Abstract
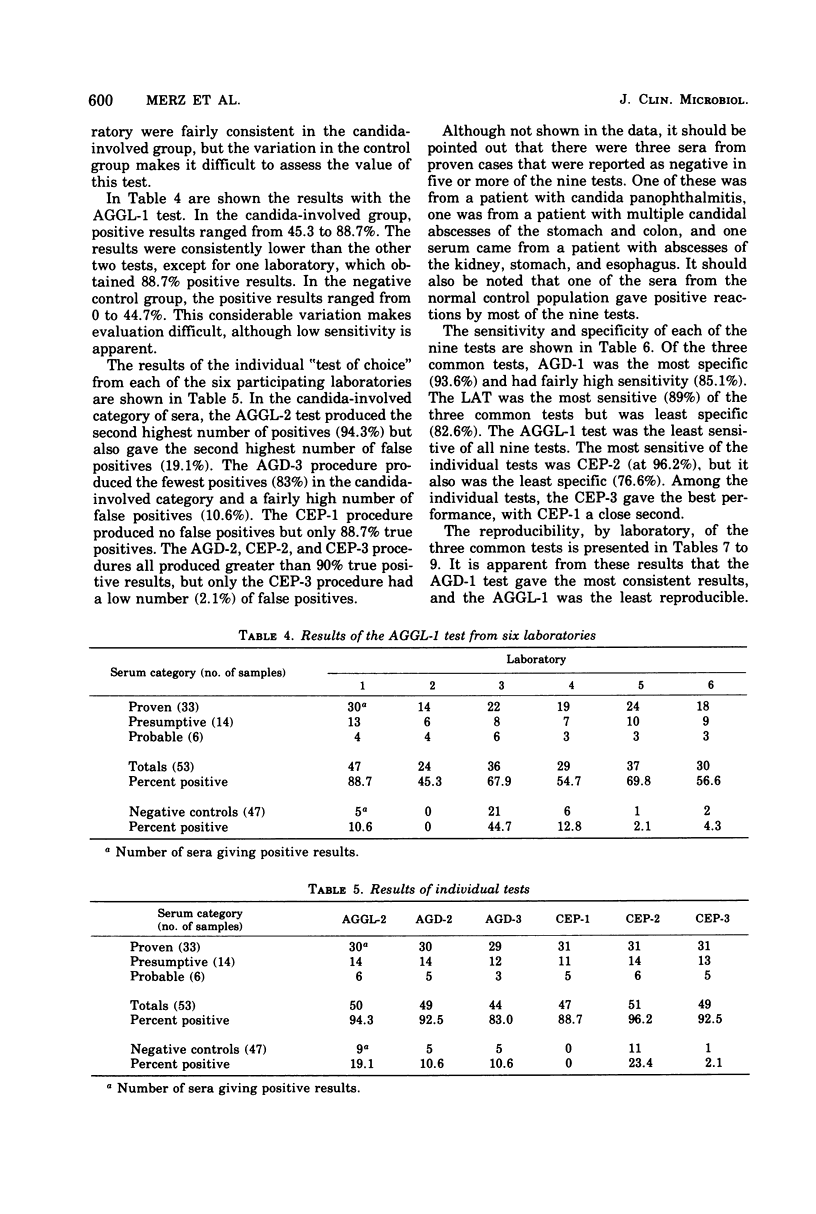
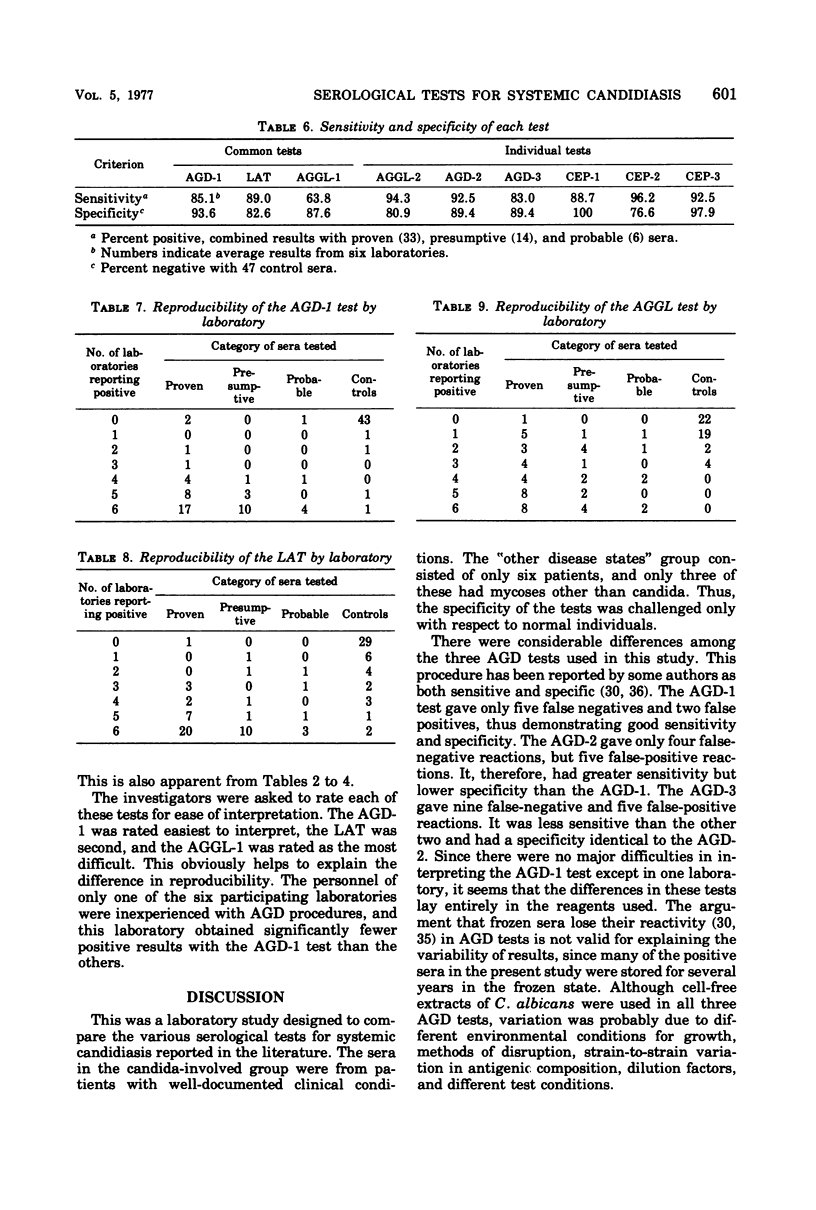
Three serological tests for candidiasis, agar gel diffusion (AGD-1), whole cell agglutination (AGGL-1), and latex agglutination (LAT), were evaluated by six laboratories with 100 coded sera. In addition, each of six laboratories performed a test of its choice, either the AGD-2, the AGD-3, the AGGL-2, or one of three counterimmunoelectrophoresis (CEP) methods (CEP-1, CEP-2, and CEP-3). Results are presented by laboratory for a group of 53 “candida-involved” cases (33 proven, 14 presumptive, and 6 probable) and 47 negative controls (41 normal and 6 other disease states). The AGD-1 test produced an overall average of 85.1% positive results in the candida-involved group and 5.0% positives in the control group. The LAT produced an overall average of 89.0% positives in the candida-involved group and 17.4% positives in the controls. The AGGL-1 test produced an overall average of 63.8% positives in the candida-involved group, with 12.3% positives in the controls. In the individual tests, the best performance was shown by the CEP-3 test (92.5% positives in the candida-involved group and 2.1% positives in controls) and the CEP-1 test (88.7% positive in the candida-involved group and no positives in the controls). The tests with the highest sensitivity were the AGGL-2 and CEP-2 (94.3 and 96.2%, respectively). These tests were also the least specific (80.9 and 76.6%, respectively). In the three common tests, the AGD-1 was the most reproducible, whereas the AGGL-1 produced considerable laboratory-to-laboratory variation. Since cell-free extracts of mechanically disrupted C. albicans were used for the LAT and all the AGD and CEP tests, the difference in performance was considered to be mainly due to antigenic composition and the conditions of the test. The results of this study confirm the value of serological tests for the diagnosis of systemic candidiasis, but point out the need for standardized reagents.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen P. L., Stenderup A. Candida albicans antibodies in candidiasis. Scand J Infect Dis. 1974;6(1):69–73. doi: 10.3109/inf.1974.6.issue-1.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelsen N. H. Antigen-antibody crossed electrophoresis (Laurell) applied to the study of the antigenic structure of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):525–527. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.525-527.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhardt H. E., Orlando J. C., Benfield J. R., Hirose F. M., Foos R. Y. Disseminated candidiasis in surgical patients. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1972 May;134(5):819–825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bläker F., Fischer K., Hellwege H. H. Bedeutung humoraler Antikörper gegen Candida albicans für den Nachweis von Candida-Infektionen. