Abstract
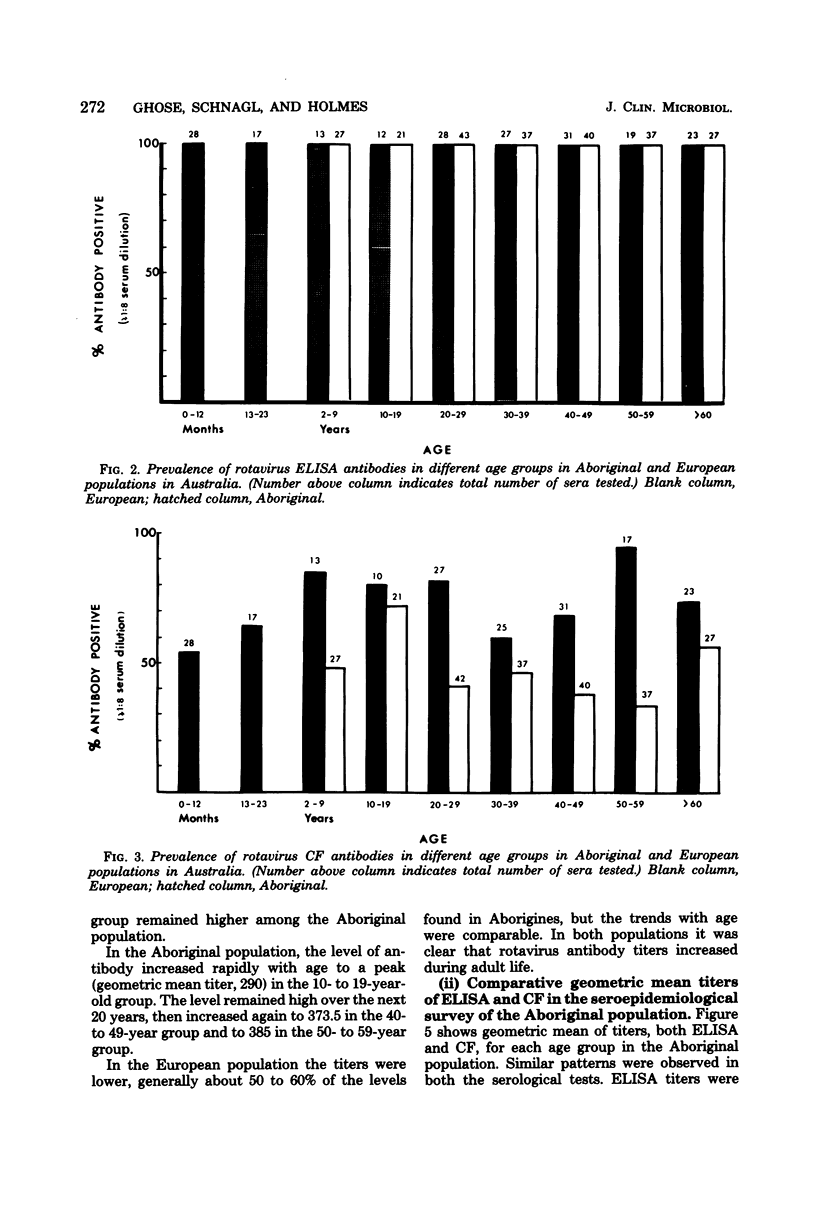
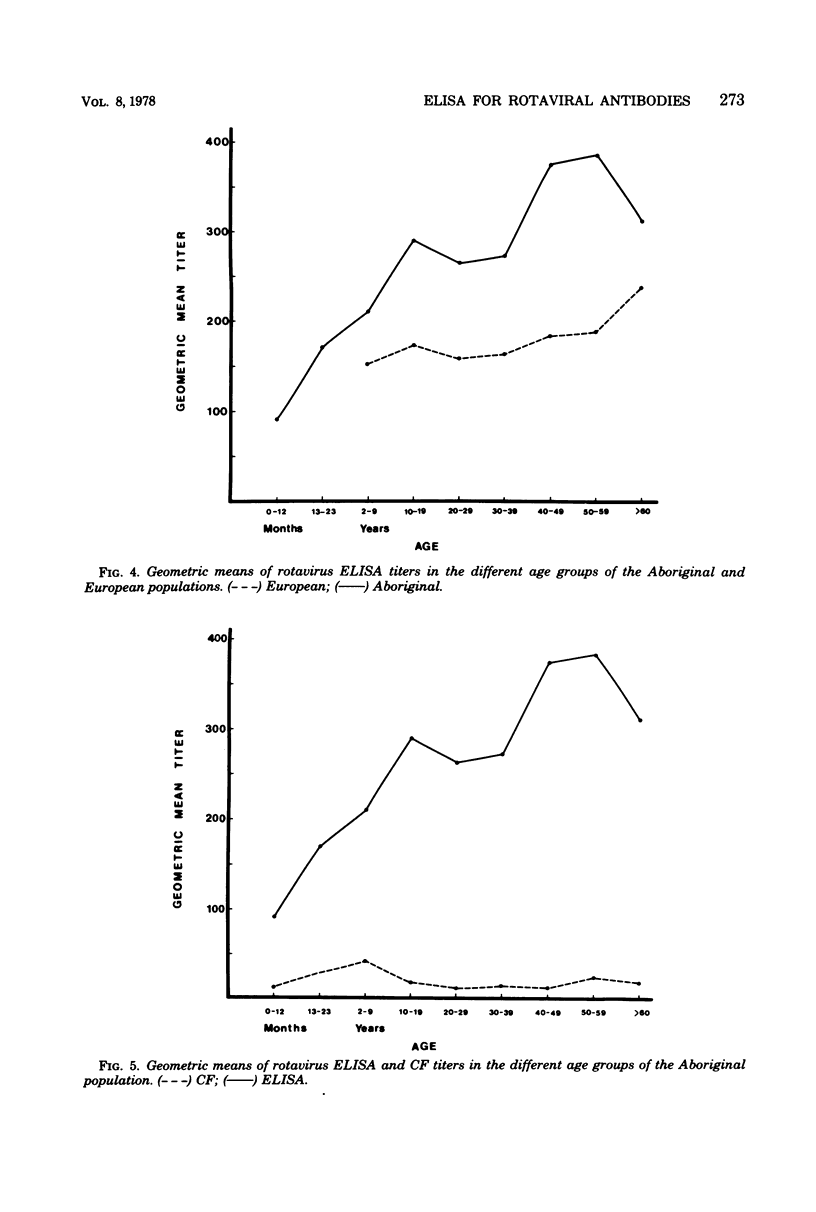
The development of a micro-scale enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) with horseradish peroxidase as the marker enzyme for the detection and measurement of human rotavirus antibodies is described. A semipurified preparation of the serologically related simian agent, SA-11 virus, was used as the antigen. Test sera were reacted with antigen-sensitized wells in disposable poly-vinyl microplates. Any attached antibody was detected by the addition of peroxidase-labeled anti-species immunoglobulin (conjugate) followed by assay of the enzyme reaction with its substrate, hydrogen peroxide plus 5-aminosalicylic acid. This micro-ELISA was compared with complement fixation in a seroepidemiological study of the age prevalence of rotavirus antibody in Aboriginal and European populations living in the same outback area in Australia. The ELISA (results read with the naked eye) proved to be approximately 16 times more sensitive than complement fixation. Of Aborigines, 71% had rotavirus complement-fixing antibody, as compared to 45% of Europeans. By ELISA 100% of both populations had rotavirus antibodies. Mean antibody titers in the different age groups were higher in Aborigines than in Europeans. Antibody levels rose steeply throughout the first 20 years of life, remained high during the next 20 years, then increased again at least up to the age of 60 years. The micro-ELISA was practical, simple to perform, and more suitable than complement fixation for large seroepidemiological rotavirus studies. It also has potential for serodiagnosis of the disease, both in the laboratory and in the field.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avrameas S., Ternynck T. Peroxidase labelled antibody and Fab conjugates with enhanced intracellular penetration. Immunochemistry. 1971 Dec;8(12):1175–1179. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90395-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
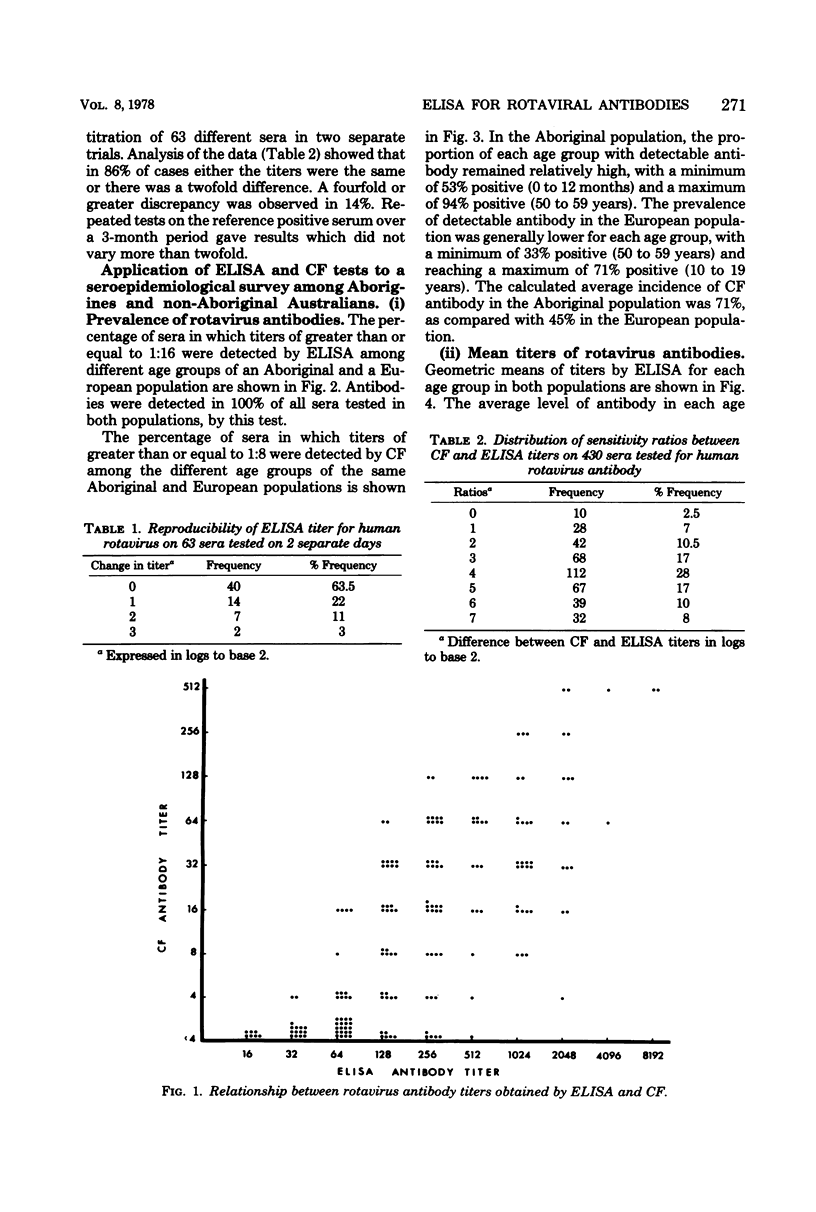
- BRADSTREET C. M., TAYLOR C. E. Technique of complementfixation test applicable to the diagnosis of virus diseases. Mon Bull Minist Health Public Health Lab Serv. 1962 May;21:96–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babiuk L. A., Acres S. D., Rouse B. T. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay for detecting bovine (neonatal calf diarrhea) rotavirus antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jul;6(1):10–15. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.1.10-15.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop R. F., Davidson G. P., Holmes I. H., Ruck B. J. Virus particles in epithelial cells of duodenal mucosa from children with acute non-bacterial gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1973 Dec 8;2(7841):1281–1283. