Abstract
A simple, rapid mixed agglutination test using sheep erythrocytes (SRBC) sensitized with rabbit hemolysin and intact viable staphylococci is described for the detection of bound staphylococcal protein A. Soluble protein A was heat extracted from 50 clinical isolates as well as the Cowan I and Wood 46 strains of Staphylococcus aureus and titered by a hemagglutination test using sensitized SRBC and dilutions of soluble protein A. Protein A could be detected in all of these supernatants including that of S. aureus Wood 46, a strain generally considered to be protein A negative. These organisms were later retested by the mixed agglutination test and even those staphylococcal isolates expressing very low heat-extractable soluble protein A concentrations (1:2 titers) were positive, confirming the sensitivity of the test. In a screen of clinical isolates, only 4 of 235 (1.8%) coagulase-positive isolates were negative in the mixed agglutination test. Of 25 coagulase-negative isolates, none yielded a positive reaction.
Full text
PDF
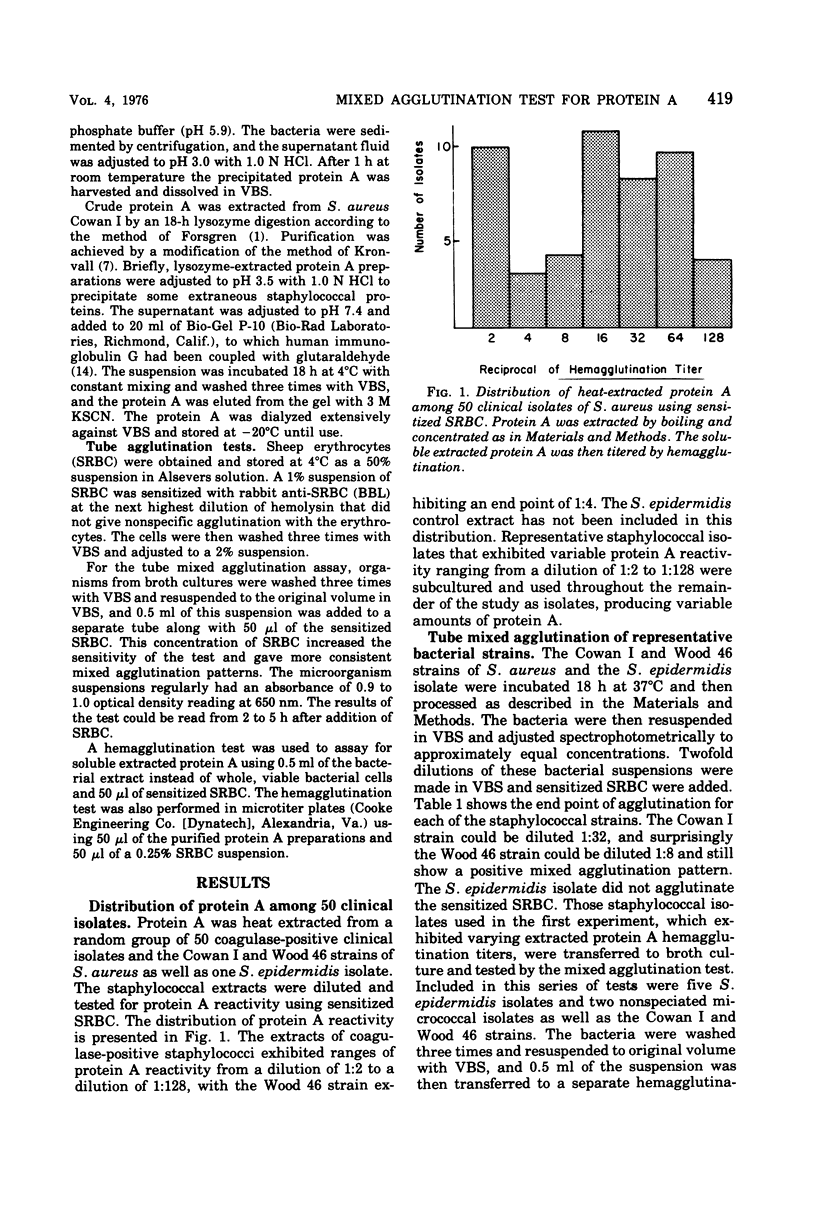
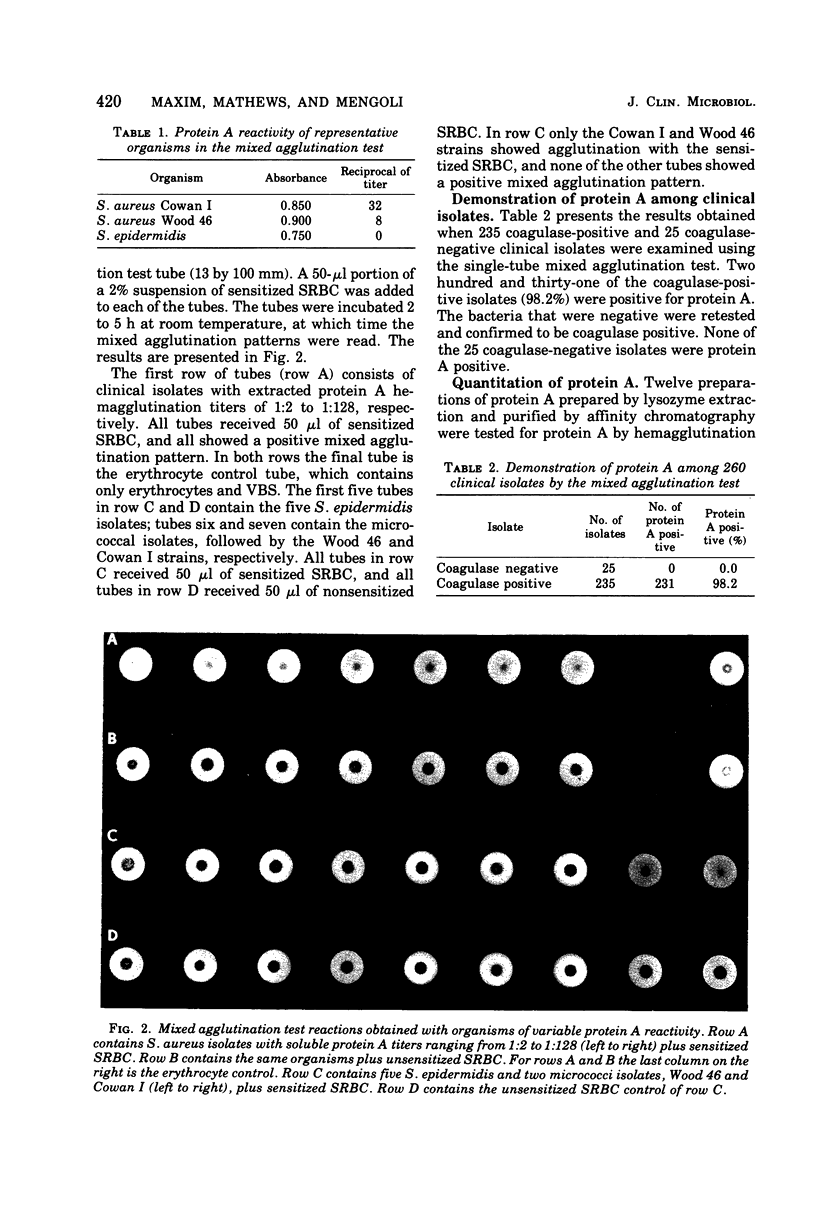


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Forsgren A., Forsum U. Role of Protein A in Nonspecific Immunofluorescence of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1970 Oct;2(4):387–391. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.4.387-391.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A. Protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. 8. Production of protein A by bacterial and L-forms of S. aureus. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1969;75(3):481–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A. Significance of protein a production by staphylococci. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):672–673. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.672-673.