Abstract
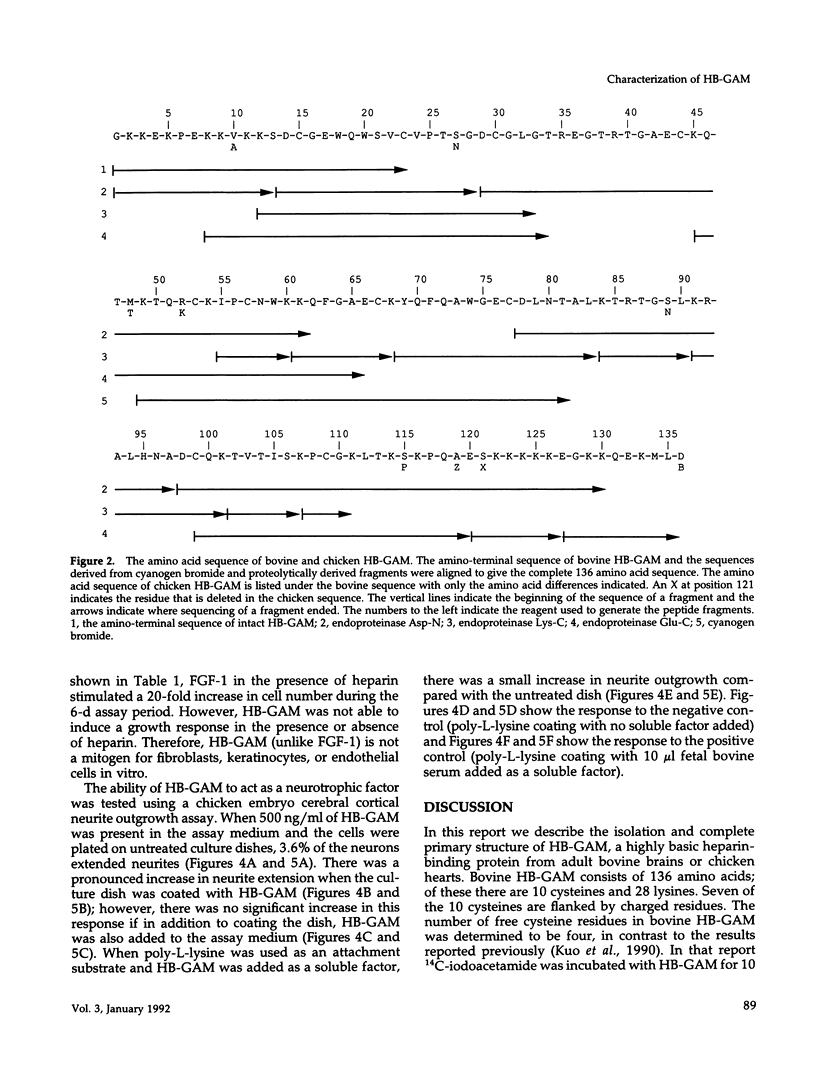
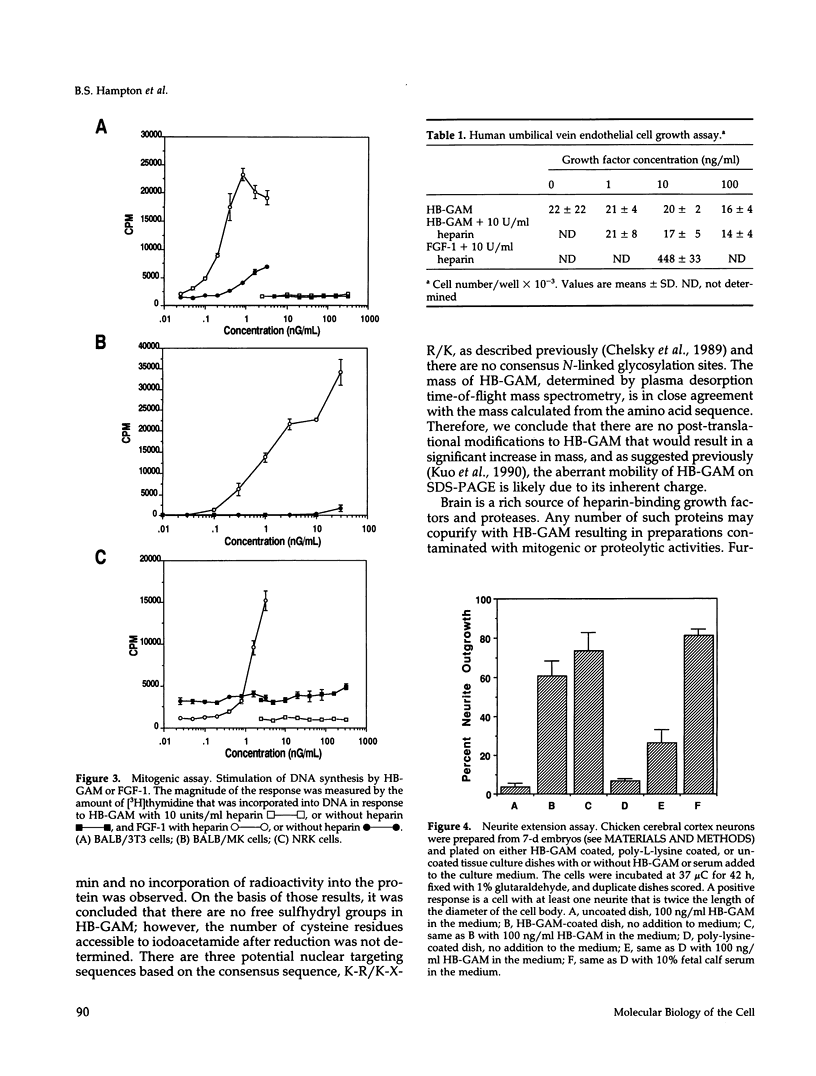
Heparin-binding growth-associated molecule (HB-GAM) was purified from adult bovine brain and chicken heart. The yield of HB-GAM is increased by 5- to 10-fold when 250 mM NaCl is added to the homogenization buffer, indicating that HB-GAM may exist as a complex with an insoluble component of the tissue. The complete amino acid sequence of the brain-derived HB-GAM was established by automated Edman degradation of the intact protein and chemically or enzymatically derived fragments. The mass of bovine HB-GAM as determined by plasma desorption time-of-flight mass spectrometry is 15,291 mass units, which compares favorably with the calculated mass of 15,289 based on the amino acid sequence. Therefore, HB-GAM has not undergone any major post-translational modifications other than cleavage of the signal peptide. These results indicate that previous amino acid sequence analysis of this protein was carried out using truncated HB-GAM. Full-length HB-GAM is not a mitogen for Balb/3T3 clone A31, Balb MK, NRK, or human umbilical vein endothelial cells. HB-GAM does, however, have adhesive properties and neurite extension activity for chick embryo cerebral cortical derived neurons when presented to these cells as a substrate. HB-GAM had little neurite extension activity when presented as a soluble factor.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgess W. H., Mehlman T., Friesel R., Johnson W. V., Maciag T. Multiple forms of endothelial cell growth factor. Rapid isolation and biological and chemical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11389–11392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess W. H., Shaheen A. M., Ravera M., Jaye M., Donohue P. J., Winkles J. A. Possible dissociation of the heparin-binding and mitogenic activities of heparin-binding (acidic fibroblast) growth factor-1 from its receptor-binding activities by site-directed mutagenesis of a single lysine residue. J Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;111(5 Pt 1):2129–2138. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.5.2129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhlen P., Müller T., Gautschi-Sova P., Albrecht U., Rasool C. G., Decker M., Seddon A., Fafeur V., Kovesdi I., Kretschmer P. Isolation from bovine brain and structural characterization of HBNF, a heparin-binding neurotrophic factor. Growth Factors. 1991;4(2):97–107. doi: 10.3109/08977199109000261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelsky D., Ralph R., Jonak G. Sequence requirements for synthetic peptide-mediated translocation to the nucleus. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2487–2492. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadomatsu K., Huang R. P., Suganuma T., Murata F., Muramatsu T. A retinoic acid responsive gene MK found in the teratocarcinoma system is expressed in spatially and temporally controlled manner during mouse embryogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):607–616. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadomatsu K., Tomomura M., Muramatsu T. cDNA cloning and sequencing of a new gene intensely expressed in early differentiation stages of embryonal carcinoma cells and in mid-gestation period of mouse embryogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Mar 30;151(3):1312–1318. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80505-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kligman D. Isolation of a protein from bovine brain which promotes neurite extension from chick embryo cerebral cortex neurons in defined medium. Brain Res. 1982 Oct 28;250(1):93–100. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90955-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Fairhurst J. L., Kretschmer P. J., Böhlen P. Heparin-binding neurotrophic factor (HBNF) and MK, members of a new family of homologous, developmentally regulated proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Oct 30;172(2):850–854. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90753-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo M. D., Oda Y., Huang J. S., Huang S. S. Amino acid sequence and characterization of a heparin-binding neurite-promoting factor (p18) from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):18749–18752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. S., Milner P. G., Chauhan A. K., Watson M. A., Hoffman R. M., Kodner C. M., Milbrandt J., Deuel T. F. Cloning and expression of a developmentally regulated protein that induces mitogenic and neurite outgrowth activity. Science. 1990 Dec 21;250(4988):1690–1694. doi: 10.1126/science.2270483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merenmies J., Rauvala H. Molecular cloning of the 18-kDa growth-associated protein of developing brain. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):16721–16724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner P. G., Li Y. S., Hoffman R. M., Kodner C. M., Siegel N. R., Deuel T. F. A novel 17 kD heparin-binding growth factor (HBGF-8) in bovine uterus: purification and N-terminal amino acid sequence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 29;165(3):1096–1103. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92715-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauvala H. An 18-kd heparin-binding protein of developing brain that is distinct from fibroblast growth factors. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2933–2941. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08443.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin J. S., Osada H., Finch P. W., Taylor W. G., Rudikoff S., Aaronson S. A. Purification and characterization of a newly identified growth factor specific for epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):802–806. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki H., Hoshi H., Hong Y. M., Suzuki T., Kato T., Sasaki H., Saito M., Youki H., Karube K., Konno S. Purification of acidic fibroblast growth factor from bovine heart and its localization in the cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17606–17612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundqvist B., Roepstorff P., Fohlman J., Hedin A., Håkansson P., Kamensky I., Lindberg M., Salehpour M., Säwe G. Molecular weight determinations of proteins by californium plasma desorption mass spectrometry. Science. 1984 Nov 9;226(4675):696–698. doi: 10.1126/science.6387912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomomura M., Kadomatsu K., Nakamoto M., Muramatsu H., Kondoh H., Imagawa K., Muramatsu T. A retinoic acid responsive gene, MK, produces a secreted protein with heparin binding activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Sep 14;171(2):603–609. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91189-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urios P., Duprez D., Le Caer J. P., Courtois Y., Vigny M., Laurent M. Molecular cloning of RI-HB, a heparin binding protein regulated by retinoic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 15;175(2):617–624. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91610-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigny M., Raulais D., Puzenat N., Duprez D., Hartmann M. P., Jeanny J. C., Courtois Y. Identification of a new heparin-binding protein localized within chick basement membranes. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Dec 22;186(3):733–740. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walicke P. A. Novel neurotrophic factors, receptors, and oncogenes. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1989;12:103–126. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.12.030189.000535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissman B. E., Aaronson S. A. BALB and Kirsten murine sarcoma viruses alter growth and differentiation of EGF-dependent balb/c mouse epidermal keratinocyte lines. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):599–606. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90479-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]