Abstract
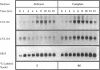
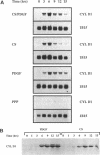
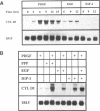
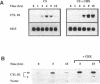
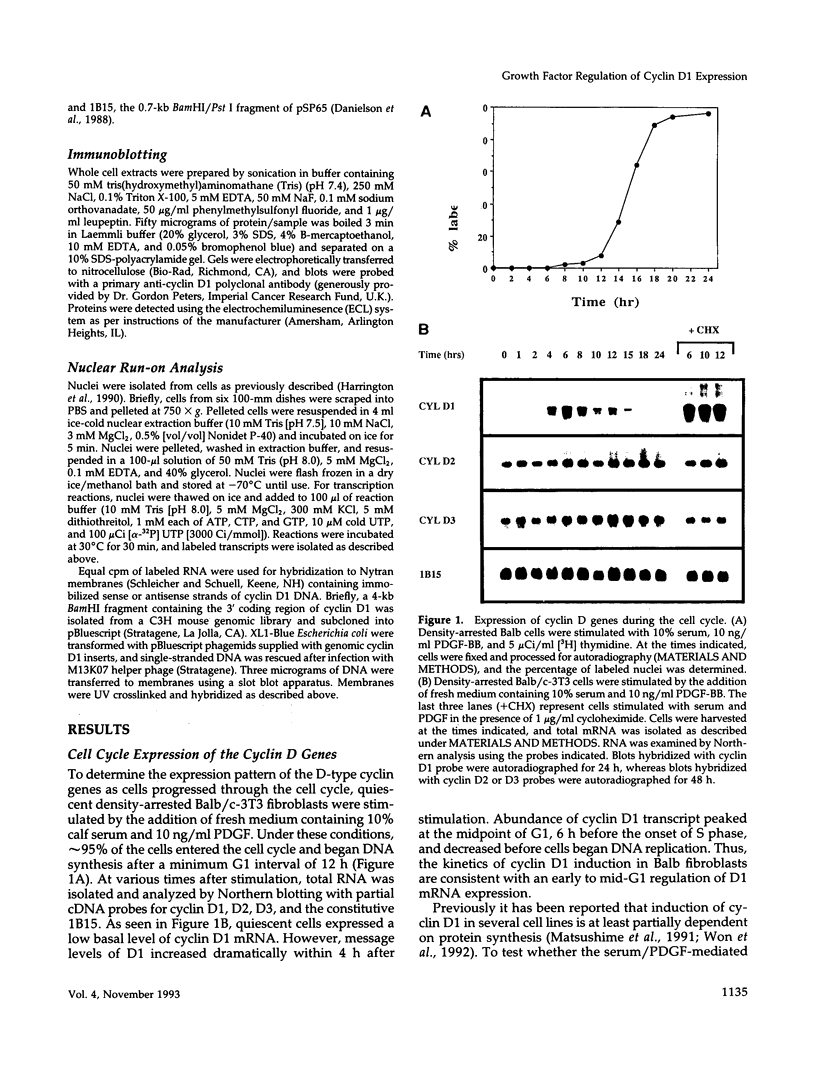
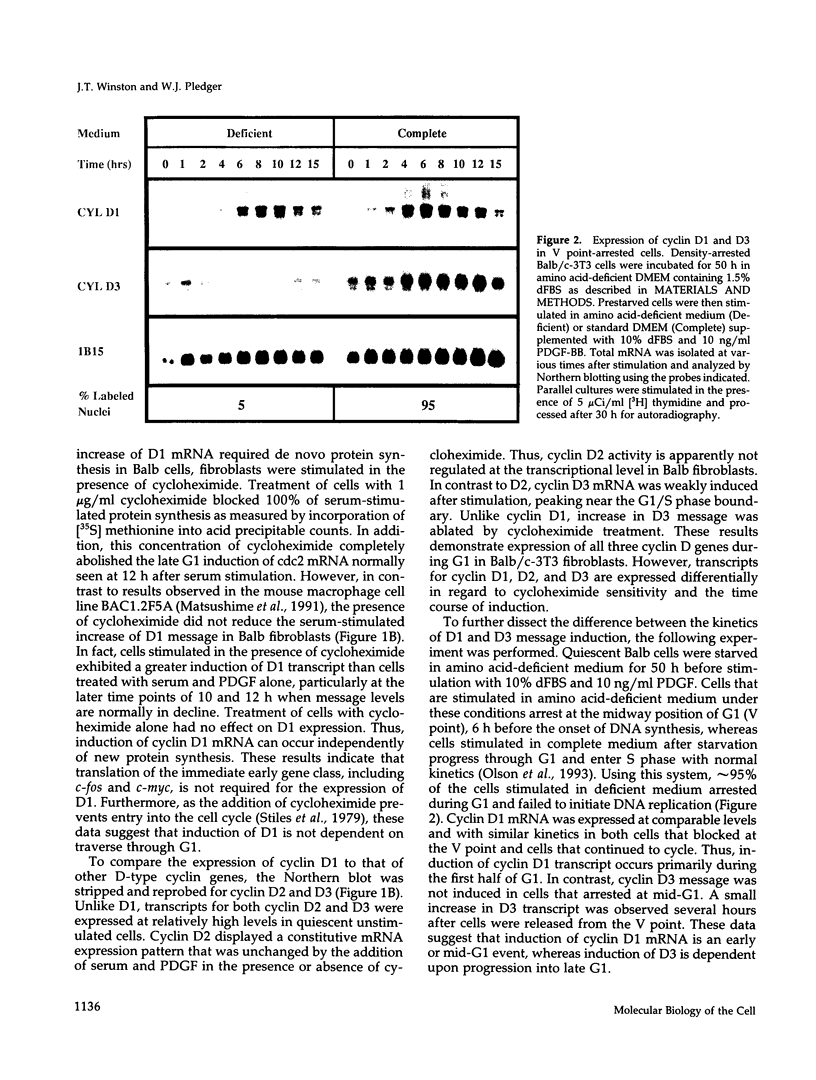
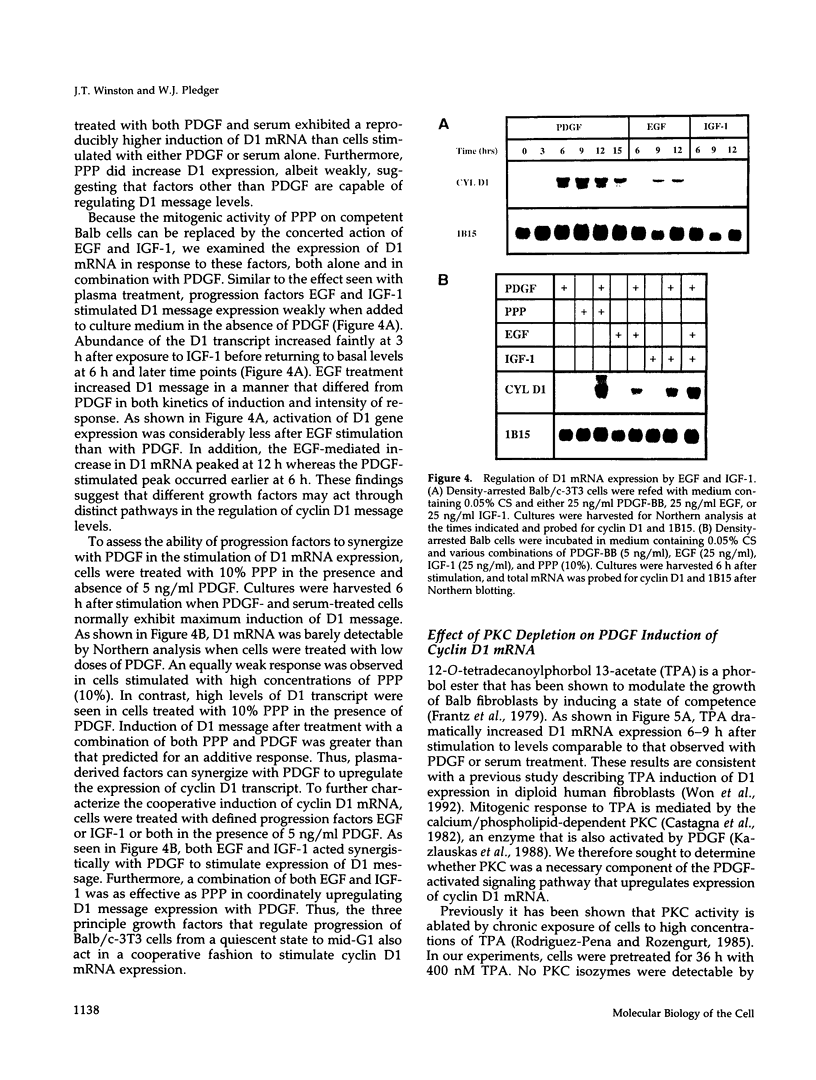
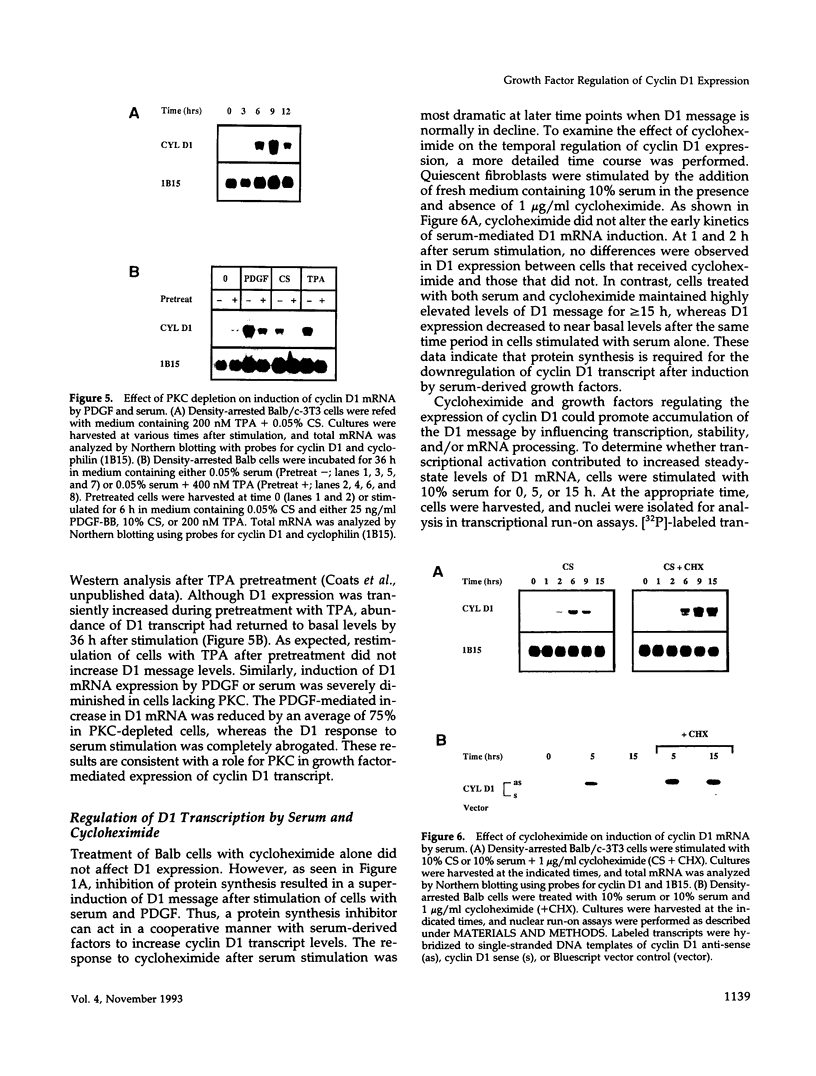
Overexpression of the cyclin D1/PRAD1 oncogene has been observed in a number of tumorigenic cell lines, suggesting that regulation of D1 expression may represent an important step in the control of cellular proliferation. We have examined the mRNA expression of cyclin D1, as well as two related D-type cyclins, D2 and D3, in response to defined growth factors that control the growth of Balb/c-3T3 fibroblasts. Transcripts for all three D-type cyclins were expressed during the G1 phase of the Balb cell cycle, however only D1 and D3 exhibited periodic induction. Although redundantly expressed, message levels of cyclin D1 and D3 were differentially regulated in regard to kinetics of induction; a modest increase in D3 mRNA was detected near the G1/S boundary, 12 h after serum stimulation of quiescent cells, while abundance of D1 transcript increased 20 to 30-fold, peaking 6 h after addition of serum. Factors such as platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) that induce competence formation in Balb cells, increased D1 message and protein levels to the same extent as serum but did not affect expression of cyclin D3 and did not stimulate entry into S phase. Progression factors contained within platelet-poor plasma stimulated D1 expression only weakly but acted synergistically with low concentrations of PDGF to increase D1 mRNA to maximum levels. Depletion of protein kinase C severely reduced the ability of PDGF and serum to induce D1 mRNA. PDGF- and serum-mediated elevation of steady-state D1 message levels was in part because of a transcriptional activation of the D1 gene that was independent of protein synthesis. However, protein synthesis was required 3-4 h after serum stimulation for the shut down of D1 transcription leading to the normal decline in message levels after peak induction. Our results indicate that overexpression of cyclin D1 message may result from a disruption of negative regulatory events that repress D1 transcription.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antoniades H. N., Scher C. D. Radioimmunoassay of a human serum growth factor for Balb/c-3T3 cells: derivation from platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):1973–1977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldin V., Lukas J., Marcote M. J., Pagano M., Draetta G. Cyclin D1 is a nuclear protein required for cell cycle progression in G1. Genes Dev. 1993 May;7(5):812–821. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.5.812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen-Pope D. F., Hart C. E., Seifert R. A. Sera and conditioned media contain different isoforms of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) which bind to different classes of PDGF receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2502–2508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Lee W. M., Williams P. W., Giels G. M., Williams L. T. c-myc gene expression is stimulated by agents that activate protein kinase C and does not account for the mitogenic effect of PDGF. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R. DAF1, a mutant gene affecting size control, pheromone arrest, and cell cycle kinetics of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4675–4684. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielson P. E., Forss-Petter S., Brow M. A., Calavetta L., Douglass J., Milner R. J., Sutcliffe J. G. p1B15: a cDNA clone of the rat mRNA encoding cyclophilin. DNA. 1988 May;7(4):261–267. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drozdoff V., Pledger W. J. Cellular response to platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-AB after down-regulation of PDGF alpha-receptors. Evidence that functional binding does not require alpha-receptors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17165–17172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewen M. E., Sluss H. K., Sherr C. J., Matsushime H., Kato J., Livingston D. M. Functional interactions of the retinoblastoma protein with mammalian D-type cyclins. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):487–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90136-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frantz C. N., Stiles C. D., Scher C. D. The tumor promoter 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate enhances the proliferative response of Balb/c-3T3 cells to hormonal growth factors. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Sep;100(3):413–424. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadwiger J. A., Wittenberg C., Richardson H. E., de Barros Lopes M., Reed S. I. A family of cyclin homologs that control the G1 phase in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6255–6259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington M. A., Falkenburg J. H., Daub R., Broxmeyer H. E. Effect of myogenic and adipogenic differentiation on expression of colony-stimulating factor genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4948–4952. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Sequential function of gene products relative to DNA synthesis in the yeast cell cycle. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 15;104(4):803–817. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90183-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P. W., Mittnacht S., Dulic V., Arnold A., Reed S. I., Weinberg R. A. Regulation of retinoblastoma protein functions by ectopic expression of human cyclins. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):993–1006. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90249-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen-Dürr P., Meichle A., Steiner P., Pagano M., Finke K., Botz J., Wessbecher J., Draetta G., Eilers M. Differential modulation of cyclin gene expression by MYC. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3685–3689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J., Matsushime H., Hiebert S. W., Ewen M. E., Sherr C. J. Direct binding of cyclin D to the retinoblastoma gene product (pRb) and pRb phosphorylation by the cyclin D-dependent kinase CDK4. Genes Dev. 1993 Mar;7(3):331–342. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.3.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Bowen-Pope D., Seifert R., Hart C. E., Cooper J. A. Different effects of homo- and heterodimers of platelet-derived growth factor A and B chains on human and mouse fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3727–3735. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03256.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff A., Cross F., Fisher A., Schumacher J., Leguellec K., Philippe M., Roberts J. M. Human cyclin E, a new cyclin that interacts with two members of the CDC2 gene family. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1217–1228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90044-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammie G. A., Fantl V., Smith R., Schuuring E., Brookes S., Michalides R., Dickson C., Arnold A., Peters G. D11S287, a putative oncogene on chromosome 11q13, is amplified and expressed in squamous cell and mammary carcinomas and linked to BCL-1. Oncogene. 1991 Mar;6(3):439–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau L. F., Nathans D. Expression of a set of growth-related immediate early genes in BALB/c 3T3 cells: coordinate regulation with c-fos or c-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1182–1186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leof E. B., Wharton W., van Wyk J. J., Pledger W. J. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) and somatomedin C regulate G1 progression in competent BALB/c-3T3 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Sep;141(1):107–115. