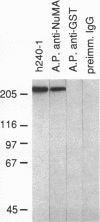
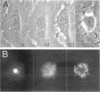
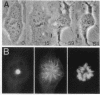
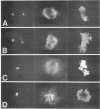
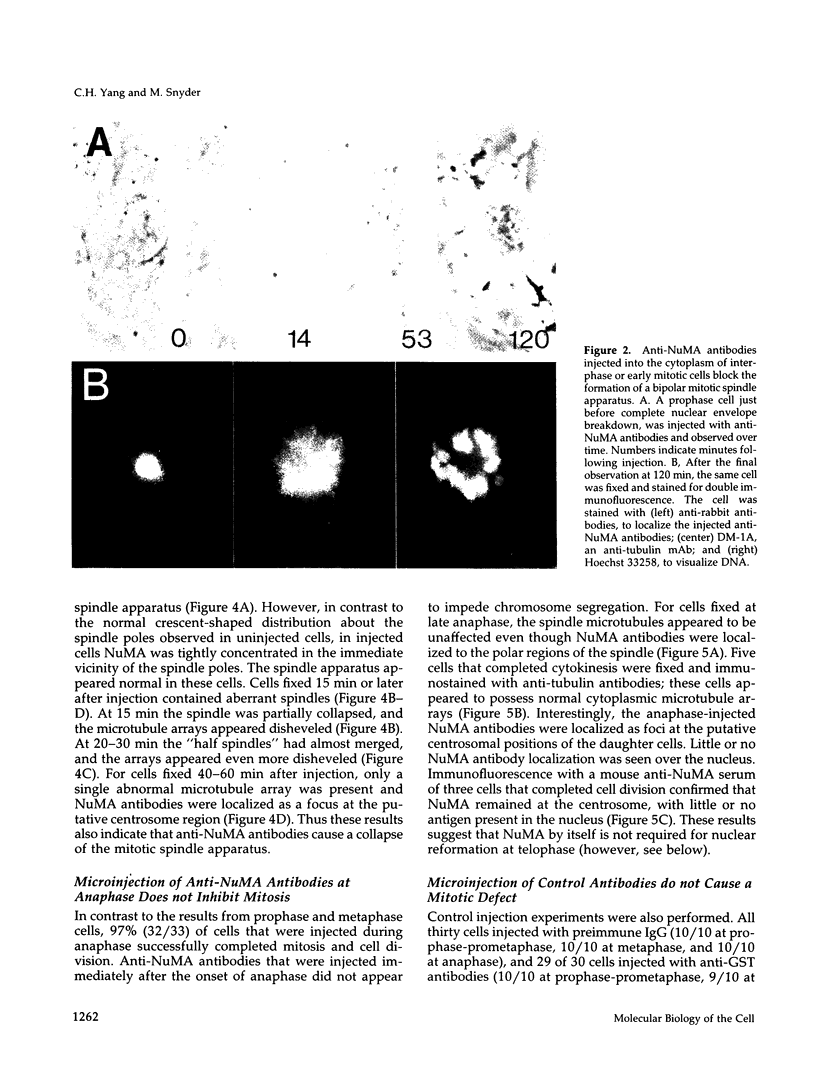
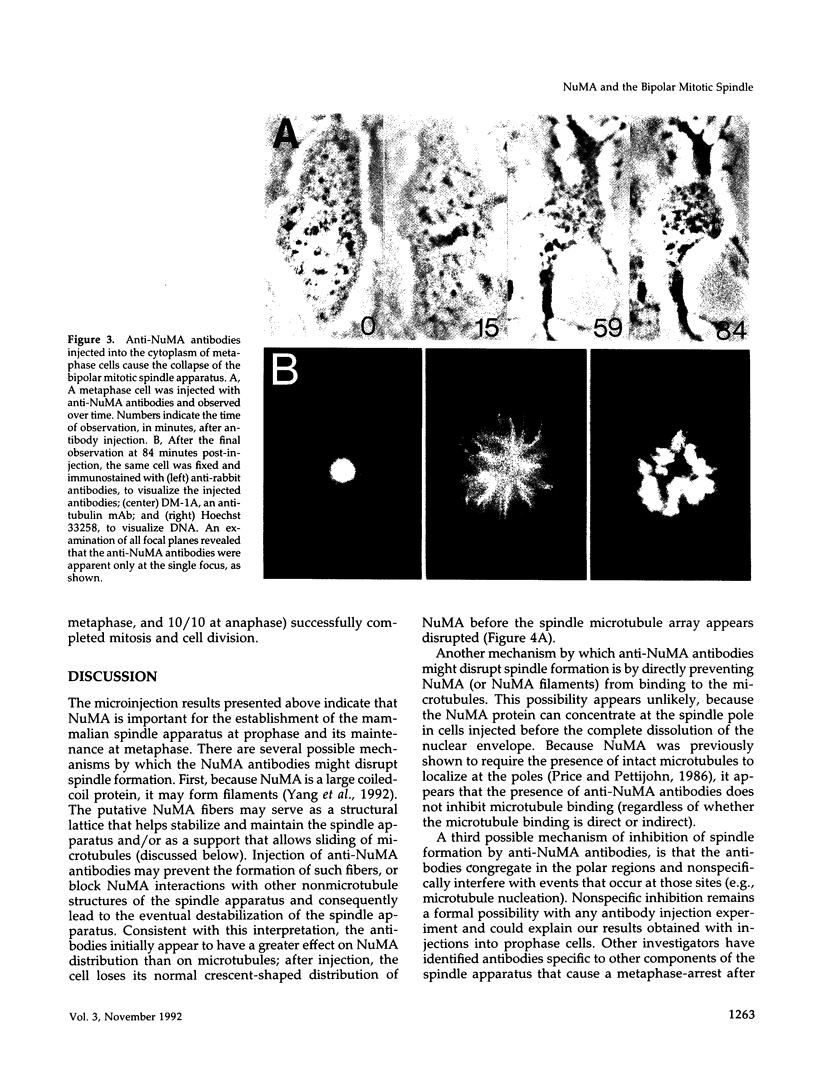
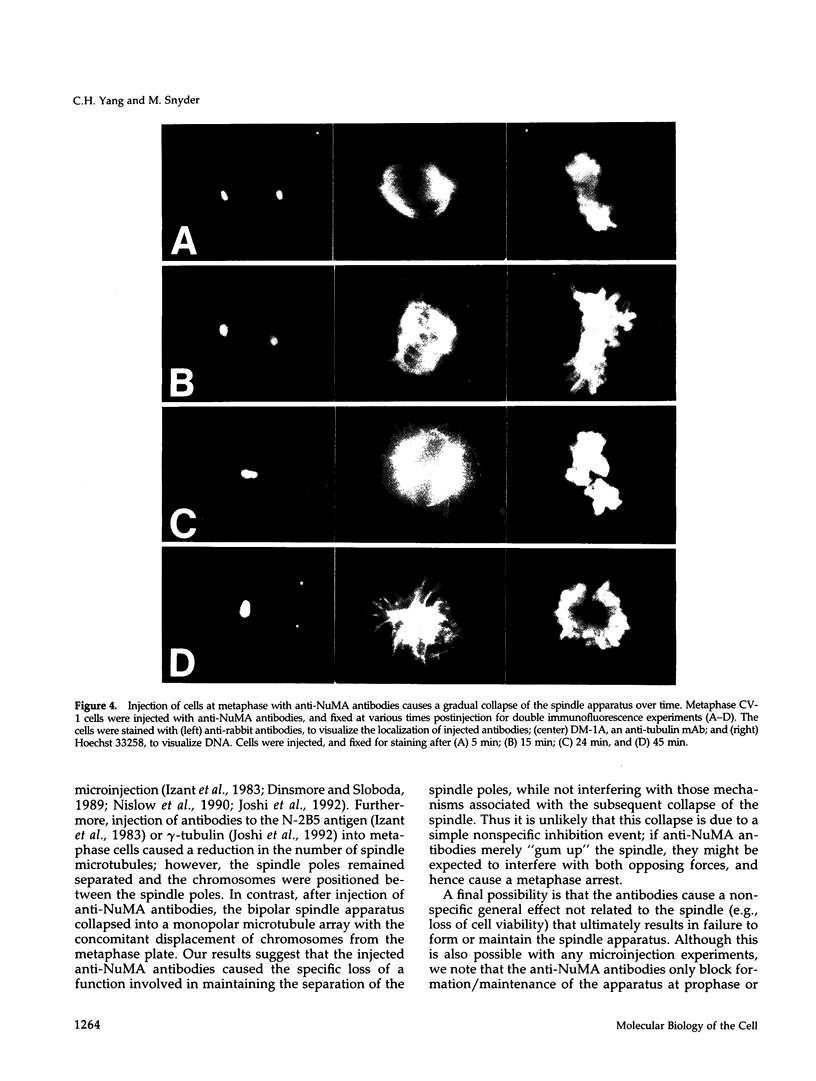
Abstract
The formation and maintenance of the bipolar mitotic spindle apparatus require a complex and balanced interplay of several mechanisms, including the stabilization and separation of polar microtubules and the action of various microtubule motors. Nonmicrotubule elements are also present throughout the spindle apparatus and have been proposed to provide a structural support for the spindle. The Nuclear-Mitotic Apparatus protein (NuMA) is an abundant 240 kD protein that is present in the nucleus of interphase cells and concentrates in the polar regions of the spindle apparatus during mitosis. Sequence analysis indicates that NuMA possesses an unusually long alpha-helical central region characteristic of many filament forming proteins. In this report we demonstrate that microinjection of anti-NuMA antibodies into interphase and prophase cells results in a failure to form a mitotic spindle apparatus. Furthermore, injection of metaphase cells results in the collapse of the spindle apparatus into a monopolar microtubule array. These results identify for the first time a nontubulin component important for both the establishment and stabilization of the mitotic spindle apparatus in multicellular organisms. We suggest that nonmicrotubule structural components may be important for these processes.
