Abstract
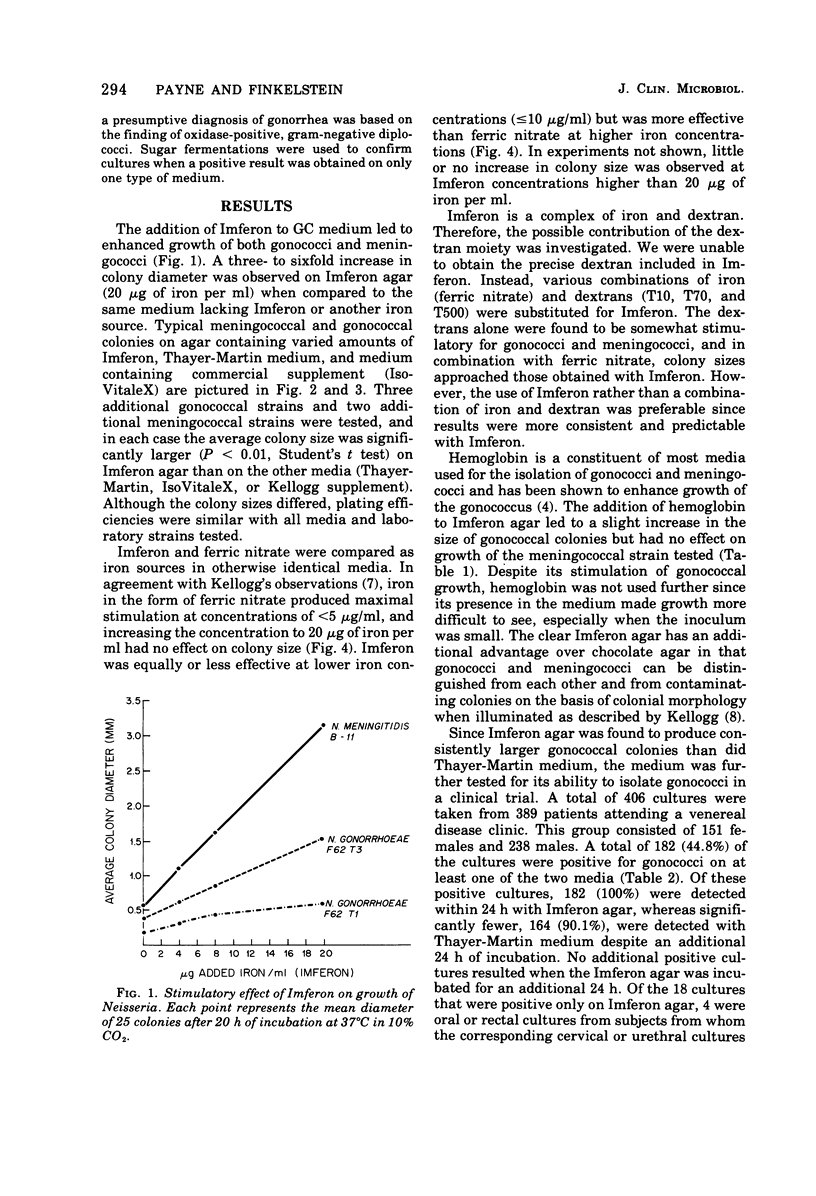
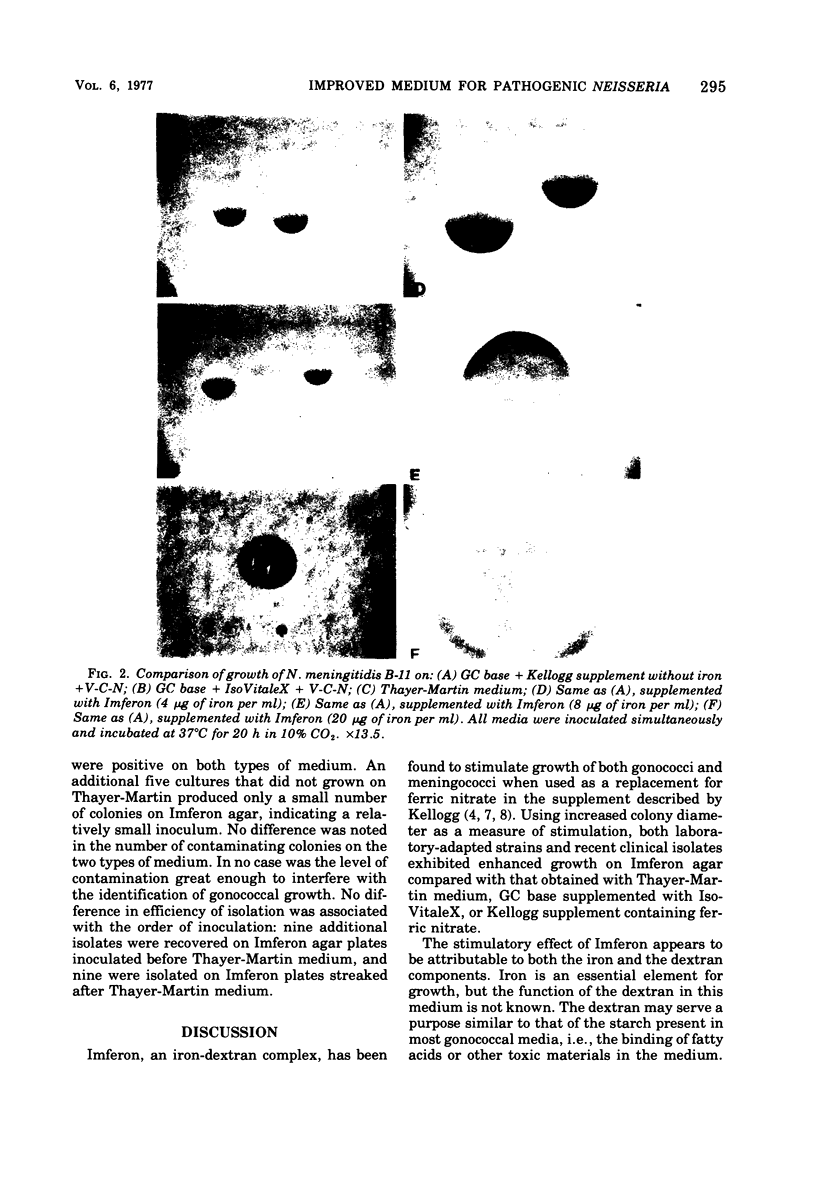
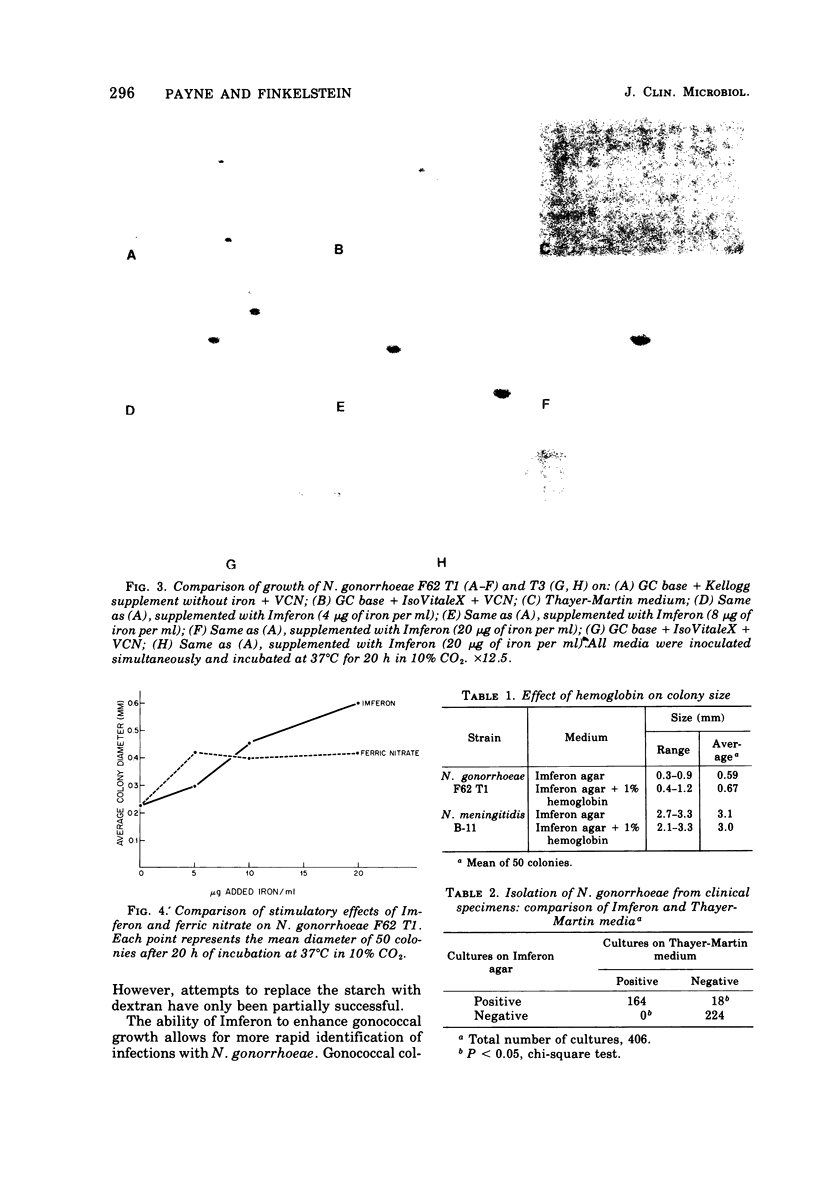
Imferon, an iron-dextran complex, enhances the growth of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and N. meningitidis. The use of Imferon as a replacement for ferric nitrate, in a defined supplement for GC agar significantly increased the average colony sizes of both gonococci and meningococci. In comparison with Thayer-Martin medium, Imferon agar increased the speed and rate of isolation of gonococci from clinical specimens.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bumgarner L. R., Finkelstein R. A. Pathogenesis and immunology of experimental gonococcal infection: virulence of colony types of Neisseria gonorrhoeae for chicken embryos. Infect Immun. 1973 Dec;8(6):919–924. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.6.919-924.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell J. G., Price E. V., Pazin G. J., Cornelius C. E., 3rd Sensitivity and reproducibility of Thayer-Martin culture mddium in diagnosing gonorrhea in women. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1971 Feb 1;109(3):463–468. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(71)90346-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler R. W., Rendtorff R. C., Curran J. W., Kellogg D. S., Jr Evaluation of media used for cultures of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and comparison of commercial and laboratory prepared supplements. J Am Vener Dis Assoc. 1974 Sep;1(1):14–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handsfield H. H., Lipman T. O., Harnisch J. P., Tronca E., Holmes K. K. Asymptomatic gonorrhea in men. Diagnosis, natural course, prevalence and significance. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jan 17;290(3):117–123. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197401172900301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. W., Holmes K. K., Kvale P. A., Halverson C. W., Hirsch W. P. An evaluation of gonorrhea case findings in the chronically infected female. Am J Epidemiol. 1969 Nov;90(5):438–448. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. S., Jr, Cohen I. R., Norins L. C., Schroeter A. L., Reising G. Neisseria gonorrhoeae. II. Colonial variation and pathogenicity during 35 months in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):596–605. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.596-605.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. M., Finkelstein R. A. Pathogenesis and immunology of experimental gonococcal infection: role of iron in virulence. Infect Immun. 1975 Dec;12(6):1313–1318. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.6.1313-1318.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thatcher R. W., McCraney W. T., Kellogg D. S., Jr, Whaley W. H. Asymptomatic gonorrhea. JAMA. 1969 Oct 13;210(2):315–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer J. D., Martin J. E., Jr Improved medium selective for cultivation of N. gonorrhoeae and N. meningitidis. Public Health Rep. 1966 Jun;81(6):559–562. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]