Abstract
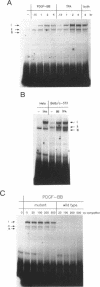
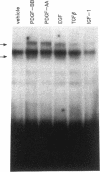
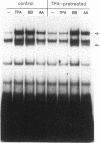
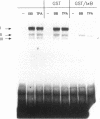
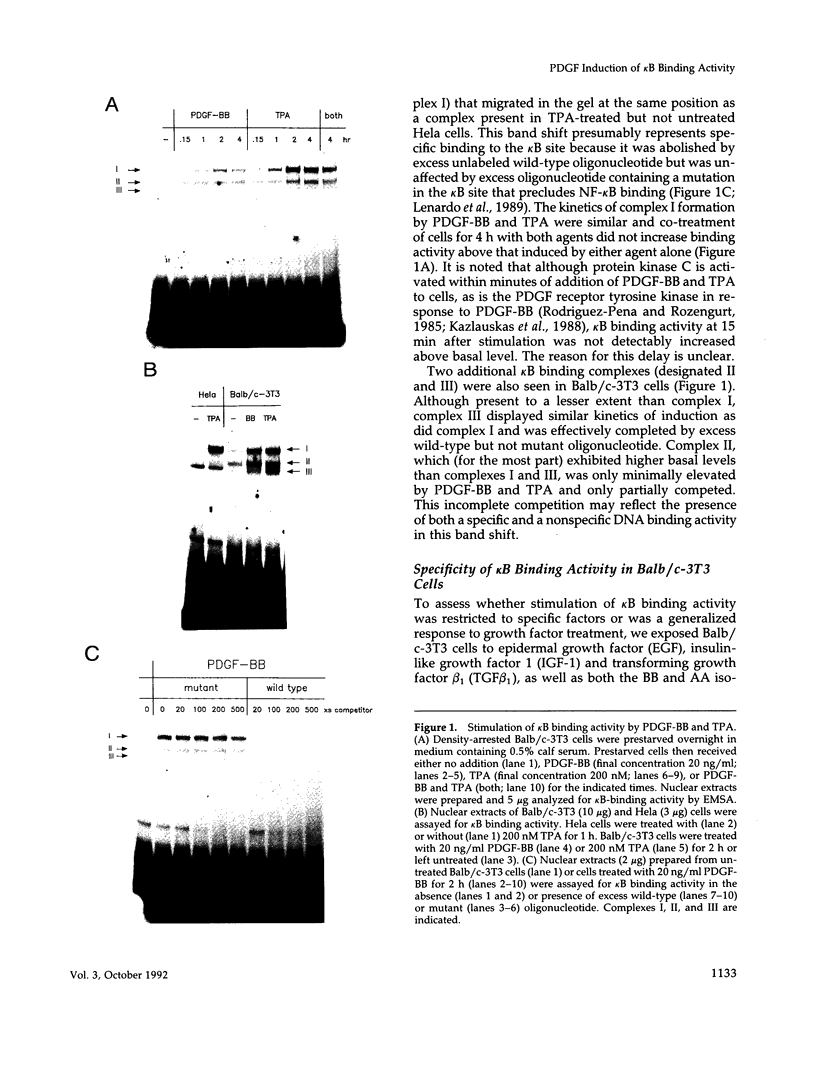
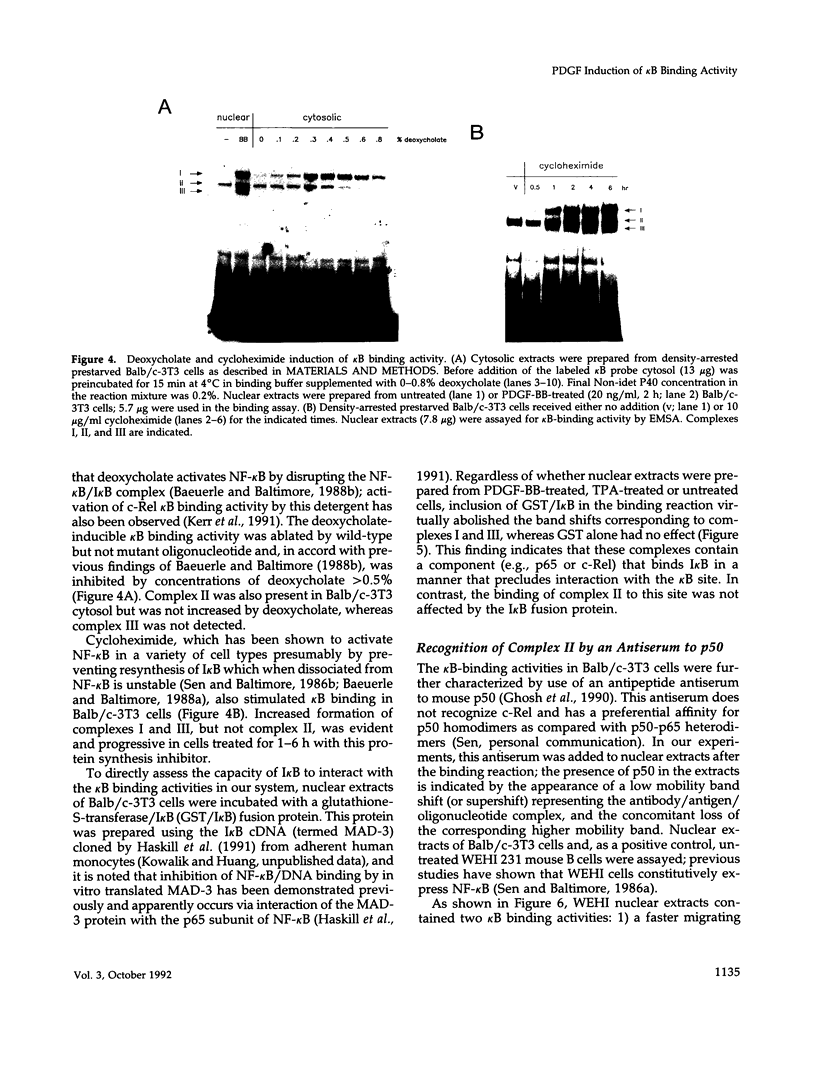
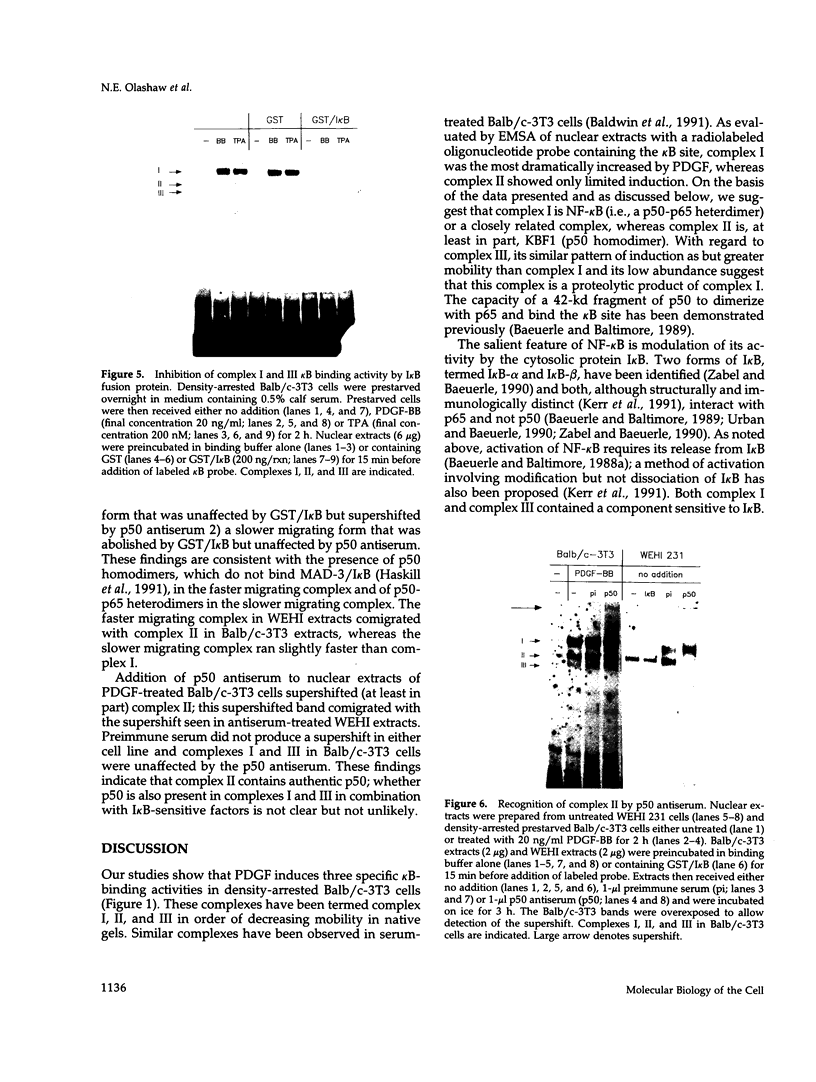
Nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappa B) modulates the expression of numerous genes via interaction with a specific DNA sequence termed the kappa B site. Its activity is modulated by a cytosolic inhibitor protein termed I kappa B, and its activation occurs in response to a variety of agents in a variety of cell types, most notably B and T lymphocytes. Data presented here show that an activity (designated complex I) that binds specifically to the kappa B site is induced in density-arrested Balb/c-3T3 mouse fibroblasts by platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), a potent mitogen for these cells. Increased levels of complex I, as evaluated by electrophoretic mobility shift assays of nuclear extracts, were observed in cells treated for 1-4 h (but not 15 min) with the BB isoform of PDGF. 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate (TPA) and the AA isoform of PDGF also stimulated this response and both isoforms, but not TPA, were effective in cells depleted of protein kinase C. Complex I most likely is authentic NF-kappa B, a p50-p65 heterodimer, or a closely related factor because it exhibited properties characteristic of those previously described for NF-kappa B including inducibility by deoxycholate and cycloheximide and sensitivity to I kappa B. A second kappa B binding activity (complex II), which apparently contained p50 homodimers, displayed limited induction by PDGF, whereas a third complex (complex III) migrated faster than but behaved similarly to complex I. These studies suggest that NF-kappa B or an NF-kappa B-like factor may participate in the expression of PDGF-inducible genes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anisowicz A., Messineo M., Lee S. W., Sager R. An NF-kappa B-like transcription factor mediates IL-1/TNF-alpha induction of gro in human fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 15;147(2):520–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. A 65-kappaD subunit of active NF-kappaB is required for inhibition of NF-kappaB by I kappaB. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1689–1698. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. Activation of DNA-binding activity in an apparently cytoplasmic precursor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. I kappa B: a specific inhibitor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):540–546. doi: 10.1126/science.3140380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A. The inducible transcription activator NF-kappa B: regulation by distinct protein subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 16;1072(1):63–80. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, Azizkhan J. C., Jensen D. E., Beg A. A., Coodly L. R. Induction of NF-kappa B DNA-binding activity during the G0-to-G1 transition in mouse fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4943–4951. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Binding of a nuclear factor to a regulatory sequence in the promoter of the mouse H-2Kb class I major histocompatibility gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):305–313. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard D. W., Böhnlein E., Lowenthal J. W., Wano Y., Franza B. R., Greene W. C. HTLV-I tax induces cellular proteins that activate the kappa B element in the IL-2 receptor alpha gene. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1652–1655. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard D. W., Walker W. H., Doerre S., Sista P., Molitor J. A., Dixon E. P., Peffer N. J., Hannink M., Greene W. C. The v-rel oncogene encodes a kappa B enhancer binding protein that inhibits NF-kappa B function. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):803–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomsztyk K., Rooney J. W., Iwasaki T., Rachie N. A., Dower S. K., Sibley C. H. Evidence that interleukin-1 and phorbol esters activate NF-kappa B by different pathways: role of protein kinase C. Cell Regul. 1991 Apr;2(4):329–335. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.4.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordoni R., Thomas G., Richmond A. Growth factor modulation of melanoma growth stimulatory activity mRNA expression in human malignant melanoma cells correlates with cell growth. J Cell Biochem. 1989 Apr;39(4):421–428. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240390408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bours V., Burd P. R., Brown K., Villalobos J., Park S., Ryseck R. P., Bravo R., Kelly K., Siebenlist U. A novel mitogen-inducible gene product related to p50/p105-NF-kappa B participates in transactivation through a kappa B site. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):685–695. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull P., Hunter T., Verma I. M. Transcriptional induction of the murine c-rel gene with serum and phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate in fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5239–5243. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N., Ghosh S., Simmons D. L., Tempst P., Liou H. C., Baltimore D., Bose H. R., Jr Rel-associated pp40: an inhibitor of the rel family of transcription factors. Science. 1991 Sep 13;253(5025):1268–1271. doi: 10.1126/science.1891714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duyao M. P., Kessler D. J., Spicer D. B., Sonenshein G. E. Binding of NF-KB-like factors to regulatory sequences of the c-myc gene. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;166:211–220. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75889-8_27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frantz C. N., Stiles C. D., Scher C. D. The tumor promoter 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate enhances the proliferative response of Balb/c-3T3 cells to hormonal growth factors. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Sep;100(3):413–424. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Nolan G. P., Ghosh S., Baltimore D. Independent modes of transcriptional activation by the p50 and p65 subunits of NF-kappa B. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):775–787. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Baltimore D. Activation in vitro of NF-kappa B by phosphorylation of its inhibitor I kappa B. Nature. 