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Sjöquist J. "Protein A" from S. aureus. I. Pseudo-immune reaction with human gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):822–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Dossett J. H., Quie P. G., Williams R. C. Occurrence of protein a in staphylococcal strains: quantitative aspects and correlation to antigenic and bacteriophage types. Infect Immun. 1971 Jan;3(1):10–15. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.1.10-15.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G. Purification of staphylococcal protein A using immunosorbents. Scand J Immunol. 1973;2(1):31–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb02013.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Williams R. C., Jr Differences in anti-protein A activity among IgG subgroups. J Immunol. 1969 Oct;103(4):828–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss J. The immunofluorescence adsorption test (IFAT) in the estimation of staphylococcal protein A. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1973;1:98–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöquist J., Movitz J., Johansson I. B., Hjelm H. Localization of protein A in the bacteria. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Oct 17;30(1):190–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02086.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöquist J., Stålenheim G. Protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. IX. Complement-fixing activity of protein A-IgG complexes. J Immunol. 1969 Sep;103(3):467–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ternynck T., Avrameas S. Polyacrylamide-protein immunoadsorbents prepared with glutaraldehyde. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jun 1;23(1):24–28. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80274-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winblad S., Ericson C. Sensitized sheep red cells as a reactant for Staphylococcus aureus protein A. Methodology and epidemiology with special reference to weakly reacting methicillin-resistant strains. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Feb;81(1):150–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]