Abstract
The ability of Serratia to hydrolyze Tween 80 can be utilized to distinguish this genus from other Enterobacteriaceae.
Full text
PDF
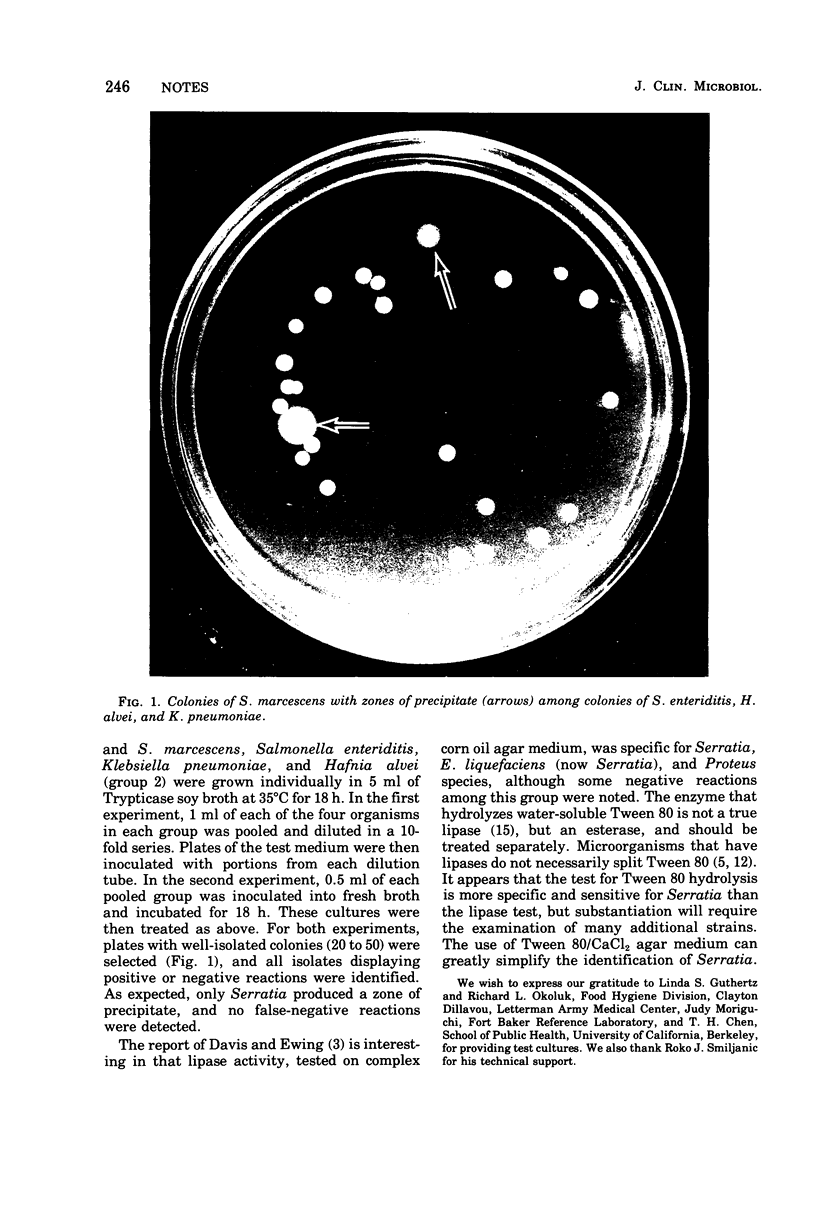

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cardos S. F., Florman A. L., Simberkoff M. S., Lanier L. Serratia marcescens: use of detailed characterization of strains to evaluate an increase of isolates in an intensive care unit. Am J Med Sci. 1973 Dec;266(6):447–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. R., EWING W. H. LIPOLYTIC, PECTOLYTIC, AND ALGINOLYTIC ACTIVITIES OF ENTEROBACTERIACEAE. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jul;88:16–19. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.1.16-19.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elston H. R., Elston J. H. Further use of deoxyribonuclease in a screening test for Serratia. J Clin Pathol. 1968 Mar;21(2):210–212. doi: 10.1136/jcp.21.2.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe T. G., Ward J. M. The utilization of Tween 80 as carbon source by Pseudomonas. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Jan;92(1):234–235. doi: 10.1099/00221287-92-1-234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki D. G., Hennekens C. G., Phillips C. W., Shaw W. V., Bennett J. V. Nosocomial urinary tract infection with Serratia marcescens: an epidemiologic study. J Infect Dis. 1973 Nov;128(5):579–587. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.5.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberg N. W., Swartz M. N. Extracellular Deoxyribonucleases in Members of the Family Enterobacteriaceae. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):294–295. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.294-295.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubon E. L., Tsurkova V. I. Lipaznaia aktivnost' Serratia marcescens, shtamm 345. Mikrobiologiia. 1973 Sep-Oct;42(5):939–940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIERRA G. A simple method for the detection of lipolytic activity of micro-organisms and some observations on the influence of the contact between cells and fatty substrates. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1957;23(1):15–22. doi: 10.1007/BF02545855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tysset C., Brisou J., Cudennec A. Activité lipidolytique de quelques groupes de bactéries à gram négatif, non sporulées, du milieu marin. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1966 Sep;111(3):363–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkowske C. J., Washington J. A., 2nd, Martin W. J., Ritts R. E., Jr Serratia marcescens. Biochemical characteristics, antibiotic susceptibility patterns, and clinical significance. JAMA. 1970 Dec 21;214(12):2157–2162. doi: 10.1001/jama.214.12.2157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills E. D. Lipases. Adv Lipid Res. 1965;3:197–240. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4831-9939-9.50012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]