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1973 Feb 2;98(5):194–201. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1106776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley H. R., Lapa E. W. The value of serological tests in the diagnosis of candidiasis. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1969 Jun;35(Suppl):E19–E20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chew W. H., Theus T. L. Candida precipitins. J Immunol. 1967 Feb;98(2):220–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan C. T., Stried R. P. Serologic diagnosis of yeast infections. Am J Clin Pathol. 1973 Jan;59(1):49–55. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/59.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everall P. H., Morris C. A., Morris D. F. Antibodies to Candida albicans in hospital patients with and without spinal injury and in normal men and women. J Clin Pathol. 1974 Sep;27(9):722–728. doi: 10.1136/jcp.27.9.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faux J. A., Stanley V. C., Buckley H. R., Partridge B. M. A comparison of differenct extracts of Candida albicans in agar gel double diffusion techniques. J Immunol Methods. 1975 Jan;6(3):235–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(75)90067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein E., Hoeprich P. D. Problems in the diagnosis and treatment of systemic candidiasis. J Infect Dis. 1972 Feb;125(2):190–193. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.2.190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASENCLEVER H. F., MITCHELL W. O. Antigenic studies of Candida. I. Observation of two antigenic groups in Candida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1961 Oct;82:570–573. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.4.570-573.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASENCLEVER H. F., MITCHELL W. O., LOEWE J. Antigenic studies of Candida. II. Antigenic relation of Candida albicans group A and group B to Candida stellatoidea and Candida tropicalis. J Bacteriol. 1961 Oct;82:574–577. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.4.574-577.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellwege H. H., Fischer K., Bläker F. Diagnostic value of Candida precipitins. Lancet. 1972 Aug 19;2(7773):386–386. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91782-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEMP G., SOLOTOROVSKY M. LOCALIZATION OF ANTIGENS IN MECHANICALLY DISRUPTED CELLS OF CERTAIN SPECIES OF THE GENERA CANDIDA AND TORULOPSIS. J Immunol. 