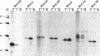
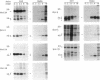
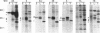Abstract
Members of the Wnt gene family are proposed to function in both normal development and differentiation as well as in mammary tumorigenesis. To understand the function of Wnt proteins in these two processes, we present here a biochemical characterization of seven Wnt family members. For these studies, AtT-20 cells, a neuroendocrine cell line previously shown to efficiently process and secrete Wnt-1, was transfected with expression vectors encoding Wnt family members. All of the newly characterized Wnt proteins are glycosylated, secreted proteins that are tightly associated with the cell surface or extracellular matrix. We have also identified native Wnt proteins in retinoic acid-treated P19 embryonal carcinoma cells, and they exhibit the same biochemical characteristics as the recombinant proteins. These data suggest that Wnt family members function in cell to cell signaling in a fashion similar to Wnt-1.
Full text
PDF

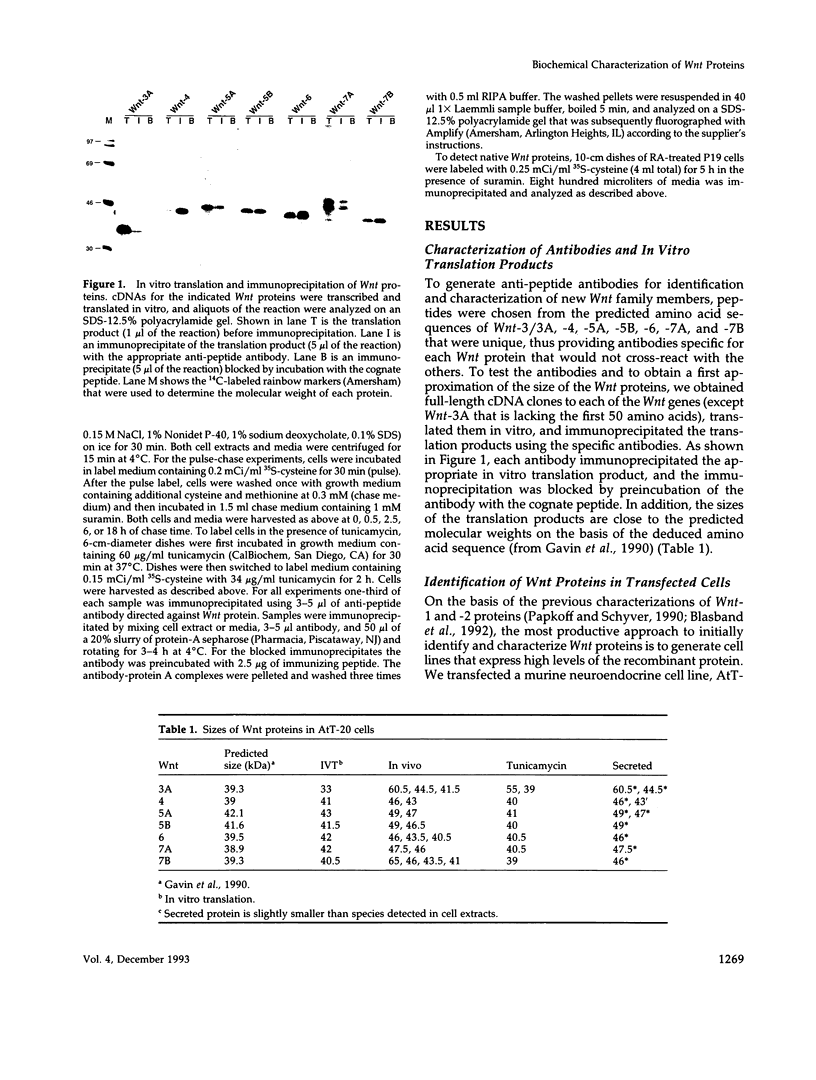
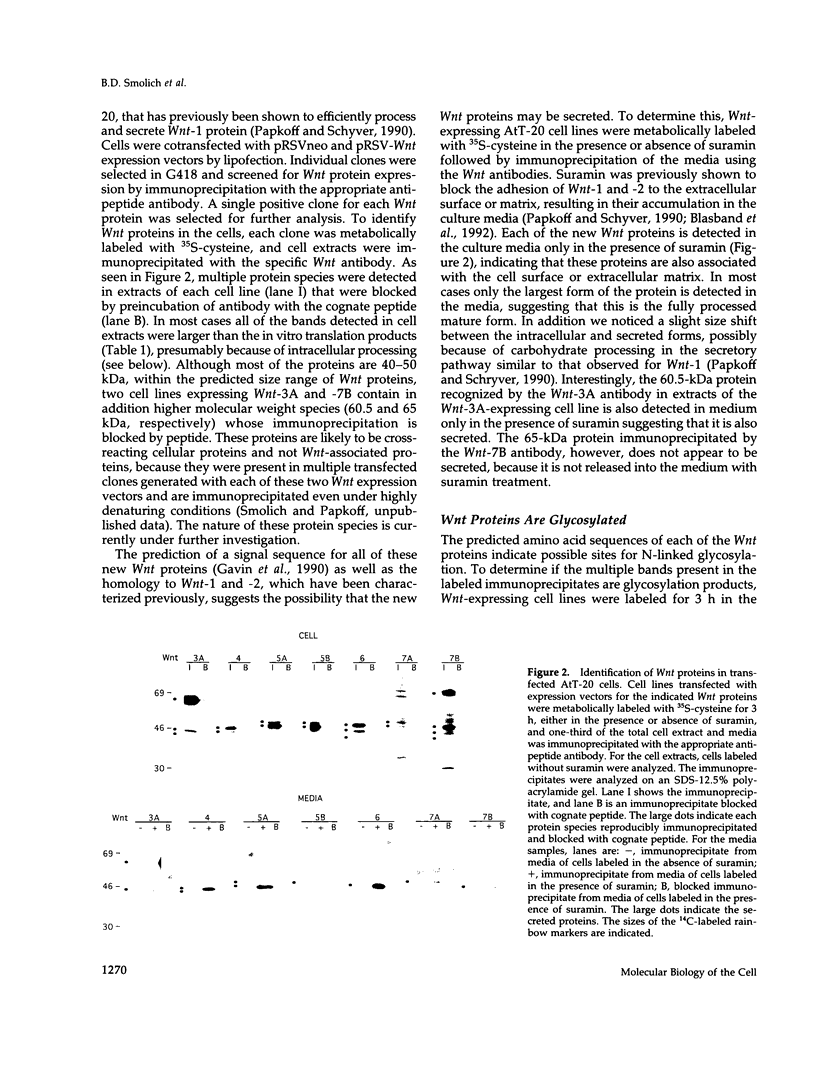





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blasband A., Schryver B., Papkoff J. The biochemical properties and transforming potential of human Wnt-2 are similar to Wnt-1. Oncogene. 1992 Jan;7(1):153–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley R. S., Brown A. M. The proto-oncogene int-1 encodes a secreted protein associated with the extracellular matrix. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1569–1575. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Papkoff J., Fung Y. K., Shackleford G. M., Varmus H. E. Identification of protein products encoded by the proto-oncogene int-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):3971–3977. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.3971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Wildin R. S., Prendergast T. J., Varmus H. E. A retrovirus vector expressing the putative mammary oncogene int-1 causes partial transformation of a mammary epithelial cell line. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1001–1009. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90699-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christian J. L., McMahon J. A., McMahon A. P., Moon R. T. Xwnt-8, a Xenopus Wnt-1/int-1-related gene responsive to mesoderm-inducing growth factors, may play a role in ventral mesodermal patterning during embryogenesis. Development. 1991 Apr;111(4):1045–1055. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.4.1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg L. M., Ingham P. W., Brown A. M. Cloning and characterization of a novel Drosophila Wnt gene, Dwnt-5, a putative downstream target of the homeobox gene distal-less. Dev Biol. 1992 Nov;154(1):73–83. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90049-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin B. J., McMahon A. P. Differential regulation of the Wnt gene family during pregnancy and lactation suggests a role in postnatal development of the mammary gland. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2418–2423. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin B. J., McMahon J. A., McMahon A. P. Expression of multiple novel Wnt-1/int-1-related genes during fetal and adult mouse development. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2319–2332. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González F., Swales L., Bejsovec A., Skaer H., Martinez Arias A. Secretion and movement of wingless protein in the epidermis of the Drosophila embryo. Mech Dev. 1991 Aug;35(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90040-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jue S. F., Bradley R. S., Rudnicki J. A., Varmus H. E., Brown A. M. The mouse Wnt-1 gene can act via a paracrine mechanism in transformation of mammary epithelial cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):321–328. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason J. O., Kitajewski J., Varmus H. E. Mutational analysis of mouse Wnt-1 identifies two temperature-sensitive alleles and attributes of Wnt-1 protein essential for transformation of a mammary cell line. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 May;3(5):521–533. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.5.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon A. P., Bradley A. The Wnt-1 (int-1) proto-oncogene is required for development of a large region of the mouse brain. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1073–1085. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90385-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon A. P., Moon R. T. Ectopic expression of the proto-oncogene int-1 in Xenopus embryos leads to duplication of the embryonic axis. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1075–1084. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90506-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusse R., Varmus H. E. Many tumors induced by the mouse mammary tumor virus contain a provirus integrated in the same region of the host genome. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):99–109. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90409-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusse R., Varmus H. E. Wnt genes. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1073–1087. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90630-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson D. J., Christian J. L., Moon R. T. Effect of wnt-1 and related proteins on gap junctional communication in Xenopus embryos. Science. 1991 May 24;252(5009):1173–1176. doi: 10.1126/science.252.5009.1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papkoff J., Brown A. M., Varmus H. E. The int-1 proto-oncogene products are glycoproteins that appear to enter the secretory pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):3978–3984. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.3978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papkoff J. Inducible overexpression and secretion of int-1 protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3377–3384. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papkoff J., Schryver B. Secreted int-1 protein is associated with the cell surface. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2723–2730. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijsewijk F., Schuermann M., Wagenaar E., Parren P., Weigel D., Nusse R. The Drosophila homolog of the mouse mammary oncogene int-1 is identical to the segment polarity gene wingless. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijsewijk F., van Deemter L., Wagenaar E., Sonnenberg A., Nusse R. Transfection of the int-1 mammary oncogene in cuboidal RAC mammary cell line results in morphological transformation and tumorigenicity. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):127–131. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04729.