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92867-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blacklow N. R., Echeverria P., Smith D. H. Serological studies with reovirus-like enteritis agent. Infect Immun. 1976 Jun;13(6):1563–1566. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.6.1563-1566.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broorsma D. M., Steefkerk J. G., Kors N. Peroxidase and fluorescein isothiocyanate as antibody markers. A quantitative comparison of two peroxidase conjugates prepared with glutaraldehyde or periodate anda fluorescein conjugate. J Histochem Cytochem. 1976 Sep;24(9):1017–1025. doi: 10.1177/24.9.184204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryden A. S., Thouless M. E., Flewett T. H. Rotavirus and rabbits. Vet Rec. 1976 Oct 16;99(16):323–323. doi: 10.1136/vr.99.16.323-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson G. P., Bishop R. F., Townley R. R., Holmes I. H. Importance of a new virus in acute sporadic enteritis in children. Lancet. 1975 Feb 1;1(7901):242–246. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91140-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson G. P., Goller I., Bishop R. F., Townley R. R., Holmes I. H., Ruck B. J. Immunofluorescence in duodenal mucosa of children with acute enteritis due to a new virus. J Clin Pathol. 1975 Apr;28(4):263–266. doi: 10.1136/jcp.28.4.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry. 1971 Sep;8(9):871–874. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90454-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewett T. H., Bryden A. S., Davies H., Woode G. N., Bridger J. C., Derrick J. M. Relation between viruses from acute gastroenteritis of children and newborn calves. Lancet. 1974 Jul 13;2(7872):61–63. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91631-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewett T. H., Davies H., Bryden A. S., Robertson M. J. Diagnostic electron microscopy of faeces. II. Acute gastroenteritis associated with reovirus-like particles. J Clin Pathol. 1974 Aug;27(8):608–614. doi: 10.1136/jcp.27.8.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gust I. D., Pringle R. C., Barnes G. L., Davidson G. P., Bishop R. F. Complement-fixing antibody response to rotavirus infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Feb;5(2):125–130. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.2.125-130.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes I. H., Rodger S. M., Schnagl R. D., Ruck B. J., Gust I. D., Bishop R. F., Barnes G. L. Is lactase the receptor and uncoating enzyme for infantile enteritis (rota) viruses? Lancet. 