Full text
PDF


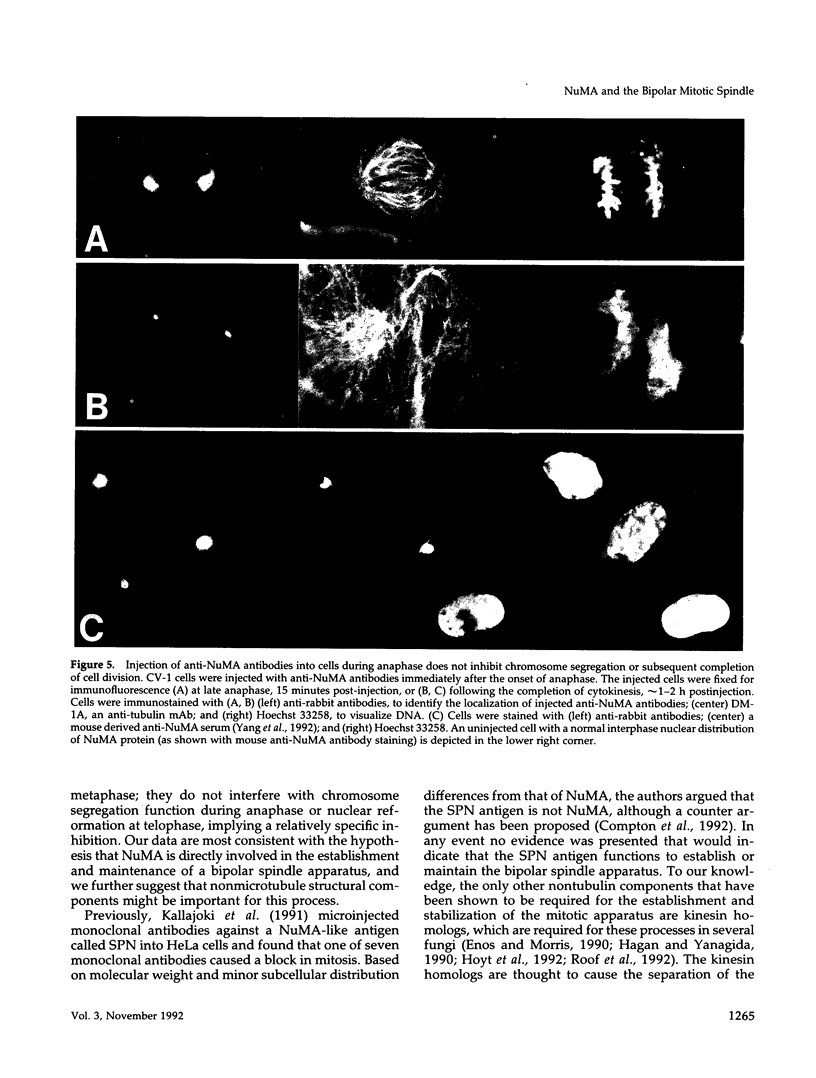


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton D. A., Szilak I., Cleveland D. W. Primary structure of NuMA, an intranuclear protein that defines a novel pathway for segregation of proteins at mitosis. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(6):1395–1408. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.6.1395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinsmore J. H., Sloboda R. D. Microinjection of antibodies to a 62 kd mitotic apparatus protein arrests mitosis in dividing sea urchin embryos. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enos A. P., Morris N. R. Mutation of a gene that encodes a kinesin-like protein blocks nuclear division in A. nidulans. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):1019–1027. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90350-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbsky G. J., Borisy G. G. Microtubules of the kinetochore fiber turn over in metaphase but not in anaphase. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):653–662. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbsky G. J. Chromosome motion in mitosis. Bioessays. 1992 Feb;14(2):73–80. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagan I., Yanagida M. Novel potential mitotic motor protein encoded by the fission yeast cut7+ gene. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):563–566. doi: 10.1038/347563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyt M. A., He L., Loo K. K., Saunders W. S. Two Saccharomyces cerevisiae kinesin-related gene products required for mitotic spindle assembly. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;118(1):109–120. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izant J. G., Weatherbee J. A., McIntosh J. R. A microtubule-associated protein antigen unique to mitotic spindle microtubules in PtK1 cells. J Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;96(2):424–434. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.2.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi H. C., Palacios M. J., McNamara L., Cleveland D. W. Gamma-tubulin is a centrosomal protein required for cell cycle-dependent microtubule nucleation. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):80–83. doi: 10.1038/356080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallajoki M., Weber K., Osborn M. A 210 kDa nuclear matrix protein is a functional part of the mitotic spindle; a microinjection study using SPN monoclonal antibodies. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3351–3362. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04899.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D. E., Mitchison T. J., Kirschner M. W. Polewards chromosome movement driven by microtubule depolymerization in vitro. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):499–504. doi: 10.1038/331499a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie R. J., Hird R. B., Wilson L., McIntosh J. R., Scholey J. M. Kinesin is associated with a nonmicrotubule component of sea urchin mitotic spindles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2771–2775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lydersen B. K., Pettijohn D. E. Human-specific nuclear protein that associates with the polar region of the mitotic apparatus: distribution in a human/hamster hybrid cell. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):489–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90359-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh J. R., Hering G. E. Spindle fiber action and chromosome movement. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:403–426. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.002155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh J. R., Koonce M. P. Mitosis. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):622–628. doi: 10.1126/science.2683078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh J. R., Pfarr C. M. Mitotic motors. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(3):577–585. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.3.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirzayan C., Copeland C. S., Snyder M. The NUF1 gene encodes an essential coiled-coil related protein that is a potential component of the yeast nucleoskeleton. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(6):1319–1332. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.6.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison T. J. Polewards microtubule flux in the mitotic spindle: evidence from photoactivation of fluorescence. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):637–652. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nislow C., Sellitto C., Kuriyama R., McIntosh J. R. A monoclonal antibody to a mitotic microtubule-associated protein blocks mitotic progression. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):511–522. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paddy M. R., Chelsky D. Spoke: a 120-kD protein associated with a novel filamentous structure on or near kinetochore microtubules in the mitotic spindle. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(1):161–171. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.1.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfarr C. M., Coue M., Grissom P. M., Hays T. S., Porter M. E., McIntosh J. R. Cytoplasmic dynein is localized to kinetochores during mitosis. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):263–265. doi: 10.1038/345263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C. M., Pettijohn D. E. Redistribution of the nuclear mitotic apparatus protein (NuMA) during mitosis and nuclear assembly. Properties of purified NuMA protein. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Oct;166(2):295–311. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90478-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieder C. L., Davison E. A., Jensen L. C., Cassimeris L., Salmon E. D. Oscillatory movements of monooriented chromosomes and their position relative to the spindle pole result from the ejection properties of the aster and half-spindle. J Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;103(2):581–591. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.2.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roof D. M., Meluh P. B., Rose M. D. Kinesin-related proteins required for assembly of the mitotic spindle. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;118(1):95–108. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurck T. P., Pickett-Heaps J. D. On the mechanism of anaphase A: evidence that ATP is needed for microtubule disassembly and not generation of polewards force. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1691–1705. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen W., Linck R. W. Evidence for a non-tubulin spindle matrix and for spindle components immunologically related to tektin filaments. J Cell Sci. 1992 Apr;101(Pt 4):809–822. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.4.809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steuer E. R., Wordeman L., Schroer T. A., Sheetz M. P. Localization of cytoplasmic dynein to mitotic spindles and kinetochores. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):266–268. doi: 10.1038/345266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuffanelli D. L., McKeon F., Kleinsmith D. M., Burnham T. K., Kirschner M. Anticentromere and anticentriole antibodies in the scleroderma spectrum. Arch Dermatol. 1983 Jul;119(7):560–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. H., Lambie E. J., Snyder M. NuMA: an unusually long coiled-coil related protein in the mammalian nucleus. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(6):1303–1317. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.6.1303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]