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelink H., Wagenaar E., Lopes da Silva S., Nusse R. Wnt-3, a gene activated by proviral insertion in mouse mammary tumors, is homologous to int-1/Wnt-1 and is normally expressed in mouse embryos and adult brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4519–4523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J., Gennissen A., Nusse R. Isolation and expression of two novel Wnt/wingless gene homologues in Drosophila. Development. 1992 Jun;115(2):475–485. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.2.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackleford G. M., Varmus H. E. Expression of the proto-oncogene int-1 is restricted to postmeiotic male germ cells and the neural tube of mid-gestational embryos. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90665-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidow A. Diversification of the Wnt gene family on the ancestral lineage of vertebrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):5098–5102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.5098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. C., Harland R. M. Injected Xwnt-8 RNA acts early in Xenopus embryos to promote formation of a vegetal dorsalizing center. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):753–765. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90070-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokol S., Christian J. L., Moon R. T., Melton D. A. Injected Wnt RNA induces a complete body axis in Xenopus embryos. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90069-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St-Arnaud R., Craig J., McBurney M. W., Papkoff J. The int-1 proto-oncogene is transcriptionally activated during neuroectodermal differentiation of P19 mouse embryonal carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 1989 Sep;4(9):1077–1080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Targeted disruption of the murine int-1 proto-oncogene resulting in severe abnormalities in midbrain and cerebellar development. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):847–850. doi: 10.1038/346847a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Musci T. S., Neumann P. E., Capecchi M. R. Swaying is a mutant allele of the proto-oncogene Wnt-1. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):969–976. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90369-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto A. S., Grosschedl R., Guzman R. C., Parslow T., Varmus H. E. Expression of the int-1 gene in transgenic mice is associated with mammary gland hyperplasia and adenocarcinomas in male and female mice. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):619–625. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90220-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wainwright B. J., Scambler P. J., Stanier P., Watson E. K., Bell G., Wicking C., Estivill X., Courtney M., Boue A., Pedersen P. S. Isolation of a human gene with protein sequence similarity to human and murine int-1 and the Drosophila segment polarity mutant wingless. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1743–1748. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03003.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. G., Bailes J. A., McMahon A. P. Expression of the proto-oncogene int-1 is restricted to specific neural cells in the developing mouse embryo. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90664-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolda S. L., Moody C. J., Moon R. T. Overlapping expression of Xwnt-3A and Xwnt-1 in neural tissue of Xenopus laevis embryos. Dev Biol. 1993 Jan;155(1):46–57. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]