1976 Jun 26;1(7974):1387–1388. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)93032-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Ishizaka K., Salmon S., Fudenberg H. Biologic activities of aggregated gamma-globulin. 8. Aggregated immunoglobulins of different classes. J Immunol. 1967 Jul;99(1):82–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Cline W. L., Kim H. W., Kalica A. R., Wyatt R. G., Vankirk D. H., Chanock R. M., James H. D., Jr, Vaughn A. L. Antigenic relationships among five reovirus-like (RVL) agents by complement fixation (CF) and development of new substitute CF antigens for the human RVL agent of infantile gastroenteritis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Sep;152(4):535–539. doi: 10.3181/00379727-152-39434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Cline W. L., Mebus C. A., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., James H. D., Jr, VanKirk D., Chanock R. M. New complement-fixation test for the human reovirus-like agent of infantile gastroenteritis. Nebraska calf diarrhea virus used as antigen. Lancet. 1975 May 10;1(7915):1056–1061. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91827-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Kim H. W., Wyatt R. G., Cline W. L., Arrobio J. O., Brandt C. D., Rodriguez W. J., Sack D. A., Chanock R. M., Parrott R. H. Human reovirus-like agent as the major pathogen associated with "winter" gastroenteritis in hospitalized infants and young children. N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 29;294(18):965–972. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197604292941801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Kim H. W., Wyatt R. G., Rodriguez W. J., Ross S., Cline W. L., Parrott R. H., Chanock R. M. Reoviruslike agent in stools: association with infantile diarrhea and development of serologic tests. Science. 1974 Sep 20;185(4156):1049–1053. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4156.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konno T., Suzuki H., Imai A., Ishida N. Reovirus-like agent in acute epidemic gastroenteritis in Japanese infants: fecal shedding and serologic response. J Infect Dis. 1977 Feb;135(2):259–266. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.2.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maiya P. P., Pereira S. M., Mathan M., Bhat P., Albert M. J., Baker S. J. Aetiology of acute gastroenteritis in infancy and early childhood in southern India. Arch Dis Child. 1977 Jun;52(6):482–485. doi: 10.1136/adc.52.6.482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malherbe H. H., Strickland-Cholmley M. Simian virus SA11 and the related O agent. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1967;22(1):235–245. doi: 10.1007/BF01240518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno S., Inouye S., Kono R. Plaque assay of neonatal calf diarrhea virus and the neutralizing antibody in human sera. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jan;5(1):1–4. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.1.1-4.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton P. J., Petric M., Hewitt C. M., Szymanski M. T., Tam J. S. Counter-immunoelectro-osmophoresis for the detection of infantile gastroenteritis virus (orbi-group) antigen and antibody. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Mar;29(3):191–197. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.3.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane P. K., Kawaoi A. Peroxidase-labeled antibody. A new method of conjugation. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1084–1091. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogra P. L., Karzon D. T. Distribution of poliovirus antibody in serum, nasopharynx and alimentary tract following segmental immunization of lower alimentary tract with poliovaccine. J Immunol. 1969 Jun;102(6):1423–1430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Schnagl R. D., Holmes I. H. Further biochemical characterization, including the detection of surface glycoproteins, of human, calf, and simian rotaviruses. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):91–98. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.91-98.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruitenberg E. J., Steerenberg P. A., Brosi B. J., Buys J. Serodiagnosis of Trichinella spiralis infections in pigs by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. Bull World Health Organ. 1974;51(1):108–109. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders G. C., Clinard E. H. Rapid micromethod of screening for antibodies to disease agents using the indirect enzyme-labeled antibody test. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jun;3(6):604–608. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.6.604-608.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnagl R. D., Holmes I. H., Moore B., Lee P., Gust I. D., Dickinson-Jones F. An extensive rotavirus outbreak in aboriginal infants in central Australia. Med J Aust. 1977 Feb 19;1(8):259–260. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1977.tb130671.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoub B. D., Lecatsas G., Prozesky O. W. Antigenic relationship between human and simian rotaviruses. J Med Microbiol. 1977 Feb;10(1):1–6. doi: 10.1099/00222615-10-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stövesand P., Behrens F., Majer M., Maass G. Sero-epidemiologische Untersuchung über die Verbreitung von Infektionen des Menschen mit Rotaviren. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1977 May;238(1):16–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thouless M. E., Bryden A. S., Flewett T. H., Woode G. N., Bridger J. C., Snodgrass D. R., Herring J. A. Serological relationships between rotaviruses from different species as studied by complement fixation and neutralization. Arch Virol. 1977;53(4):287–294. doi: 10.1007/BF01315627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tufvesson B., Johnsson T. Occurrence of reo-like calf viruses in young children with acute gastroenteritis. Diagnoses established by electron microscopy and complement fixation, using the reo-like virus as antigen. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1976 Feb;84(1):22–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Holmes I. H. Filter paper solid-phase radioimmunoassay for human rotavirus surface immunoglobulins. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Oct;6(4):319–324. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.4.319-324.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Bridger J. C., Jones J. M., Flewett T. H., Davies H. A., Davis H. A., White G. B. Morphological and antigenic relationships between viruses (rotaviruses) from acute gastroenteritis of children, calves, piglets, mice, and foals. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):804–810. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.804-810.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N. Pathogenic rotaviruses isolated from pigs and calves. Ciba Found Symp. 1976;(42):251–271. doi: 10.1002/9780470720240.ch15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., Sly D. L., London W. T., Palmer A. E., Kalica A. R., Van Kirk D. H., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Induction of diarrhea in colostrum-deprived newborn rhesus monkeys with the human reovirus-like agent of infantile gastroenteritis. Arch Virol. 1976;50(1-2):17–27. doi: 10.1007/BF01317997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Wyatt R. G., Kim H. W., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Immunological response to infection with human reovirus-like agent: measurement of anti-human reovirus-like agent immunoglobulin G and M levels by the method of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):540–546. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.540-546.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zissis G., Lambert J. P., Fonteyne J., De Kegel D. Letter: Child-mother transmission of rotavirus. Lancet. 1976 Jan 10;1(7950):96–96. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90196-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


