Abstract
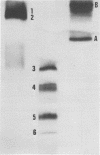
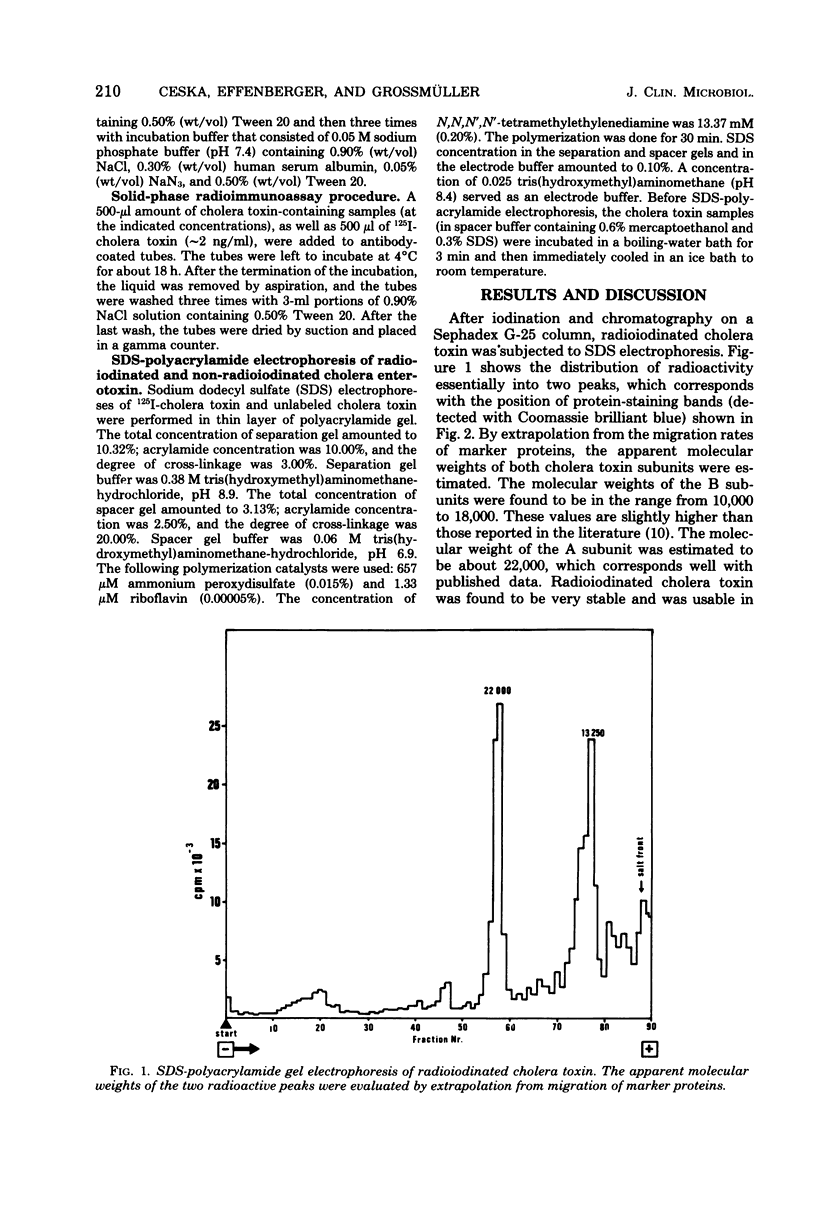
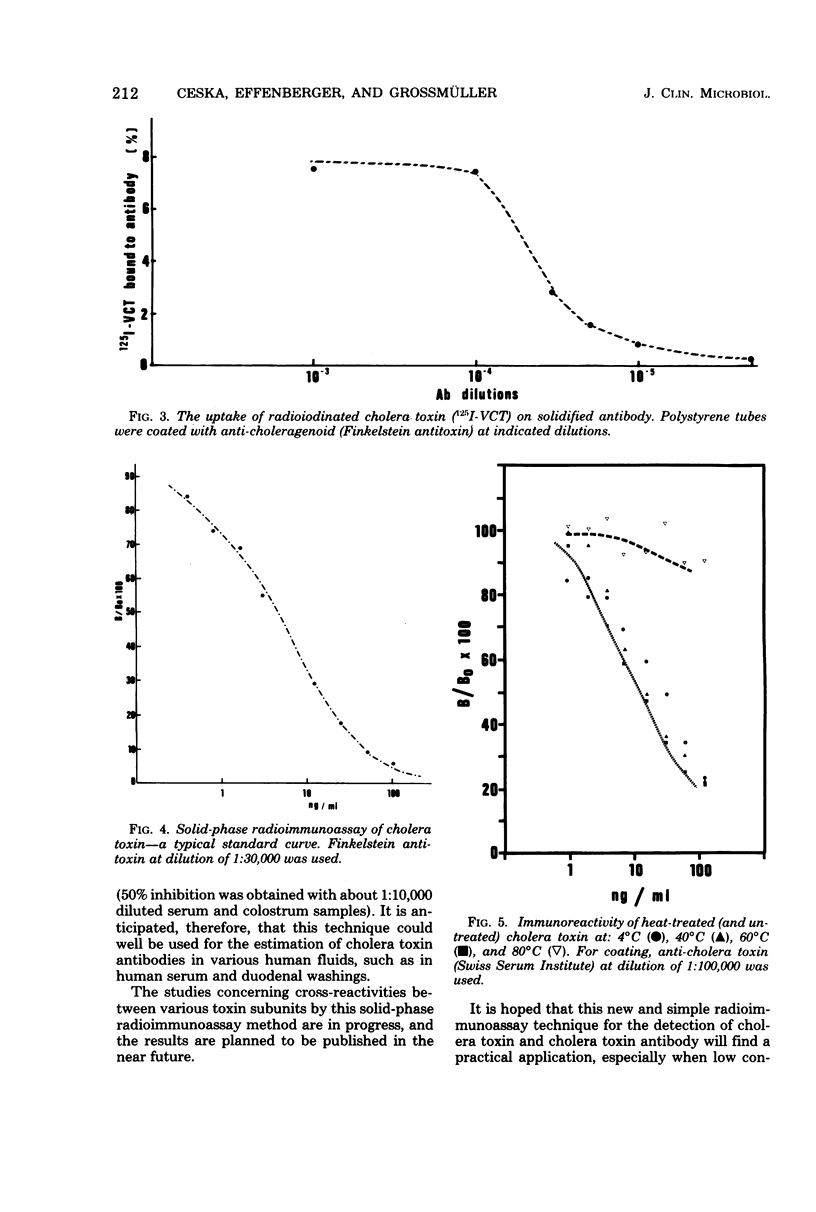
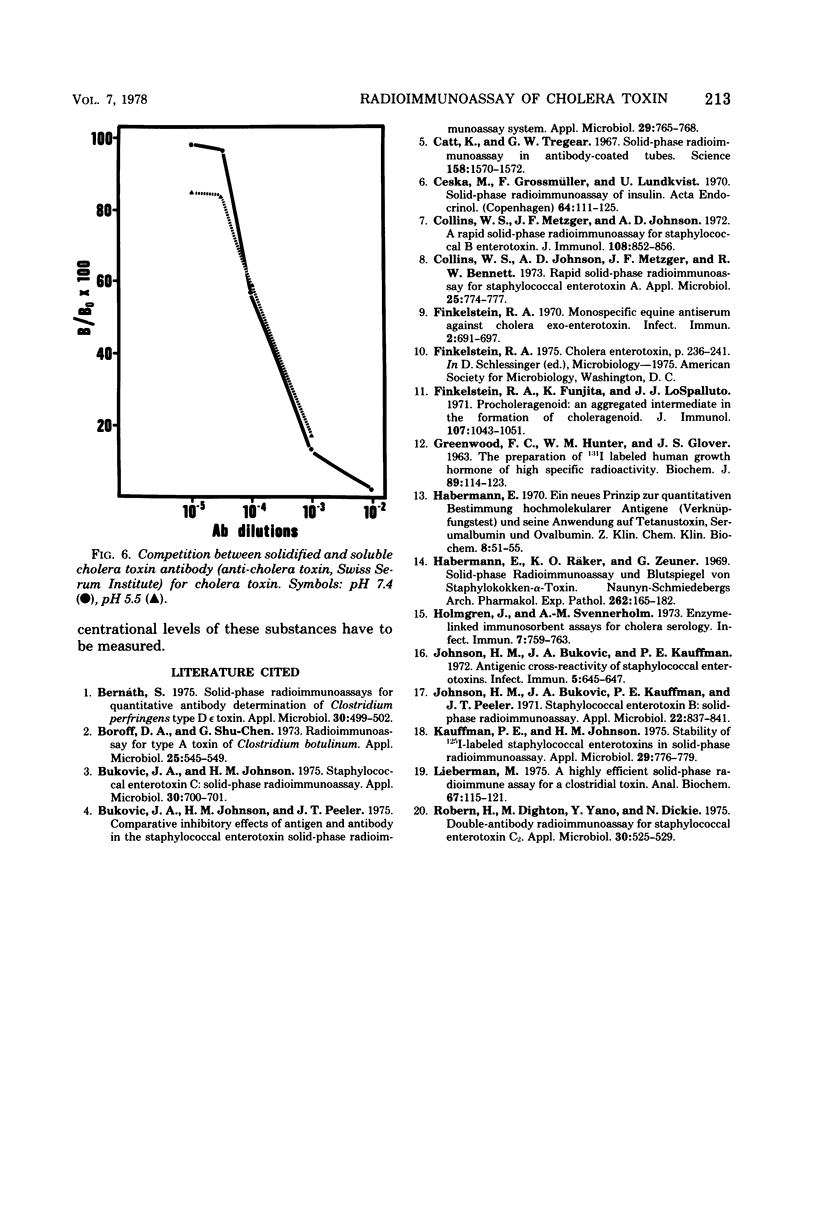
A direct solid-phase radioimmunoassay procedure was developed for the determination of cholera toxin and cholera toxin antibody. The reported method employed anti-choleragenoid antibody attached to polystyrene tubes as a solidified binder for cholera toxin. The binding of radioidinated cholera toxin on its solidified antibody was inhibitable by unlabeled cholera toxin and cholera toxin antibody. With the help of this method, the heat stability of cholera toxin was also studied. Radioiodinated cholera toxin was shown to be labeled in both of its subunits. The stability of the iodinated cholera toxin at the reported specific radioactivity is remarkable. It was found that the labeled cholera toxin can be used in the solid-phase radioimmunoassay even 4 months after iodination.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernáth S. Solid-phase radioimmunoassays for quantitative antibody determination of Clostridium perfringens type D epsilon toxin. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Oct;30(4):499–502. doi: 10.1128/am.30.4.499-502.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boroff D. A., Chu-Chen G. Radioimmunoassay for type A toxin of Clostridium botulinum. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Apr;25(4):545–549. doi: 10.1128/am.25.4.545-549.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukovic J. A., Johnson H. M., Peeler J. T. Comparative inhibitory effects of antigen and antibody in the staphylococcal enterotoxin solid-phase radioimmunoassay system. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jun;29(6):765–768. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.765-768.