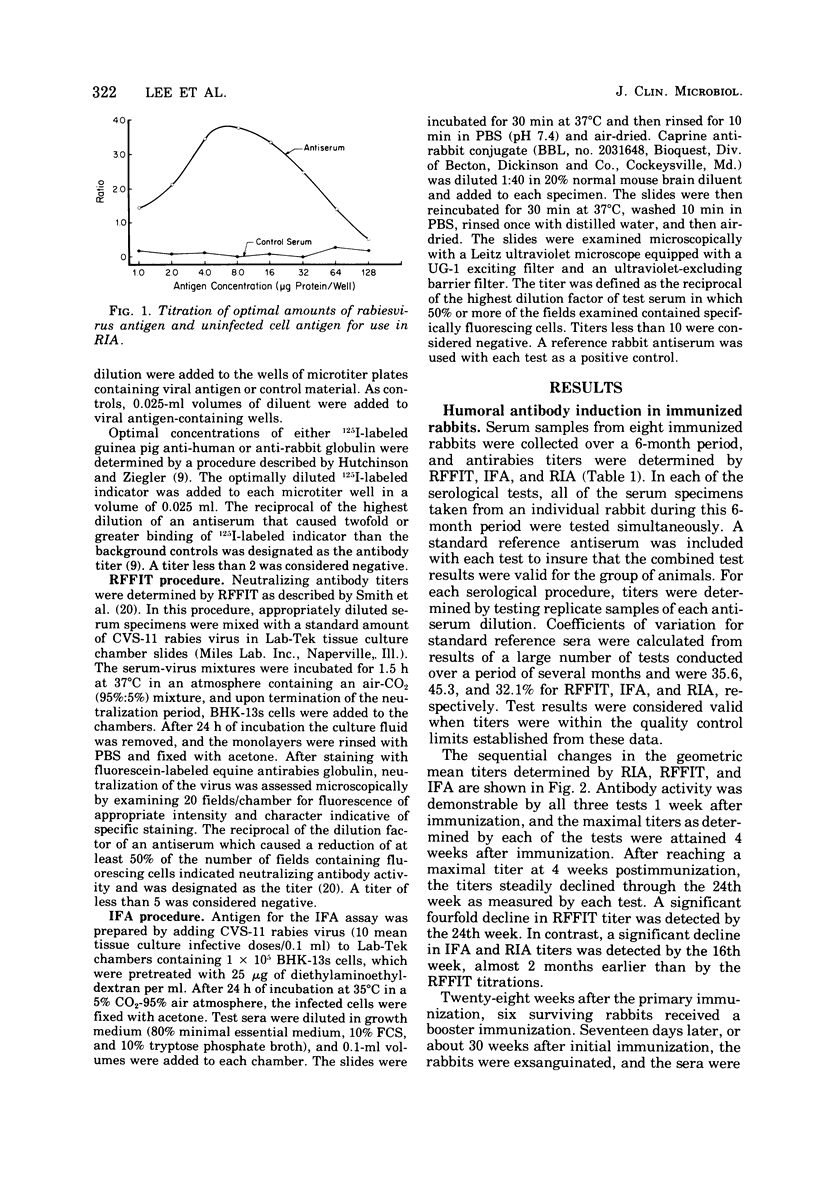
Abstract
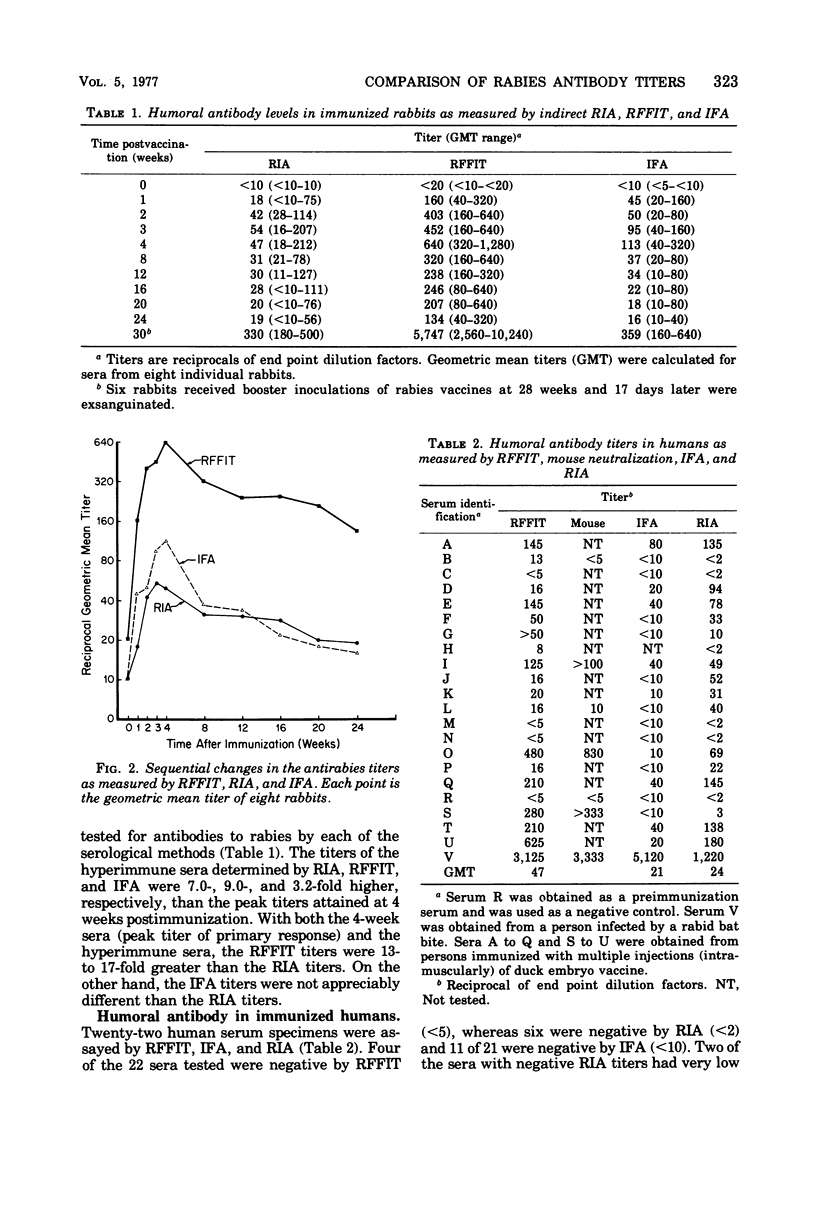
Rabies humoral antibodies were induced in eight New Zealand rabbits by a single intramuscular injection of inactivated suckling mouse brain rabies vaccine. The primary response to immunization was measured in blood samples taken at selected intervals for 6 months. The anamnestic response was measured in blood samples obtained 2 weeks after the rabbits received a booster immunization. The humoral antibody concentrations were measured by the rapid-fluorescent-focus-inhibition technique (RFFIT), indirect fluorescent-antibody assay (IFA), and indirect radioimmunoassay (RIA). The maximal neutralizing antibody titers as measured by RFFIT were attained by the 4th week and persisted into the 24th week. After booster immunization the antibody response was almost 10-fold higher than the highest level attained in the primary response. The antibody levels as measured by IFA and RIA were similar, but the titers as measured by either procedure were almost 10-fold lower than those determined by RFFIT. After booster immunizations the antibody levels, as measured by IFA and RIA, were three- and sixfold higher, respectively, than the maximal levels attained in the primary response. Twenty-two human serum specimens were tested by the same serological procedures, with disparate results. Both RIA and RFFIT effectively differentiated antirabies-positive sera from antirabies-negative sera.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Debbie J. G., Andrulonis J. A., Abelseth M. K. Rabies antibody determination by immunofluorescence in tissue culture. Infect Immun. 1972 Jun;5(6):902–904. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.6.902-904.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellenbogen C., Slugg P. Rabies neutralizing antibody: inadequate response to equine antiserum and duck-embryo vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1973 Apr;127(4):433–436. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.4.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GISPEN R., SAATHOF B. NEUTRALIZING AND FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY RESPONSE IN MAN AFTER ANTIRABIES TREATMENT WITH SUCKLING RABBIT BRAIN VACCINE. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1965;15:377–386. doi: 10.1007/BF01241765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattwick M. A., Weis T. T., Stechschulte C. J., Baer G. M., Gregg M. B. Recovery from rabies. A case report. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Jun;76(6):931–942. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-76-6-931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattwick M., Sikes R. K. Preexposure rabies prophylaxis. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1972 Jan 15;160(2):136–passim. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson H. D., Ziegler D. W. Criteria for preparing, evaluating, and standardizing iodinated globulins for radioimmunoassay procedures. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Dec;28(6):935–942. doi: 10.1128/am.28.6.935-942.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson H. D., Ziegler D. W., Feorino P. M. Radioimmunoassay for detection of antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus in human infectious mononucleosis serum specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 May;1(5):429–433. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.5.429-433.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson H. D., Ziegler D. W. Simplified radioimmunoassay for diagnostic serology. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Nov;24(5):742–749. doi: 10.1128/am.24.5.742-749.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki Y., Wiktor T. J., Koprowski H. Early events of rabies virus replicaton in tissue cultures. An electron microscopic study. Lab Invest. 1973 Feb;28(2):142–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. M., Wiktor T. J., Maes R. F., Campbell J. B., Koprowski H. Effect of polyions on the infectivity of rabies virus in tissue culture: construction of a single-cycle growth curve. J Virol. 1967 Feb;1(1):145–151. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.1.145-151.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappus K. D. Canine rabies in the United States, 1971-1973: study of reported cases with reference to vaccination history. Am J Epidemiol. 1976 Feb;103(2):242–249. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch I., Berger J., Kammann M. Tollwutantikörperbestimmungen mit dem Virusneutralisationstest (N-Test) und dem Indirekten Floreszenzantikörpertest (IFA-Test) im Vergleich. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1974 Mar;226(3):291–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal J. D., Hayashi K., Notkins A. L. Comparison of direct and indirect solid-phase microradioimmunoassays for the detection of viral antigens and antiviral antibody. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Apr;25(4):567–573. doi: 10.1128/am.25.4.567-573.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal J. D., Hayashi K., Notkins A. L. Rapid micro-radioimmunoassay for the measurement of antiviral antibody. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):171–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider L. G., Dietzschold B., Dierks R. E., Matthaeus W., Enzmann P. J., Strohmaier K. Rabies group-specific ribonucleoprotein antigen and a test system for grouping and typing of rhabdoviruses. J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):748–755. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.748-755.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Yager P. A., Baer G. M. A rapid reproducible test for determining rabies neutralizing antibody. Bull World Health Organ. 1973 May;48(5):535–541. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokol F., Stancek D., Koprowski H. Structural proteins of rabies virus. J Virol. 1971 Feb;7(2):241–249. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.2.241-249.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiktor T. J., György E., Schlumberger D., Sokol F., Koprowski H. Antigenic properties of rabies virus components. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):269–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiktor T. J., Koprowski H., Dixon F. Radioimmunoassay procedure for rabies binding antibodies. J Immunol. 1972 Sep;109(3):464–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler D. W., Hutchinson H. D., Koplan J. P., Nakano J. H. Detection by radioimmunoassay of antibodies in human smallpox patients and vaccinees. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Mar;1(3):311–317. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.3.311-317.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