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew D. J., Dulić V., Reed S. I. Isolation of three novel human cyclins by rescue of G1 cyclin (Cln) function in yeast. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1197–1206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90042-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushime H., Ewen M. E., Strom D. K., Kato J. Y., Hanks S. K., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J. Identification and properties of an atypical catalytic subunit (p34PSK-J3/cdk4) for mammalian D type G1 cyclins. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):323–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90360-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushime H., Roussel M. F., Ashmun R. A., Sherr C. J. Colony-stimulating factor 1 regulates novel cyclins during the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):701–713. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90101-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motokura T., Bloom T., Kim H. G., Jüppner H., Ruderman J. V., Kronenberg H. M., Arnold A. A novel cyclin encoded by a bcl1-linked candidate oncogene. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):512–515. doi: 10.1038/350512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash R., Tokiwa G., Anand S., Erickson K., Futcher A. B. The WHI1+ gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae tethers cell division to cell size and is a cyclin homolog. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4335–4346. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03332.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P., Bissett Y. Gene required in G1 for commitment to cell cycle and in G2 for control of mitosis in fission yeast. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):558–560. doi: 10.1038/292558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson J. E., Winston J. T., Whitlock J. A., Pledger W. J. Cell cycle-dependent gene expression in V point-arrested BALB/c-3T3 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1993 Feb;154(2):333–342. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041540217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. G1 events and regulation of cell proliferation. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):603–608. doi: 10.1126/science.2683075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pledger W. J., Stiles C. D., Antoniades H. N., Scher C. D. Induction of DNA synthesis in BALB/c 3T3 cells by serum components: reevaluation of the commitment process. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4481–4485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid B. J., Hartwell L. H. Regulation of mating in the cell cycle of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1977 Nov;75(2 Pt 1):355–365. