Abstract
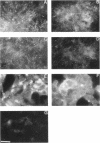
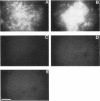
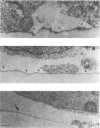
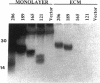
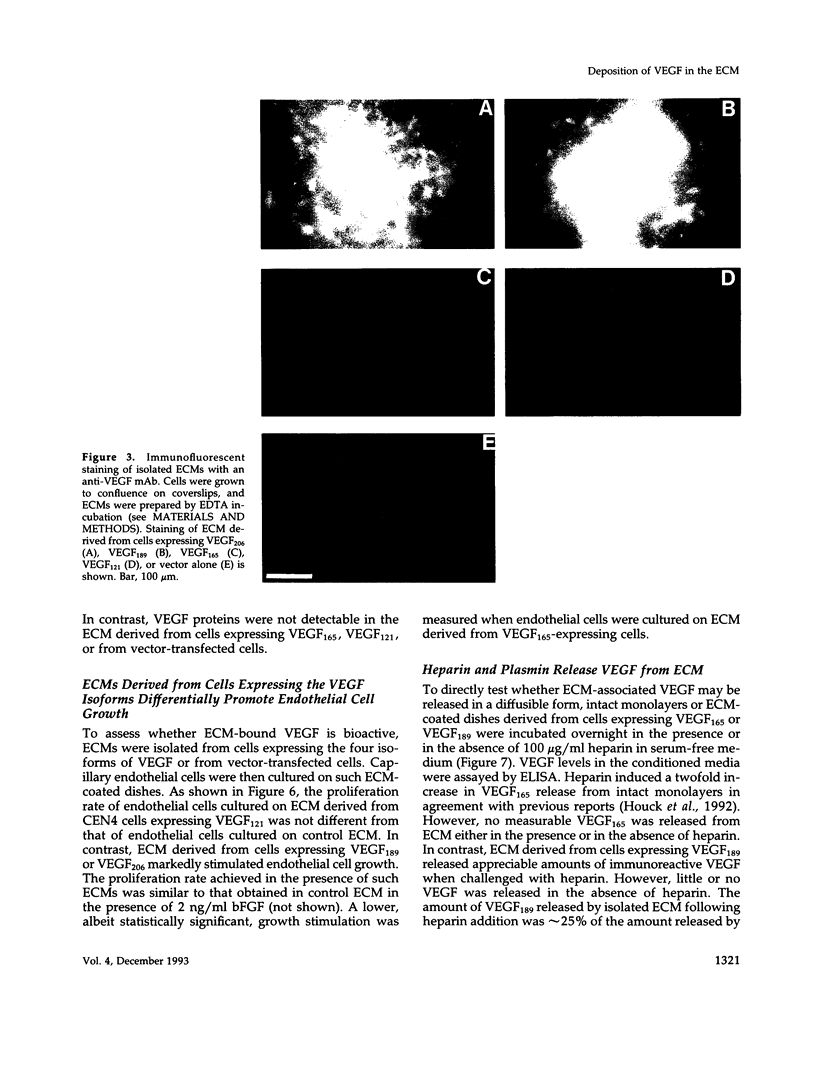
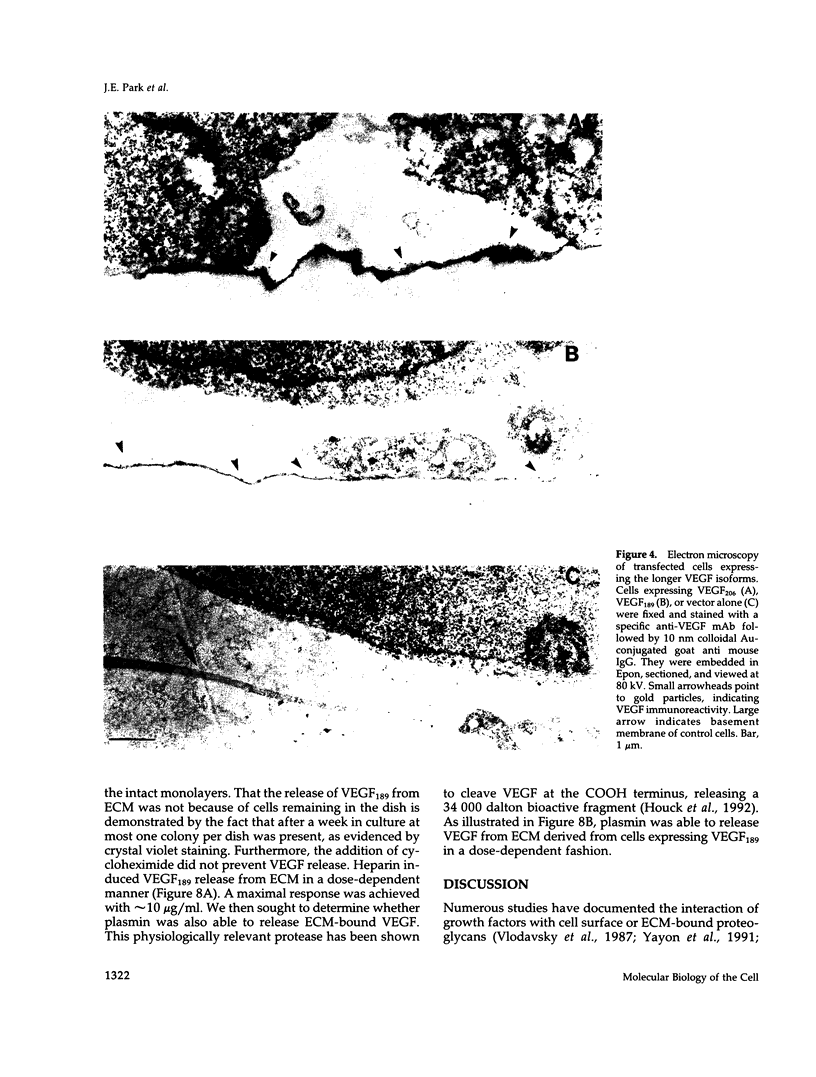
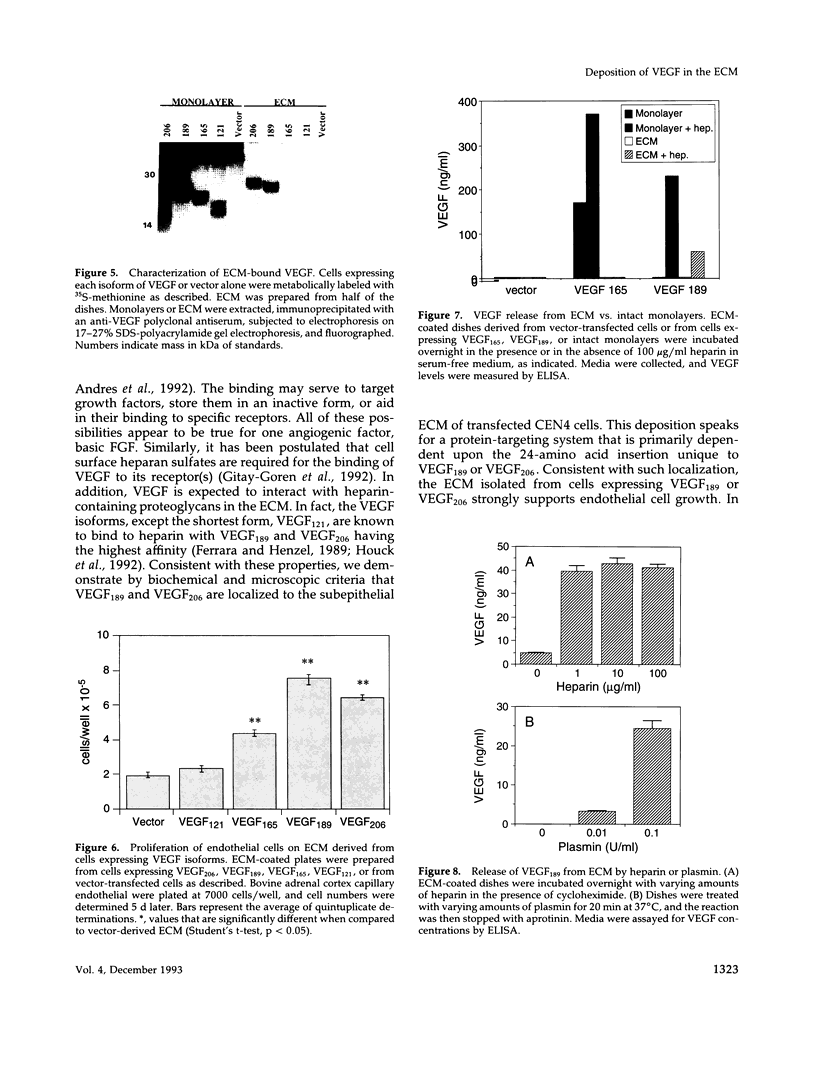
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)mRNA undergoes alternative splicing events that generate four different homodimeric isoforms, VEGF121, VEGF165, VEGF189, or VEGF206. VEGF121 is a nonheparin-binding acidic protein, which is freely diffusible. The longer forms, VEGF189 or VEGF206, are highly basic proteins tightly bound to extracellular heparin-containing proteoglycans. VEGF165 has intermediate properties. To determine the localization of VEGF isoforms, transfected human embryonic kidney CEN4 cells expressing VEGF165, VEGF189, or VEGF206 were stained by immunofluorescence with a specific monoclonal antibody. The staining was found in patches and streaks suggestive of extracellular matrix (ECM). VEGF165 was observed largely in Golgi apparatus-like structures. Immunogold labeling of cells expressing VEGF189 or VEGF206 revealed that the staining was localized to the subepithelial ECM. VEGF associated with the ECM was bioactive, because endothelial cells cultured on ECM derived from cells expressing VEGF189 or VEGF206 were markedly stimulated to proliferate. In addition, ECM-bound VEGF can be released into a soluble and bioactive form by heparin or plasmin. ECM-bound VEGF189 and VEGF206 have molecular masses consistent with the intact polypeptides. The ECM may represent an important source of VEGF and angiogenic potential.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham J. A., Mergia A., Whang J. L., Tumolo A., Friedman J., Hjerrild K. A., Gospodarowicz D., Fiddes J. C. Nucleotide sequence of a bovine clone encoding the angiogenic protein, basic fibroblast growth factor. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):545–548. doi: 10.1126/science.2425435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler R. R., Brenner C. A., Werb Z. Expression of extracellular matrix-degrading metalloproteinases and metalloproteinase inhibitors is developmentally regulated during endoderm differentiation of embryonal carcinoma cells. Development. 1990 Sep;110(1):211–220. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.1.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andres J. L., DeFalcis D., Noda M., Massagué J. Binding of two growth factor families to separate domains of the proteoglycan betaglycan. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):5927–5930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andres J. L., Stanley K., Cheifetz S., Massagué J. Membrane-anchored and soluble forms of betaglycan, a polymorphic proteoglycan that binds transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):3137–3145. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basilico C., Moscatelli D. The FGF family of growth factors and oncogenes. Adv Cancer Res. 1992;59:115–165. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60305-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassols A., Massagué J. Transforming growth factor beta regulates the expression and structure of extracellular matrix chondroitin/dermatan sulfate proteoglycans. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):3039–3045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berse B., Brown L. F., Van de Water L., Dvorak H. F., Senger D. R. Vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) gene is expressed differentially in normal tissues, macrophages, and tumors. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Feb;3(2):211–220. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breier G., Albrecht U., Sterrer S., Risau W. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor during embryonic angiogenesis and endothelial cell differentiation. Development. 1992 Feb;114(2):521–532. doi: 10.1242/dev.114.2.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly D. T., Heuvelman D. M., Nelson R., Olander J. V., Eppley B. L., Delfino J. J., Siegel N. R., Leimgruber R. M., Feder J. Tumor vascular permeability factor stimulates endothelial cell growth and angiogenesis. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1470–1478. doi: 10.1172/JCI114322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djakiew D., Pflug B., Delsite R., Lynch J. H., Onoda M. Density dependent polarized secretion of a prostatic epithelial cell line. Prostate. 1992;20(1):15–27. doi: 10.1002/pros.2990200104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara N., Henzel W. J. Pituitary follicular cells secrete a novel heparin-binding growth factor specific for vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jun 15;161(2):851–858. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92678-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara N., Houck K., Jakeman L., Leung D. W. Molecular and biological properties of the vascular endothelial growth factor family of proteins. Endocr Rev. 1992 Feb;13(1):18–32. doi: 10.1210/edrv-13-1-18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara N., Leung D. W., Cachianes G., Winer J., Henzel W. J. Purification and cloning of vascular endothelial growth factor secreted by pituitary folliculostellate cells. Methods Enzymol. 