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukovic J. A., Johnson H. M. Staphylococcal enterotoxin C: solid-phase radioimmunoassay. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Oct;30(4):700–701. doi: 10.1128/am.30.4.700-701.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catt K., Tregear G. W. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay in antibody-coated tubes. Science. 1967 Dec 22;158(3808):1570–1572. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3808.1570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceska M., Grossmüller F., Lundkvist U. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay of insulin. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1970 May;64(1):111–125. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0640111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins W. S., 2nd, Metzger J. F., Johnson A. D. A rapid solid phase radioimmunoassay for staphylococcal B enterotoxin. J Immunol. 1972 Mar;108(3):852–856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins W. S., Johnson A. D., Metzger J. F., Bennett R. W. Rapid solid-phase radioimmunoassay for staphylococcal enterotoxin A. Appl Microbiol. 1973 May;25(5):774–777. doi: 10.1128/am.25.5.774-777.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Fujita K., LoSpalluto J. J. Procholeragenoid: an aggregated intermediate in the formation of choleragenoid. J Immunol. 1971 Oct;107(4):1043–1051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A. Monospecific equine antiserum against cholera exo-enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1970 Dec;2(6):691–697. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.6.691-697.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann E. Ein neues Prinzip zur quantitativen Bestimmung hochmolekularer Antigene (Verknüpfungstest) und seine Anwendung auf Tetanustoxin, Serumalbumin und Ovalbumin. Z Klin Chem Klin Biochem. 1970 Jan;8(1):51–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann E., Räker K. O., Zeuner G. Solid-phase-Radioimmunassay und Blutspiegel von Staphylokokken-alpha-Toxin. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1969;262(2):165–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Svennerholm A. M. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for cholera serology. Infect Immun. 1973 May;7(5):759–763. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.5.759-763.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. M., Bukovic J. A., Kauffman P. E. Antigenic cross-reactivity of staphylococcal enterotoxins. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):645–647. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.645-647.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. M., Bukovic J. A., Kauffman P. E., Peeler J. T. Staphylococcal enterotoxin B: solid-phase radioimmunoassay. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Nov;22(5):837–841. doi: 10.1128/am.22.5.837-841.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman P. E., Johnson H. M. Stability of 125I-labeled staphylococcal enterotoxins in solid-phase radioimmunoassay. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jun;29(6):776–779. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.776-779.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman M. A highly efficient solid-phase radioimmune assay for a clostridial toxin. Anal Biochem. 1975 Jul;67(1):115–121. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90278-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robern H., Dighton M., Yano Y., Dickie N. Double-antibody radioimmunoassay for staphylococcal enterotoxin C2. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Oct;30(4):525–529. doi: 10.1128/am.30.4.525-529.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]