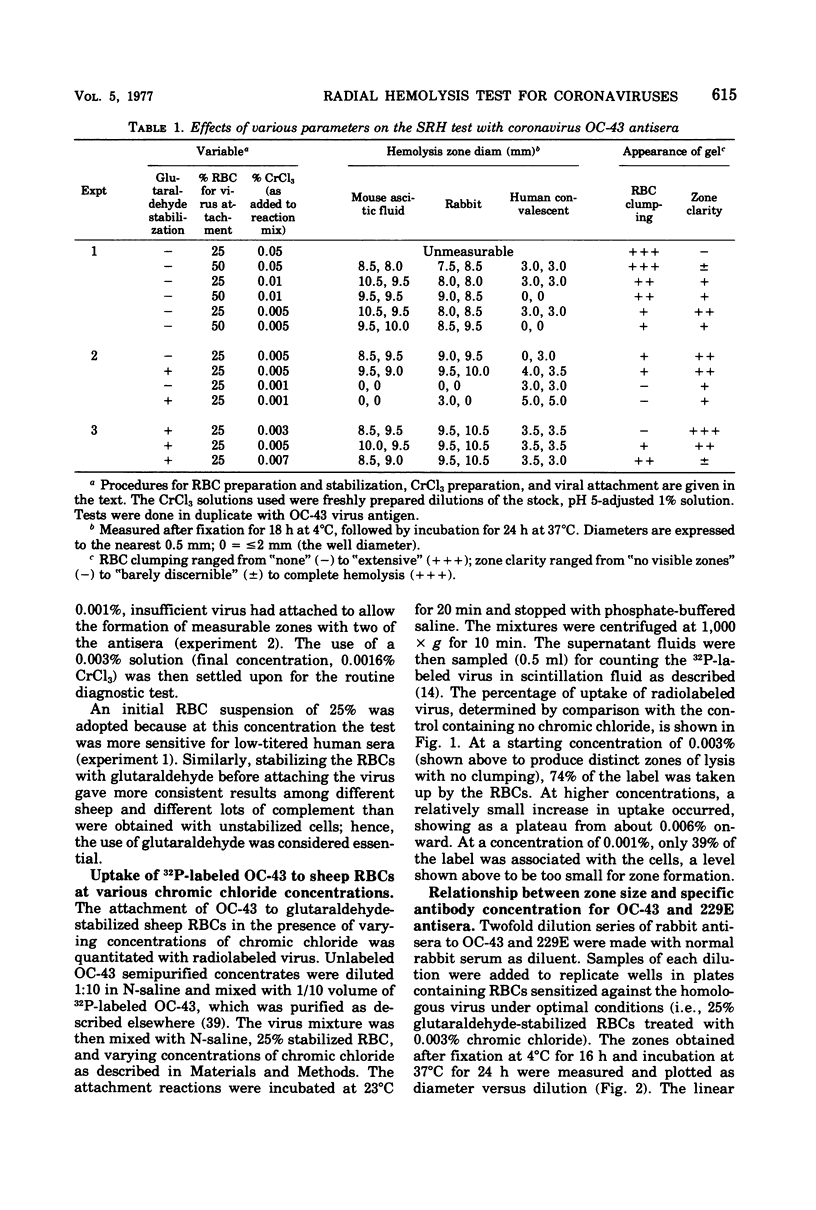
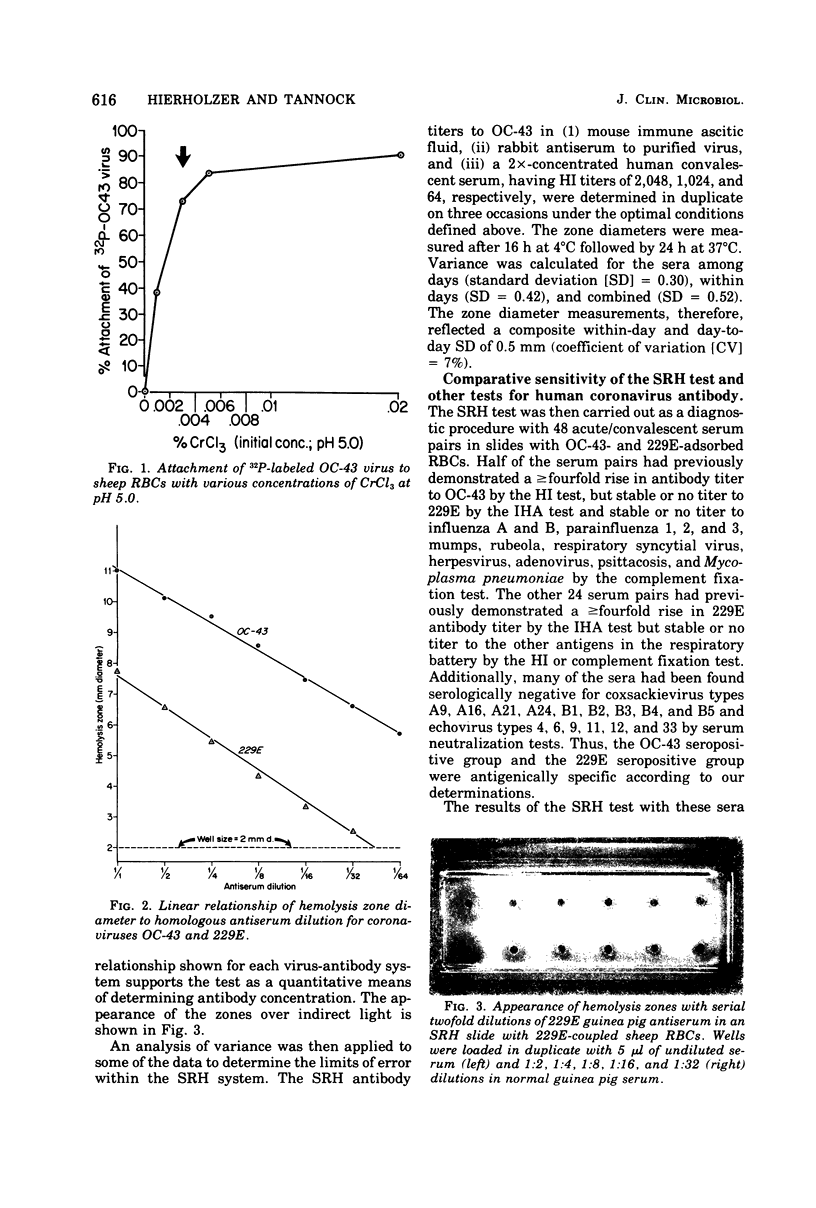
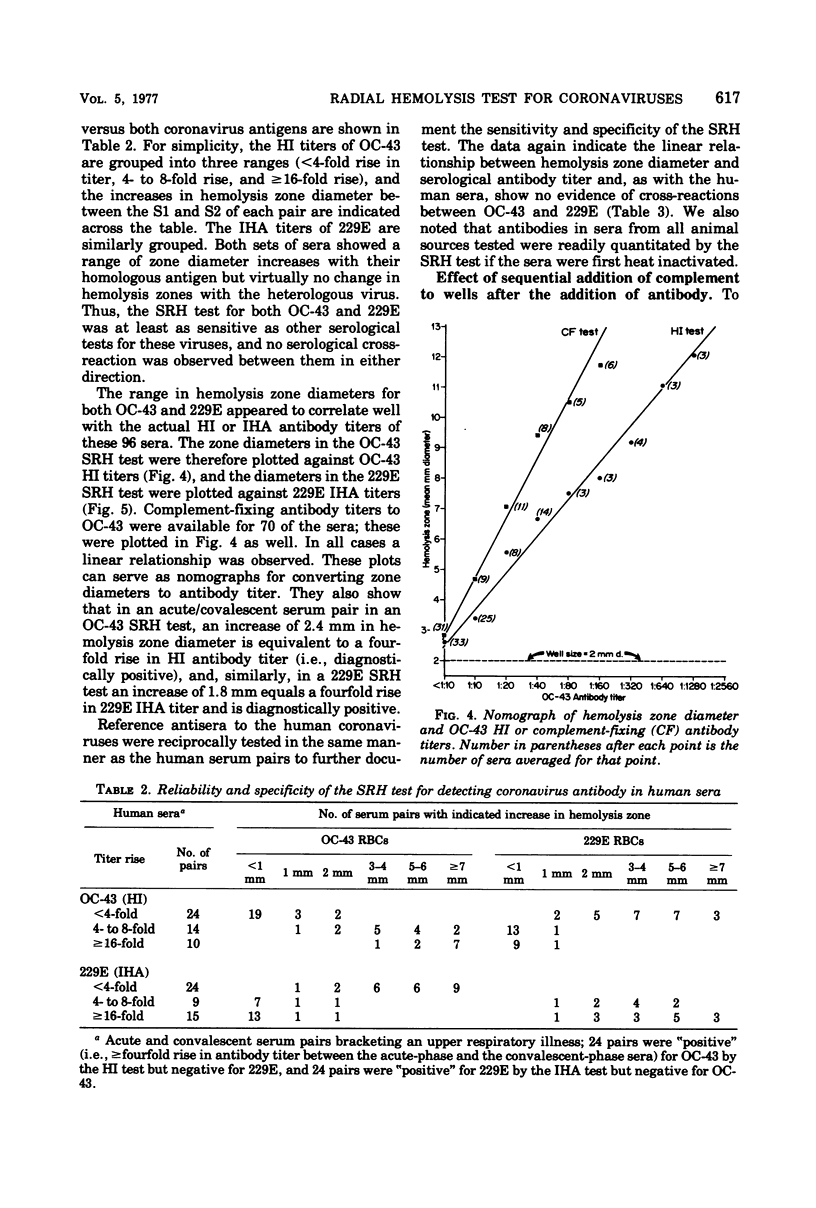
Abstract
A single radial hemolysis test was developed for quantitation of specific antibody to non-hemagglutinating viruses. With the human coronaviruses as models, this test utilizes the binding properties of the chromic cation to attach viruses to glutaraldehyde-treated sheep erythrocytes. The most satisfactory system consisted of stabilizing washed sheep erythrocytes with 0.0073% glutaraldehyde for 15 min at 23°C, binding a high concentration of virus to a 25% erythrocyte suspension with 0.0016% chromic chloride for 20 min at 23°C, stopping the reaction with phosphate-saline, and finally mixing the treated, rewashed cells with complement and agarose at 45°C to prepare a slide gel. The gel mix, which was dispensed in plastic plates (23 by 73 mm) in 3-ml volumes, consisted of 1% agarose, 0.1% sodium azide, 5% reconstituted complement, and 0.82% treated cells. Wells 2 mm in diameter were loaded with 5 μl of antiserum, incubated for 18 h at 4°C for diffusion of antiserum and fixation of complement, and then incubated for 8 to 24 h at 37°C for development of hemolysis zones. The diameter of a zone was linearly related to antibody concentration, as determined by conventional serological tests. This single radial hemolysis test was applicable to human and animal coronaviruses and to selected serotypes of the adenovirus, picornavirus, rhabdovirus, and rotavirus groups.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradburne A. F. Antigenic relationships amongst coronaviruses. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1970;31(3):352–364. doi: 10.1007/BF01253769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callow K. A., Beare A. S. Measurement of antibody to influenza virus neuraminidase by single radial hemolysis in agarose gels. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.1-8.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUDENBERG H. H., DREWS G., NISONOFF A. SEROLOGIC DEMONSTRATION OF DUAL SPECIFICITY OF RABBIT BIVALENT HYBRID ANTIBODY. J Exp Med. 1964 Jan 1;119:151–166. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghanta V. K., McGhee J. R., Soong S. J., Hamlin N. M., Hurst D. C., Hiramoto R. N. Methodology. A study of the single radial hemolysis in gel system. 3. Quantitation of complement. Immunochemistry. 1973 Sep;10(9):645–649. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(73)90167-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. The chromic chloride method of coupling antigens to erythrocytes: definition of some important parameters. J Immunol Methods. 1976;10(1):61–66. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold E. R., Fudenberg H. H. Chromic chloride: a coupling reagent for passive hemagglutination reactions. J Immunol. 1967 Nov;99(5):859–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grillner L., Blomberg J. Hemolysis-in-gel and neutralization tests for determination of antibodies to mumps virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jul;4(1):11–15. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.1.11-15.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grillner L., Strannegård O. Evaluation of the hemolysis-in-gel test for the screening of rubella immunity and the demonstration of recent infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Feb;3(2):86–90. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.2.86-90.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habicht G. S., Miller F. Preparation of conjugated erythrocytes for long term use in hemolytic plaque assays, complement fixation studies, or passive hemagglutinations: a comparative study of several methods. J Immunol Methods. 1976;11(2):117–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90139-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. M. Specificity of antibody formation after intravitreal immunization with bovine gamma globulin and ovalbumin. I. Primary response. Invest Ophthalmol. 1971 Oct;10(10):775–783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamre D., Procknow J. J. A new virus isolated from the human respiratory tract. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Jan;121(1):190–193. doi: 10.3181/00379727-121-30734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hierholzer J. C., Palmer E. L., Whitfield S. G., Kaye H. S., Dowdle W. R. Protein composition of coronavirus OC 43. Virology. 1972 May;48(2):516–527. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90062-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hierholzer J. C. Purification and biophysical properties of human coronavirus 229E. Virology. 1976 Nov;75(1):155–165. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90014-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hierholzer J. C., Suggs M. T., Hall E. C. Standardized viral hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition tests. II. Description and statistical evaluation. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Nov;18(5):824–833. doi: 10.1128/am.18.5.824-833.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiramoto R. N., McGhee J. R., Hurst D. C., Hamlin N. M. A simple method for quantitation of hemolytic antibodies. Immunochemistry. 1970 Dec;7(12):992–996. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiramoto R. N., McGhee J. R., Hurst D. C., Hamlin N. M. A study of the single radial hemolysis in gel system. I. Factors affecting the model. Immunochemistry. 1971 May;8(5):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90499-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANDL J. H., SIMMONS R. L. The agglutination and sensitization of red cells by metallic cations: interactions between multivalent metals and the red-cell membrane. Br J Haematol. 1957 Jan;3(1):19–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1957.tb05768.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson W. B., O'Connor G. R., Hall J. M. Plate hemolysin test for the rapid screening of toxoplasma antibodies. Appl Microbiol. 1974 May;27(5):896–900. doi: 10.1128/am.27.5.896-900.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRITZMAN J. Studies of rheumatoid serum employing a modified Coombs' slide test. J Lab Clin Med. 1958 Aug;52(2):328–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye H. S., Dowdle W. R. Seroepidemiologic survey of coronavirus (strain 229E) infections in a population of children. Am J Epidemiol. 1975 Mar;101(3):238–244. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye H. S., Dowdle W. R. Some characteristics of hemagglutination of certain strains of "IBV-like" virus. J Infect Dis. 1969 Nov;120(5):576–581. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.5.576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye H. S., Hierholzer J. C., Dowdle W. R. Purification and further characterization of an "IBV-like" virus (coronavirus). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Nov;135(2):457–463. doi: 10.3181/00379727-135-35074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye H. S., Marsh H. B., Dowdle W. R. Seroepidemiologic survey of coronavirus (strain OC 43) related infections in a children's population. Am J Epidemiol. 1971 Jul;94(1):43–49. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye H. S., Ong S. B., Dowdle W. R. Detection of coronavirus 229E antibody by indirect hemagglutination. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Nov;24(5):703–707. doi: 10.1128/am.24.5.703-707.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycke E., Peterson M. Hemolysis-in-gel test for demonstration of Chlamydia antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Nov;4(5):450–452. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.5.450-452.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. R., Hurst D. C., Hamlin N. M., Hiramoto R. N. A study of the single radial hemolysis in gel system. II. Application of the model to mouse 19S hemolytic antibodies. Immunochemistry. 1971 May;8(5):367–373. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90500-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh K., Becker W. B., Chanock R. M. Growth in suckling-mouse brain of "IBV-like" viruses from patients with upper respiratory tract disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Dec;58(6):2268–2273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.6.2268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh K., Kapikian A. Z., Hardison K. A., Hartley J. W., Chanock R. M. Antigenic relationships among the coronaviruses of man and between human and animal coronaviruses. J Immunol. 1969 May;102(5):1109–1118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probert M., Russell S. M. Measurement of parainfluenza-3 virus antibody by the single radial hemolysis technique. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Sep;2(3):157–161. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.3.157-161.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeyn J. A., Cook J. Anti-immunoglobulin analysis by diffusion patterns of inhibition and facilitation of complementary lysis in agar. I. Diffusion-lysis patterns of heterologous guinea pig anti-immunoglobulins. J Immunol Methods. 1975 Feb;6(4):363–373. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(75)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell S. M., McCahon D., Beare A. S. A single radial haemolysis technique for the measurement of influenza antibody. J Gen Virol. 1975 Apr;27(1):1–10. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-27-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schild G. C., Oxford J. S., Virelizier J. L. Immunity to influenza. Dev Biol Stand. 1975;28:253–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skaug K., Orstavik I., Ulstrup J. C. Application of the passive haemolysis test for the determination of rubella virus antibodies. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1975 Aug;83(4):367–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb00114.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strannegård O., Grillner L., Lindberg I. M. Hemolysis-in-gel test for the demonstration of antibodies to rubella virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jun;1(6):491–494. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.6.491-494.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiler E., Melletz E. W., Breuninger-Peck E. Facilitation of immune hemolysis by an interaction between red cell-sensitizing antibody and gamma-globulin allotype antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Nov;54(5):1310–1317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.5.1310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]