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson H. E., Wittenberg C., Cross F., Reed S. I. An essential G1 function for cyclin-like proteins in yeast. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1127–1133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90768-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Pena A., Rozengurt E. Disappearance of Ca2+-sensitive, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase activity in phorbol ester-treated 3T3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):1053–1059. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg C. L., Kim H. G., Shows T. B., Kronenberg H. M., Arnold A. Rearrangement and overexpression of D11S287E, a candidate oncogene on chromosome 11q13 in benign parathyroid tumors. Oncogene. 1991 Mar;6(3):449–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles C. D., Isberg R. R., Pledger W. J., Antoniades H. N., Scher C. D. Control of the Balb/c-3T3 cell cycle by nutrients and serum factors: analysis using platelet-derived growth factor and platelet-poor plasma. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Jun;99(3):395–405. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040990314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton W. Hormonal regulation of discrete portions of the cell cycle: commitment to DNA synthesis is commitment to cellular division. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Dec;117(3):423–429. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041170318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Withers D. A., Harvey R. C., Faust J. B., Melnyk O., Carey K., Meeker T. C. Characterization of a candidate bcl-1 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4846–4853. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittenberg C., Sugimoto K., Reed S. I. G1-specific cyclins of S. cerevisiae: cell cycle periodicity, regulation by mating pheromone, and association with the p34CDC28 protein kinase. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):225–237. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90361-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Won K. A., Xiong Y., Beach D., Gilman M. Z. Growth-regulated expression of D-type cyclin genes in human diploid fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9910–9914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Connolly T., Futcher B., Beach D. Human D-type cyclin. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):691–699. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90100-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]