1990 Apr 12;344(6267):678–682. doi: 10.1038/344678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Gifford A. M., Riviere L. R., Tempst P., Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. Cloning of the p50 DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B: homology to rel and dorsal. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90276-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart C. E., Forstrom J. W., Kelly J. D., Seifert R. A., Smith R. A., Ross R., Murray M. J., Bowen-Pope D. F. Two classes of PDGF receptor recognize different isoforms of PDGF. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1529–1531. doi: 10.1126/science.2836952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskill S., Beg A. A., Tompkins S. M., Morris J. S., Yurochko A. D., Sampson-Johannes A., Mondal K., Ralph P., Baldwin A. S., Jr Characterization of an immediate-early gene induced in adherent monocytes that encodes I kappa B-like activity. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1281–1289. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90022-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Bäckström G., Ostman A., Hammacher A., Rönnstrand L., Rubin K., Nistér M., Westermark B. Binding of different dimeric forms of PDGF to human fibroblasts: evidence for two separate receptor types. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1387–1393. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02955.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyos B., Ballard D. W., Böhnlein E., Siekevitz M., Greene W. C. Kappa B-specific DNA binding proteins: role in the regulation of human interleukin-2 gene expression. Science. 1989 Apr 28;244(4903):457–460. doi: 10.1126/science.2497518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue J., Kerr L. D., Kakizuka A., Verma I. M. I kappa B gamma, a 70 kd protein identical to the C-terminal half of p110 NF-kappa B: a new member of the I kappa B family. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1109–1120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90082-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue J., Kerr L. D., Ransone L. J., Bengal E., Hunter T., Verma I. M. c-rel activates but v-rel suppresses transcription from kappa B sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3715–3719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip Y. T., Kraut R., Levine M., Rushlow C. A. The dorsal morphogen is a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein that interacts with a long-range repression element in Drosophila. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):439–446. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90651-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël A., Kimura A., Kieran M., Yano O., Kanellopoulos J., Le Bail O., Kourilsky P. A common positive trans-acting factor binds to enhancer sequences in the promoters of mouse H-2 and beta 2-microglobulin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2653–2657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabrun N., Hodgson J. W., Doemer M., Mak G., Franza B. R., Jr, Enrietto P. J. Interaction of the v-rel protein with an NF-kappa B DNA binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1783–1787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Bowen-Pope D., Seifert R., Hart C. E., Cooper J. A. Different effects of homo- and heterodimers of platelet-derived growth factor A and B chains on human and mouse fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3727–3735. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03256.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr L. D., Inoue J., Davis N., Link E., Baeuerle P. A., Bose H. R., Jr, Verma I. M. The rel-associated pp40 protein prevents DNA binding of Rel and NF-kappa B: relationship with I kappa B beta and regulation by phosphorylation. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1464–1476. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohase M., May L. T., Tamm I., Vilcek J., Sehgal P. B. A cytokine network in human diploid fibroblasts: interactions of beta-interferons, tumor necrosis factor, platelet-derived growth factor, and interleukin-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):273–280. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Fan C. M., Maniatis T., Baltimore D. The involvement of NF-kappa B in beta-interferon gene regulation reveals its role as widely inducible mediator of signal transduction. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):287–294. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90966-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leof E. B., Proper J. A., Goustin A. S., Shipley G. D., DiCorleto P. E., Moses H. L. Induction of c-sis mRNA and activity similar to platelet-derived growth factor by transforming growth factor beta: a proposed model for indirect mitogenesis involving autocrine activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2453–2457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leof E. B., Van Wyk J. J., O'Keefe E. J., Pledger W. J. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) is required only during the traverse of early G1 in PDGF stimulated density-arrested BALB/c-3T3 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Aug;147(1):202–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90285-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leof E. B., Wharton W., van Wyk J. J., Pledger W. J. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) and somatomedin C regulate G1 progression in competent BALB/c-3T3 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Sep;141(1):107–115. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung K., Nabel G. J. HTLV-1 transactivator induces interleukin-2 receptor expression through an NF-kappa B-like factor. Nature. 1988 Jun 23;333(6175):776–778. doi: 10.1038/333776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meichle A., Schütze S., Hensel G., Brunsing D., Krönke M. Protein kinase C-independent activation of nuclear factor kappa B by tumor necrosis factor. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8339–8343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan G. P., Ghosh S., Liou H. C., Tempst P., Baltimore D. DNA binding and I kappa B inhibition of the cloned p65 subunit of NF-kappa B, a rel-related polypeptide. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):961–969. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90320-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pledger W. J., Stiles C. D., Antoniades H. N., Scher C. D. Induction of DNA synthesis in BALB/c 3T3 cells by serum components: reevaluation of the commitment process. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4481–4485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransone L. J., Verma I. M. Nuclear proto-oncogenes fos and jun. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:539–557. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.002543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Pena A., Rozengurt E. Disappearance of Ca2+-sensitive, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase activity in phorbol ester-treated 3T3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):1053–1059. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Pena A., Rozengurt E. Serum, like phorbol esters, rapidly activates protein kinase C in intact quiescent fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):71–76. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02319.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S. M., Dillon P. J., Schreck R., Henkel T., Chen C. H., Maher M., Baeuerle P. A., Rosen C. A. Isolation of a rel-related human cDNA that potentially encodes the 65-kD subunit of NF-kappa B. Science. 1991 Mar 22;251(5000):1490–1493. doi: 10.1126/science.2006423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryseck R. P., Bull P., Takamiya M., Bours V., Siebenlist U., Dobrzanski P., Bravo R. RelB, a new Rel family transcription activator that can interact with p50-NF-kappa B. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):674–684. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90807-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa F., Mizel S. B. In vitro activation and nuclear translocation of NF-kappa B catalyzed by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2424–2430. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staal F. J., Roederer M., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Intracellular thiols regulate activation of nuclear factor kappa B and transcription of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9943–9947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern J. B., Smith K. A. Interleukin-2 induction of T-cell G1 progression and c-myb expression. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):203–206. doi: 10.1126/science.3523754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toledano M. B., Leonard W. J. Modulation of transcription factor NF-kappa B binding activity by oxidation-reduction in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4328–4332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban M. B., Baeuerle P. A. The 65-kD subunit of NF-kappa B is a receptor for I kappa B and a modulator of DNA-binding specificity. Genes Dev. 1990 Nov;4(11):1975–1984. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.11.1975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton W., Leof E. B., Olashaw N., Earp H. S., Pledger W. J. Increases in cyclic AMP potentiate competence formation in BALB/c-3T3 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1982 May;111(2):201–206. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041110212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabel U., Baeuerle P. A. Purified human I kappa B can rapidly dissociate the complex of the NF-kappa B transcription factor with its cognate DNA. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):255–265. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90806-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]