1964 Aug;93:305–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozinn P. J., Hasenclever H. F., Taschdjian C. L., Mackenzie D. W., Protzman W., Seelig M. S. Problems in the diagnosis and treatment of systemic candidiasis. J Infect Dis. 1972 Nov;126(5):548–550. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.5.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T., Buckley H. R., Murray I. G. The relationship between fluorescent, agglutinating, and precipitating antibodies to Candida albicans and their immunoglobulin classes. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Apr;25(4):344–348. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.4.344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louria D. B., Smith J. K., Brayton R. G., Buse M. Anti-Candida factors in serum and their inhibitors. I. Clinical and laboratory observations. J Infect Dis. 1972 Feb;125(2):102–114. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.2.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray I. G., Buckley H. R., Turner G. C. Serological evidence of Candida infection after open-heart surgery. J Med Microbiol. 1969 Nov 4;2(4):463–469. doi: 10.1099/00222615-2-4-463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C., EVANS E. G., Holland K. T. Detection of Candida precipitins. a comparison of double diffusion and counter immunoelectrophoresis. J Immunol Methods. 1975 Jun;7(2-3):211–218. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(75)90018-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys J., Faux J. A., McCarthy D. S., Hargreave F. E. Candida albicans precipitins in respiratory disease in man. J Allergy. 1968 Jun;41(6):305–318. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(68)90073-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preisler H. D., Hasenclever H. F., Levitan A. A., Henderson E. S. Serologic diagnosis of disseminated candidiasis in patients with acute leukemia. Ann Intern Med. 1969 Jan;70(1):19–30. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-70-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Gaines J. D., Gilmer M. A. Demonstration of Candida precipitins in human sera by counterimmunoelectrophoresis. Lancet. 1972 Feb 19;1(7747):413–413. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90860-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosener F., Gabriel F. D., Taschdjian C., Cuesta M. B., Kozinn P. J. Serologic diagnosis of systemic candidiasis in patients with acute leukemia. Am J Med. 1971 Jul;51(1):54–62. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(71)90323-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley V. C., Hurley R., Carroll C. J. Distribution and significance of candida precipitins in sera from pregnant women. J Med Microbiol. 1972 Aug;5(3):313–320. doi: 10.1099/00222615-5-3-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stickle D., Kaufman L., Blumer S. O., McLaughlin D. W. Comparison of a newly developed latex agglutination test and an immunodiffusion test in the diagnosis of systemic candidiasis. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Mar;23(3):490–499. doi: 10.1128/am.23.3.490-499.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taschdjian C. L., Cuesta M. B., Kozinn P. J., Caroline L. A modified antigen for serodiagnosis of systemic candidiasis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1969 Oct;52(4):468–472. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/52.4.468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taschdjian C. L., Dobkin G. B., Caroline L., Kozinn P. J. Immune studies relating to candidiasis. II. Experimental and preliminary clinical studies on antibody formation in systemic candidiasis. Sabouraudia. 1964 Feb;3(2):129–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taschdjian C. L., Kozinn P. J., Caroline L. Immune studies in candidiasis. 3. Precipitating antibodies in systemic candidiasis. Sabouraudia. 1964 Oct;3(4):312–320. doi: 10.1080/00362176485190551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taschdjian C. L., Kozinn P. J., Cuesta M. B., Toni E. F. Serodiagnosis of Candidal infections. Am J Clin Pathol. 1972 Feb;57(2):195–205. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/57.2.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taschdjian C. L., Kozinn P. J., Fink H., Cuesta M. B., Caroline L., Kantrowitz A. B. Post mortem studies of systemic candidiasis: I. Diagnostic validity of precipitin reaction and probable origin of sensitization to cytoplasmic candidal antigens. Sabouraudia. 1969 Jun;7(2):110–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taschdjian C. L., Kozinn P. J., Okas A., Caroline L., Halle M. A. Serodiagnosis of systemic candidiasis. J Infect Dis. 1967 Apr;117(2):180–187. doi: 10.1093/infdis/117.2.180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taschdjian C. L., Kozinn P. J., Toni E. F. Opportunistic yeast infections, with special reference to candidiasis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1970 Oct 30;174(2):606–622. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1970.tb45586.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taschdjian C. L., Seelig M. S., Kozinn P. J. Serological diagnosis of candidal infections. CRC Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 1973 Jul;4(1):19–59. doi: 10.3109/10408367309151683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toala P., Schroeder S. A., Daly A. K., Finland M. Candida at Boston City Hospital. Clinical and epidemiological characteristics and susceptibility to eight antimicrobial agents. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Dec;126(6):983–989. doi: 10.1001/archinte.126.6.983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


