Abstract
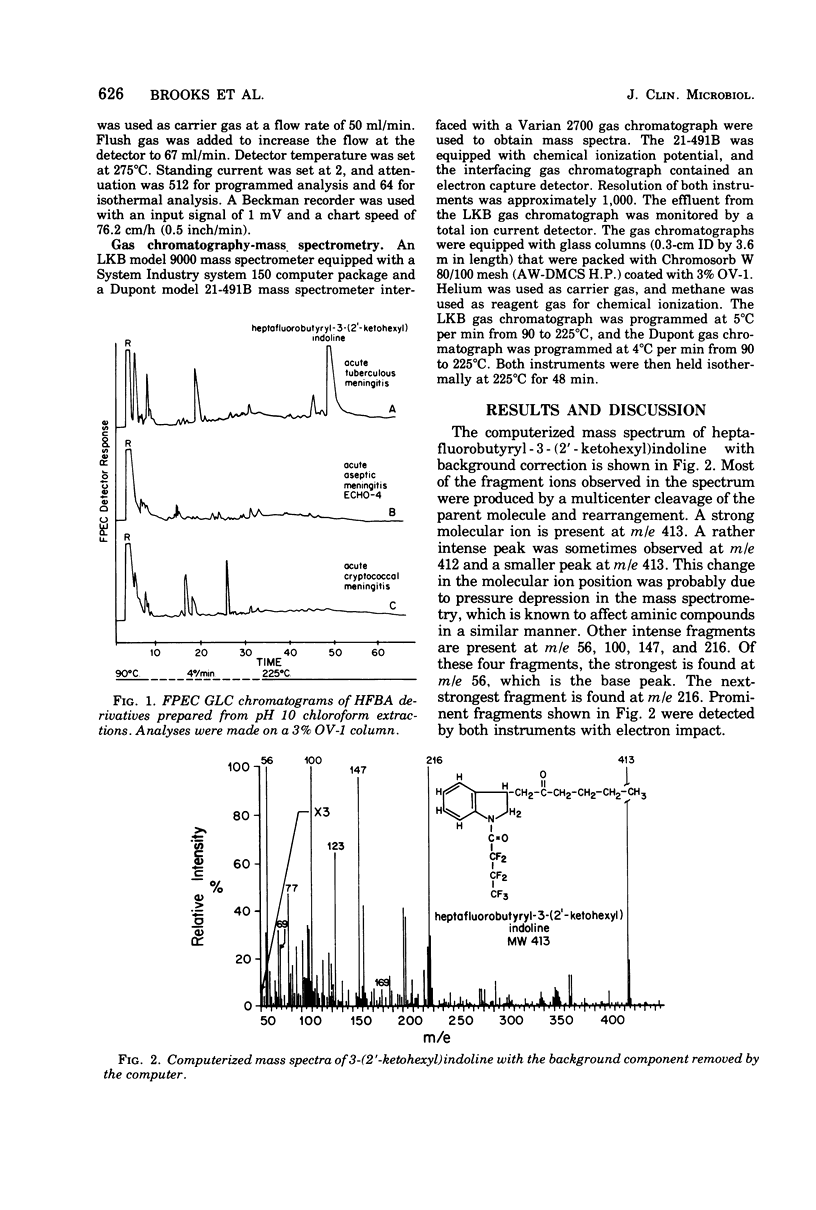
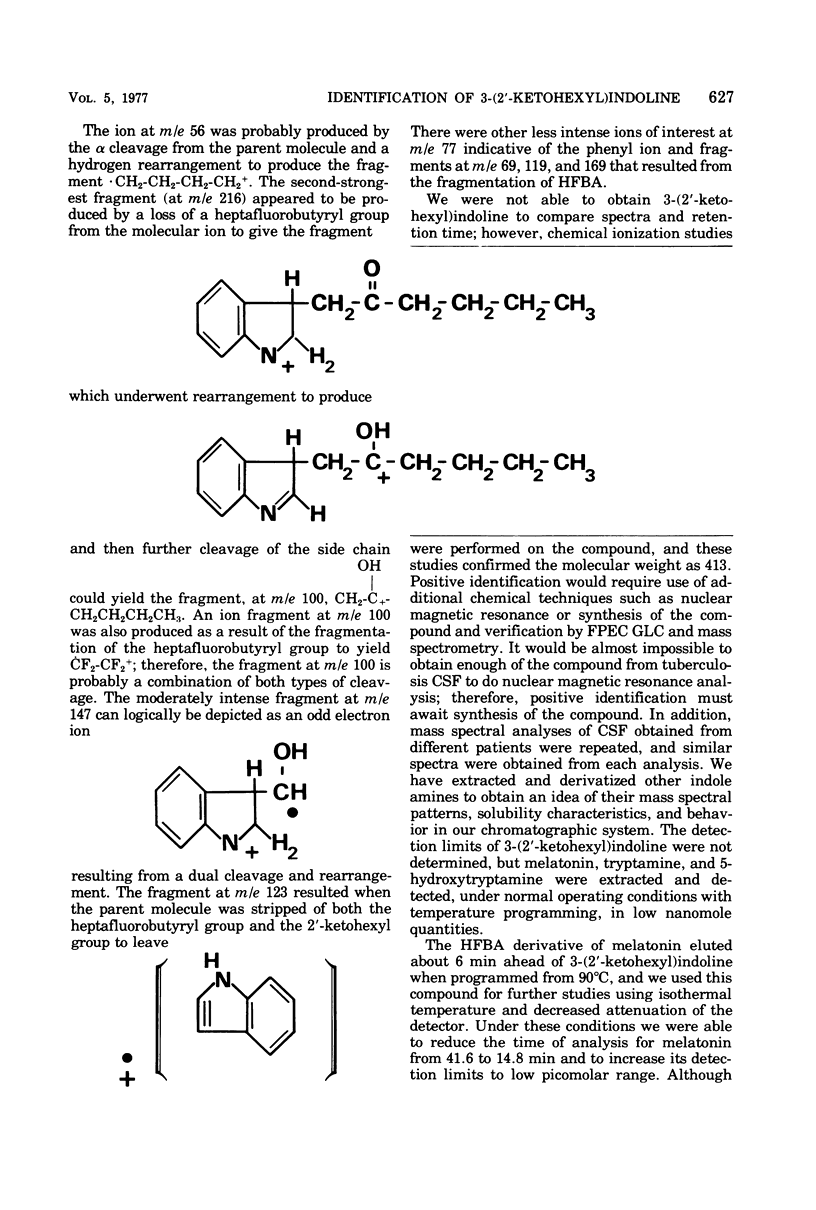
A basic, extractable, indolic type of compound, which was derivatized with heptafluorobutyric anhydride and pyridine, was obtained from the cerebrospinal fluids of patients with acute tuberculous meningitis. The compound was detected by frequency-pulsed, modulated electron capture gas-liquid chromatography, and it was tentatively identified by mass spectrometry as 3-(2'-ketohexyl)indoline. The compound was found to be valuable for differentiating between tuberculous, cryptococcal, and aseptic meningitides.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Koslow S. H., Green A. R. Analysis of pineal and brain indole alkylamines by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1973;7:33–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


