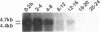Abstract
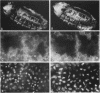
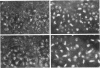
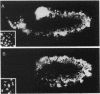
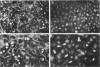
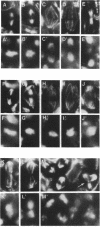
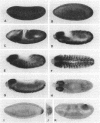
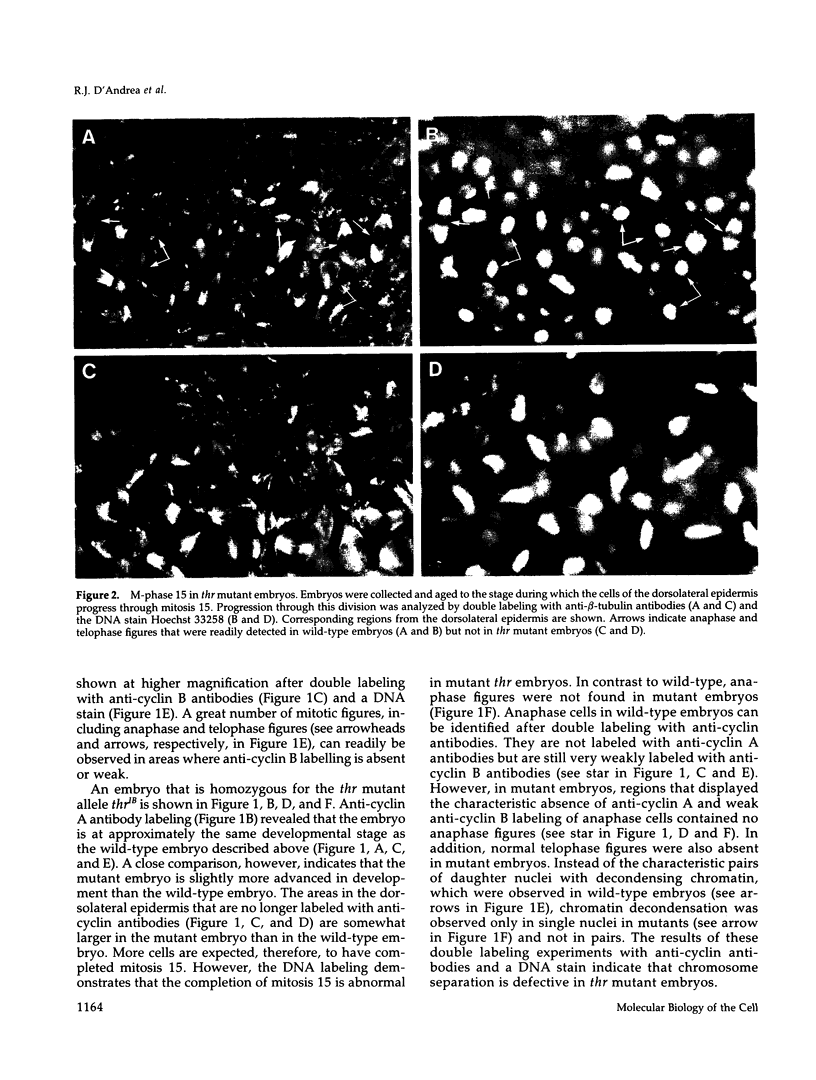
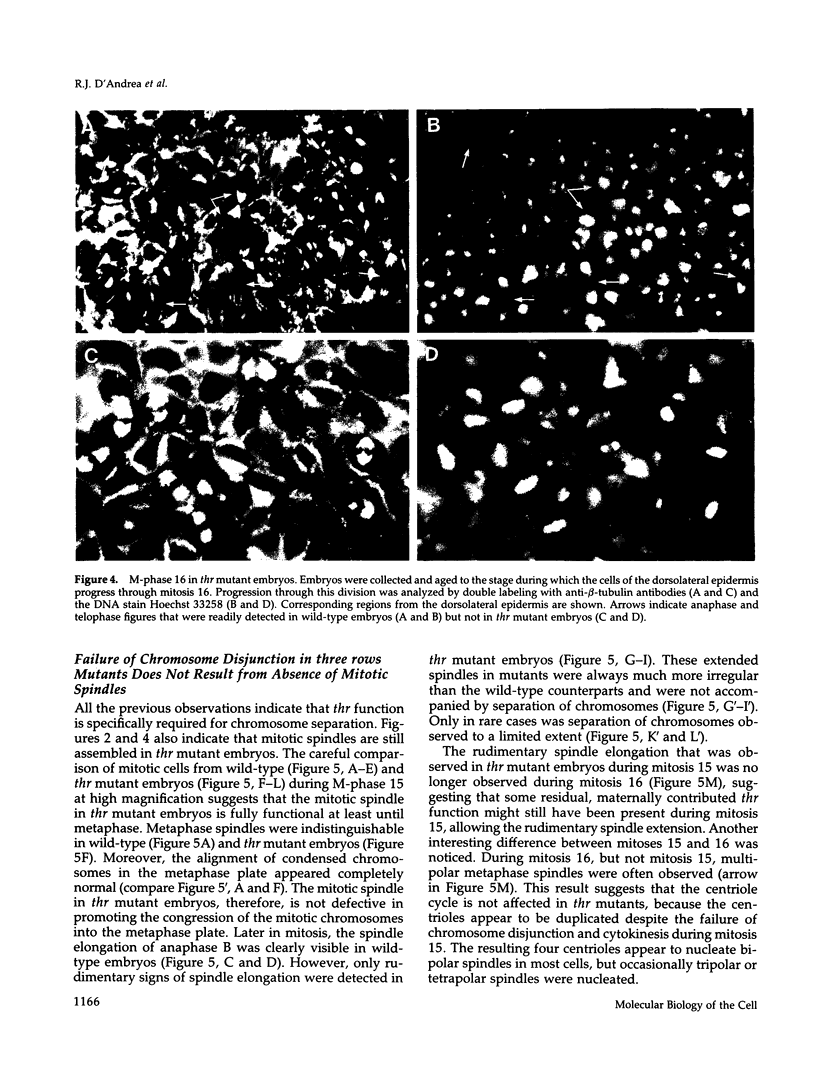
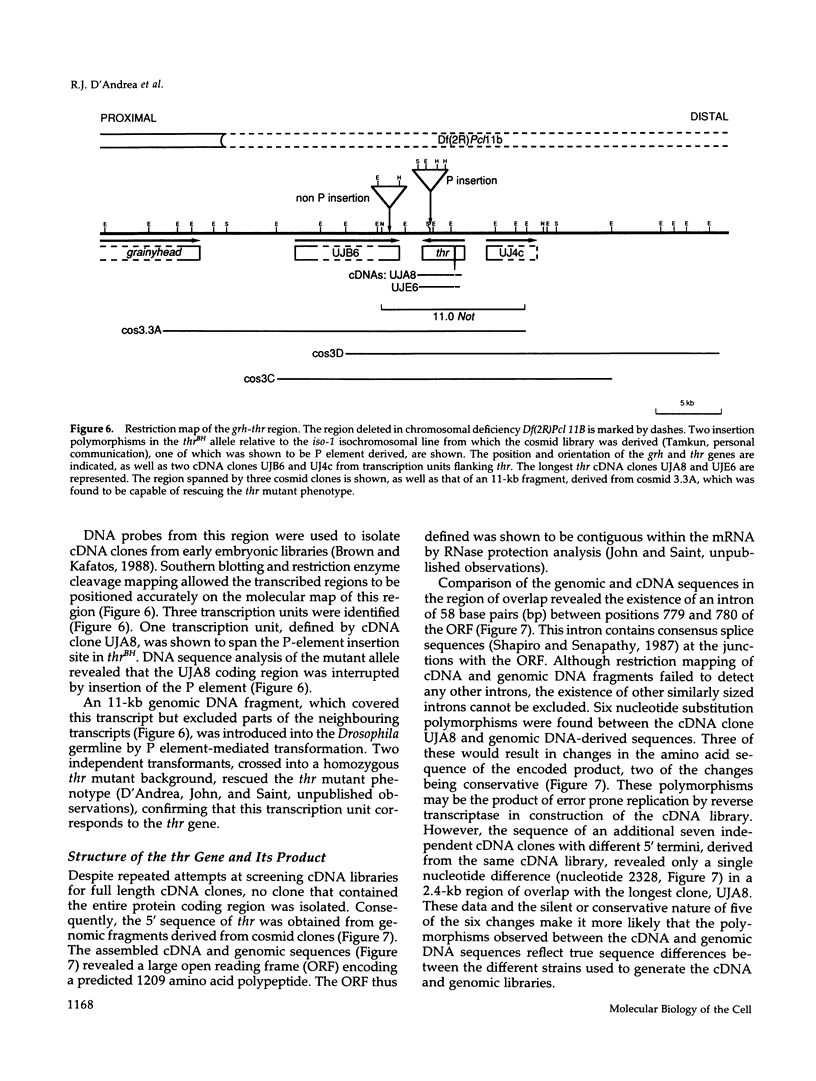
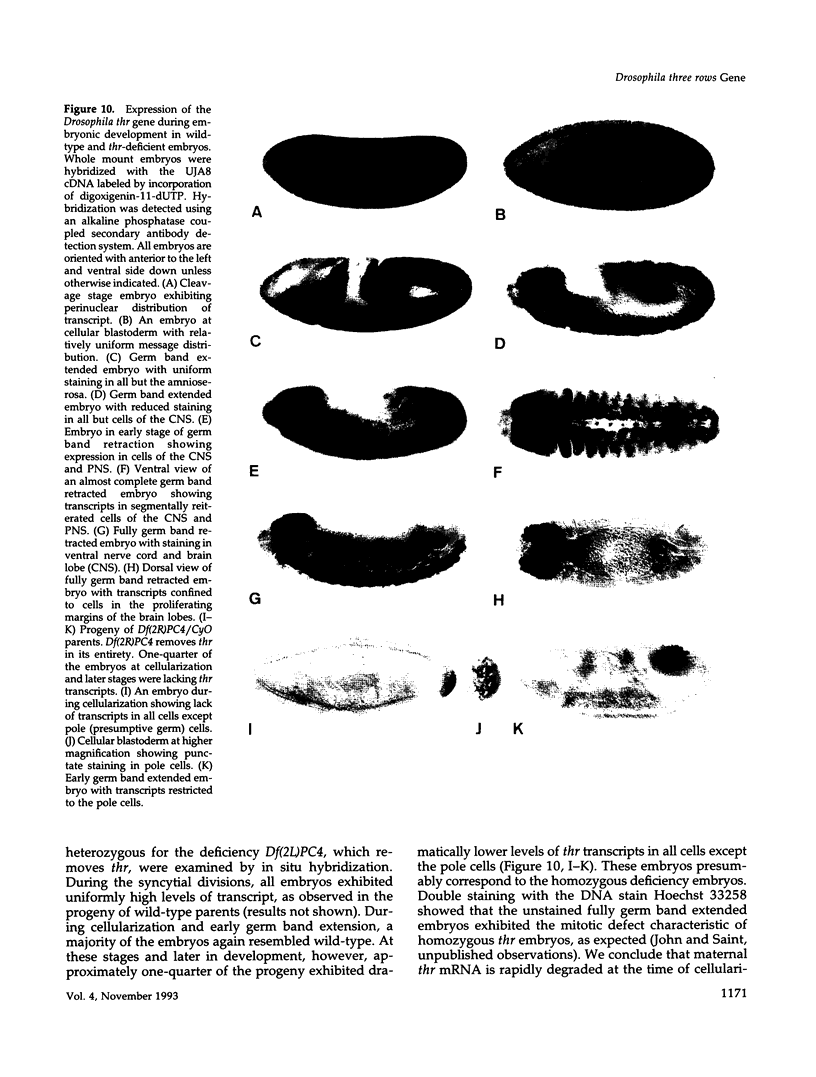
Zygotic expression of the three rows (thr) gene of Drosophila melanogaster is required for normal cell proliferation during embryogenesis. Mitotic defects in thr mutant embryos begin during mitosis 15, and all subsequent divisions are disrupted. Chromosome disjunction and consequently cytokinesis fail during these defective mitoses, although the initial mitotic processes (chromosome condensation, spindle assembly, metaphase plate formation, and cyclin degradation) are not affected. Despite the failure of chromosome disjunction and cytokinesis, later mitotic events (chromosome decondensation) and subsequent cell cycle progression continue. The thr gene has been isolated and shown to encode a 1209 amino acid protein that shares no extended sequence similarity with known proteins. thr mRNA is present as maternal mRNA that degrades at the time of cellularization. At this and all subsequent times during embryogenesis, zygotic expression correlates with mitotic proliferation. These observations, together with the observation that the zygotic phenotype of thr mutant embryos is influenced by the maternal genotype, suggest that the embryonic phenotype results from exhaustion of the maternal thr contribution and does not reflect a developmentally restricted requirement for thr function. Our results indicate that the novel thr product is required specifically for chromosome disjunction during all mitoses.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray S. J., Kafatos F. C. Developmental function of Elf-1: an essential transcription factor during embryogenesis in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1672–1683. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. H., Kafatos F. C. Functional cDNA libraries from Drosophila embryos. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 20;203(2):425–437. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchenau P., Saumweber H., Arndt-Jovin D. J. Consequences of topoisomerase II inhibition in early embryogenesis of Drosophila revealed by in vivo confocal laser scanning microscopy. J Cell Sci. 1993 Apr;104(Pt 4):1175–1185. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104.4.1175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalby B., Glover D. M. 3' non-translated sequences in Drosophila cyclin B transcripts direct posterior pole accumulation late in oogenesis and peri-nuclear association in syncytial embryos. Development. 1992 Aug;115(4):989–997. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.4.989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Laskey R. A. Nuclear targeting sequences--a consensus? Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Dec;16(12):478–481. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90184-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombrádi V., Axton J. M., Glover D. M., Cohen P. T. Molecular cloning and chromosomal localization of a novel Drosophila protein phosphatase. FEBS Lett. 1989 Apr 24;247(2):391–395. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81377-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar B. A., Kiehle C. P., Schubiger G. Cell cycle control by the nucleo-cytoplasmic ratio in early Drosophila development. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):365–372. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90771-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar B. A., O'Farrell P. H. Genetic control of cell division patterns in the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):177–187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90183-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar B. A., O'Farrell P. H. The three postblastoderm cell cycles of Drosophila embryogenesis are regulated in G2 by string. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):469–480. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90012-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatti M., Baker B. S. Genes controlling essential cell-cycle functions in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):438–453. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hime G., Saint R. Zygotic expression of the pebble locus is required for cytokinesis during the postblastoderm mitoses of Drosophila. Development. 1992 Jan;114(1):165–171. doi: 10.1242/dev.114.1.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Hiraoka Y., Yanagida M. A temperature-sensitive mutation of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe gene nuc2+ that encodes a nuclear scaffold-like protein blocks spindle elongation in mitotic anaphase. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1171–1183. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Kinoshita N., Morikawa K., Yanagida M. Snap helix with knob and hole: essential repeats in S. pombe nuclear protein nuc2+. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):319–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90746-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karr T. L., Alberts B. M. Organization of the cytoskeleton in early Drosophila embryos. J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;102(4):1494–1509. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.4.1494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner C. F., O'Farrell P. H. Expression and function of Drosophila cyclin A during embryonic cell cycle progression. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):957–968. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90629-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner C. F., O'Farrell P. H. The roles of Drosophila cyclins A and B in mitotic control. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):535–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90535-m. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell K. L., Osmani A. H., Osmani S. A., Morris N. R. bimA encodes a member of the tetratricopeptide repeat family of proteins and is required for the completion of mitosis in Aspergillus nidulans. J Cell Sci. 1991 Aug;99(Pt 4):711–719. doi: 10.1242/jcs.99.4.711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare K., Rubin G. M. Structures of P transposable elements and their sites of insertion and excision in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. Poly(A) signals. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):671–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90495-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff J. W., Whitfield W. G., Glover D. M. Two distinct mechanisms localise cyclin B transcripts in syncytial Drosophila embryos. Development. 1990 Dec;110(4):1249–1261. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.4.1249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S., Wells R., Rechsteiner M. Amino acid sequences common to rapidly degraded proteins: the PEST hypothesis. Science. 1986 Oct 17;234(4774):364–368. doi: 10.1126/science.2876518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M. B., Senapathy P. RNA splice junctions of different classes of eukaryotes: sequence statistics and functional implications in gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7155–7174. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearn A., Rice T., Garen A., Gehring W. Imaginal disc abnormalities in lethal mutants of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2594–2598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Boguski M. S., Goebl M., Hieter P. A repeating amino acid motif in CDC23 defines a family of proteins and a new relationship among genes required for mitosis and RNA synthesis. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):307–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90745-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. V., Orr-Weaver T. L. The regulation of the cell cycle during Drosophila embryogenesis: the transition to polyteny. Development. 1991 Aug;112(4):997–1008. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.4.997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. A new computer method for the storage and manipulation of DNA gel reading data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3673–3694. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Pfeifle C. A non-radioactive in situ hybridization method for the localization of specific RNAs in Drosophila embryos reveals translational control of the segmentation gene hunchback. Chromosoma. 1989 Aug;98(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00291041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]