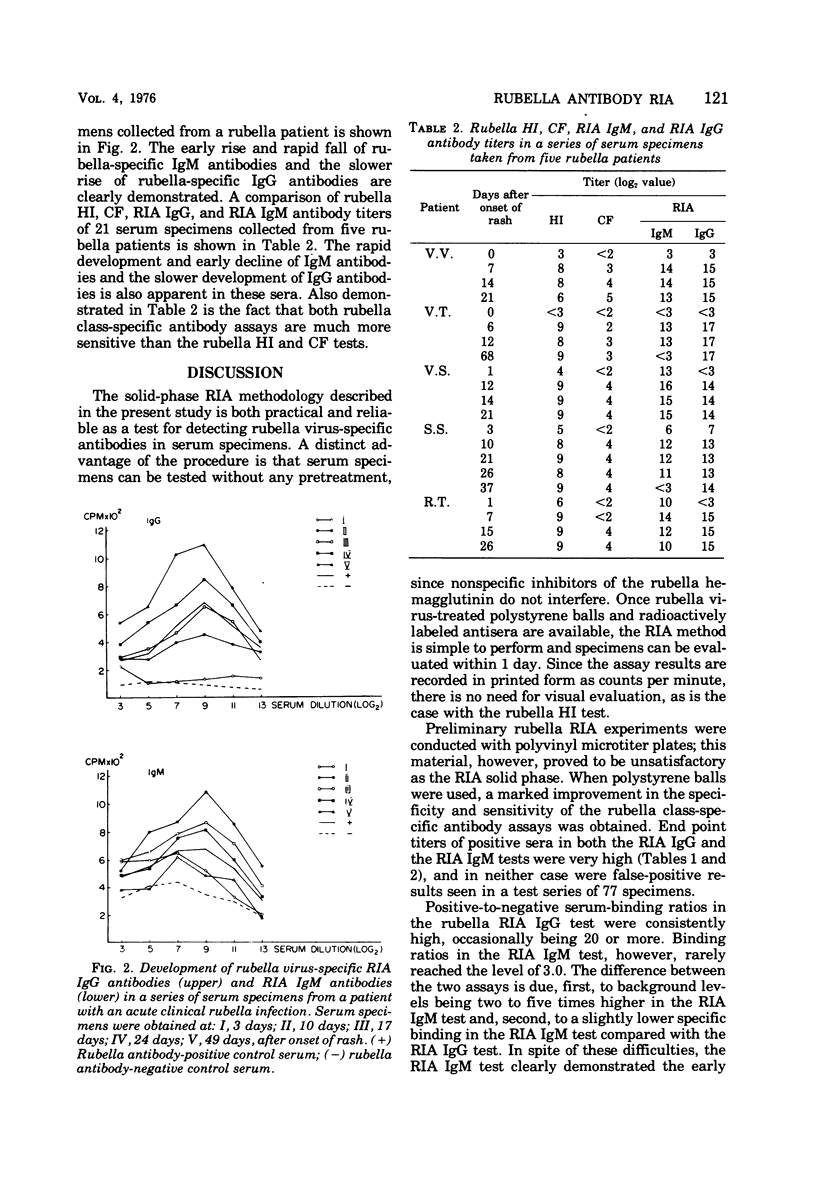
Abstract
A solid-phase radioimmunoassay method has been developed for the detection of rubella virus-specific immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgM antibodies in human serum specimens. Purified rubella virus was adsorbed onto polystyrene balls, and antibodies that attached to the virus-treated balls were detected by subsequent binding of 125I-labeled anti-human gamma or anti-human mu immunoglobulins. A total of 77 serum specimens were tested. Binding ratios between positive and negative sera were as high as 22 in the IgG assay but rarely exceeded 3 in the IgM assay. The sensitivity of the IgG assay was found to be 16 to 256 times higher than that of the rubella virus hemagglutination inhibition test. The IgG radioimmunoassay can be readily adopted for routine diagnostic use. The IgM radioimmunoassay, however, due to its lower sensitivity, must be modified before being routinely applied.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ankerst J., Christensen P., Kjellén L., Kronvall G. A rountine diagnostic test for IgA and IgM antibodies to rubella virus: absorption of IgG with Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1974 Sep;130(3):268–273. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.3.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banatvala J. E., Best J. M., Kennedy E. A., Smith E. E., Spence M. E. A serological method for demonstrating recent infection by rubella virus. Br Med J. 1967 Jul 29;3(5560):285–286. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5560.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlton D., Blandford G. A solid phase micro-radioimmunoassay to detect minute amounts of Ig class specific anti-viral antibody in a mouse model system. J Immunol Methods. 1975 Oct;8(4):319–330. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(75)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cradock-Watson J. E., Bourne M. S., Vandervelde E. M. IgG, IgA and IgM responses in acute rubella determined by the immunofluorescent technique. J Hyg (Lond) 1972 Sep;70(3):473–485. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400063063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daugharty H., Davis M. L., Kaye H. S. Immunoglobulin class of influenza antibodies investigated by radioimmunoassay (RIA). J Immunol. 1972 Oct;109(4):849–856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daugharty H. Preferential radioassay of influenza-specific 7S (IgG) over 19S (IgM) class of antibodies. J Immunol. 1973 Aug;111(2):404–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daugharty H., Warfield D. T., Hemingway W. D., Casey H. L. Mumps class-specific immunoglobulins in radioimmunoassay and conventional serology. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):380–385. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.380-385.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forghani B., Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H. Demonstration of rubella IgM antibody by indirect fluorescent antibody staining, sucrose density gradient centrifugation and mercaptoethanol reduction. Intervirology. 1973;1(1):48–59. doi: 10.1159/000148832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forghani B., Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H. Solid phase radioimmunoassay for identification of Herpesvirus hominis types 1 and 2 from clinical materials. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):661–667. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.661-667.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta J. D., Peterson V., Stout M., Murphy A. M. Single-sample diagnosis of recent rubella by fractionation of antibody on Sephadex G-200 column. J Clin Pathol. 1971 Sep;24(6):547–550. doi: 10.1136/jcp.24.6.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haire M., Hadden D. S. Rapid diagnosis of rubella by demonstrating rubella-specific IgM antibodies in ther serum by indirect immunofluorescence. J Med Microbiol. 1972 May;5(2):237–242. doi: 10.1099/00222615-5-2-237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halonen P. D., Casey H. L., Stewart J. A., Hall A. D. Rubella complement fixing antigen prepared by alkaline extraction of virus grown in suspension culture of BHK-211 cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 May;125(1):167–172. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halonen P. E., Stewart J. A., Hall A. D. Rubella hemagglutinin prepared in serum free suspension culture of BHK-21 cells. Ann Med Exp Biol Fenn. 1967;45(2):182–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haukenes G., Blom H. False positive rubella virus haemagglutination inhibition reactions: occurrence and disclosure. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1975;161(2):99–106. doi: 10.1007/BF02121750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollinger F. B., Vorndam V., Dreesman G. R. Assay of Australia antigen and antibody employing double-antibody and solid-phase radioimmunoassay techniques and comparison with the passive hemagglutination methods. J Immunol. 1971 Oct;107(4):1099–1111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson H. D., Ziegler D. W., Feorino P. M. Radioimmunoassay for detection of antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus in human infectious mononucleosis serum specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 May;1(5):429–433. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.5.429-433.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson H. D., Ziegler D. W. Simplified radioimmunoassay for diagnostic serology. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Nov;24(5):742–749. doi: 10.1128/am.24.5.742-749.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwakata S., Rhodes A. H., Labzoffsky N. A. Laboratory diagnosis of rubella virus infections. Can Med Assoc J. 1973 Apr 7;108(7):894–passim. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwakata S., Rhodes A. J., Labzoffsky N. A. The significance of specific IgM antibody in the diagnosis of rubella employing the immunofluorescence technique. Can Med Assoc J. 1972 Feb 19;106(4):327–330. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nassau E., Parsons E. R., Johnson G. D. Detection of antibodies to mycobacterium tuberculosis by solid phase radioimmunoassay. J Immunol Methods. 1975 Jan;6(3):261–271. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(75)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson W. R., Smith K. O. Improvements of a radioimmunoassay for measurement of viral antibody in human sera. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Aug;2(2):130–133. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H., Wong D. C., Alter H. J., Holland P. V. Microtiter solid-phase radioimmunoassay for hepatitis B antigen. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Oct;26(4):478–484. doi: 10.1128/am.26.4.478-484.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal J. D., Hayashi K., Notkins A. L. Comparison of direct and indirect solid-phase microradioimmunoassays for the detection of viral antigens and antiviral antibody. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Apr;25(4):567–573. doi: 10.1128/am.25.4.567-573.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Vaheri A., Estola T., Sandelin K. Antibodies against avian GS antigen in chickens infected naturally and experimentally with avian RNA tumor viruses. Int J Cancer. 1973 May;11(3):595–603. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. O., Gehle W. D., McCracken A. W. Radioimmunoassay techniques for detecting naturally occurring viral antibody in human sera. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Oct;5(4):337–344. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suni J., Vaheri A., Ruoslahti E. Radioimmunoassay of avian RNA tumor virus group-specific antigen. Intervirology. 1973;1(2):119–126. doi: 10.1159/000148838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesikari T., Vaheri A. Rubella: a method for rapid diagnosis of a recent infection by demonstration of the IgM antibodies. Br Med J. 1968 Jan 27;1(5586):221–223. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5586.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viljanen M. K., Granfors K., Toivanen P. Radioimmunoassay of class-specific antibodies (RIACA): chicken antibodies to bovine serum albumin. Immunochemistry. 1975 Aug;12(8):699–705. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(75)90218-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner L. P., Johnson R. T., Herndon R. M. Viral infections and demyelinating diseases. N Engl J Med. 1973 May 24;288(21):1103–1110. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197305242882106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler D. W., Hutchinson H. D., Koplan J. P., Nakano J. H. Detection by radioimmunoassay of antibodies in human smallpox patients and vaccinees. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Mar;1(3):311–317. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.3.311-317.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


