Abstract
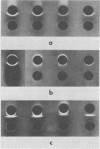
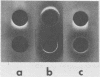
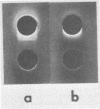
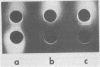
Rapid identification of Streptococcus pneumoniae has been reported using counterimmunoelectrophoresis for the detection of specific capsular antigens in serum, cerebrospinal fluid, and urine. Previous clinical studies have failed to detect type VII or XIV pneumococcal antigen. These two types, however, account for a significant portion of pneumococcal disease. The incorporation of a sulfonated derivative of phenylboronic acid in the buffer system provides a method for the sensitive detection of these types in artificial mixtures without greatly reducing the sensitivity for the detection of other pneumococcal types. A problem with false positives encountered using human serum and barbitalbuffer was reduced by the use of buffer containing sulfonated phenylboronic acid.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartram C. E., Jr, Crowder J. G., Beeler B., White A. Diagnosis of bacterial diseases by detection of serum antigens by counterimmunoelectrophoresis, sensitivity, and specificity of detecting Pseudomonas and pneumococcal antigens. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Apr;83(4):591–598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coonrod J. D. Physical and immunologic properties of pneumococcal capsular polysaccharide produced during human infection. J Immunol. 1974 Jun;112(6):2193–2201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coonrod J. D., Rytel M. W. Detection of type-specific pneumococcal antigens by counterimmunoelectrophoresis. I. Methodology and immunologic properties of pneumococcal antigens. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 May;81(5):770–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coonrod J. D., Rytel M. W. Detection of type-specific pneumococcal antigens by counterimmunoelectrophoresis. II. Etiologic diagnosis of pneumococcal pneumonia. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 May;81(5):778–786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOSTER A. B. Zone electrophoresis of carbohydrates. Adv Carbohydr Chem. 1957;12:81–115. doi: 10.1016/s0096-5332(08)60205-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fossieck B., Jr, Craig R., Paterson P. Y. Counterimmunoelectrophoresis for rapid diagnosis of meningitis due to Diplococcus pneumoniae. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jan;127(1):106–109. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.1.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser A. B., Schaffner W. Prospectus: the prevention of bacteremic pneumococcal pneumonia. A conservative appraisal of vaccine intervention. JAMA. 1974 Oct 21;230(3):404–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E., Wentworth B. B., Beasley R. P., Foy H. M. Correlation of circulating capsular polysaccharide with bacteremia in pneumococcal pneumonia. Infect Immun. 1972 Oct;6(4):431–437. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.4.431-437.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUND E. Laboratory diagnosis of Pneumococcus infections. Bull World Health Organ. 1960;23:5–13. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mufson M. A., Kruss D. M., Wasil R. E., Metzger W. I. Capsular types and outcome of bacteremic pneumococcal disease in the antibiotic era. Arch Intern Med. 1974 Sep;134(3):505–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson S., Hammarström S. G., Kabat E. A. The effect of borate on polysaccharide-protein and antigen-antibody reactions and its use for the purification and fractionation of crossreacting antibodies. Immunochemistry. 1970 May;7(5):413–422. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90223-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tugwell P., Greenwood B. M. Pneumococcal antigen in lobar pneumonia. J Clin Pathol. 1975 Feb;28(2):118–123. doi: 10.1136/jcp.28.2.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIGEL H. PAPER ELECTROPHORESIS OF CARBOHYDRATES. Adv Carbohydr Chem. 1963;18:61–97. doi: 10.1016/s0096-5332(08)60240-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins W. M. Blood-group substances. Science. 1966 Apr 8;152(3719):172–181. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3719.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]