1991;198:391–405. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)98040-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. G., Chan D. C., Leder P. Transmembrane form of the kit ligand growth factor is determined by alternative splicing and is missing in the Sld mutant. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):1025–1035. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90326-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flenniken A. M., Williams B. R. Developmental expression of the endogenous TIMP gene and a TIMP-lacZ fusion gene in transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1094–1106. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M., Sasse J., Wadzinski M., Ingber D., Vlodavsky I. A heparin-binding angiogenic protein--basic fibroblast growth factor--is stored within basement membrane. Am J Pathol. 1988 Feb;130(2):393–400. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbisa S., Scagliotti G., Masiero L., Di Francesco C., Caenazzo C., Onisto M., Micela M., Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Liotta L. A. Correlation of serum metalloproteinase levels with lung cancer metastasis and response to therapy. Cancer Res. 1992 Aug 15;52(16):4548–4549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitay-Goren H., Soker S., Vlodavsky I., Neufeld G. The binding of vascular endothelial growth factor to its receptors is dependent on cell surface-associated heparin-like molecules. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6093–6098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon M. Y., Riley G. P., Watt S. M., Greaves M. F. Compartmentalization of a haematopoietic growth factor (GM-CSF) by glycosaminoglycans in the bone marrow microenvironment. 1987 Mar 26-Apr 1Nature. 326(6111):403–405. doi: 10.1038/326403a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houck K. A., Ferrara N., Winer J., Cachianes G., Li B., Leung D. W. The vascular endothelial growth factor family: identification of a fourth molecular species and characterization of alternative splicing of RNA. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Dec;5(12):1806–1814. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-12-1806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houck K. A., Leung D. W., Rowland A. M., Winer J., Ferrara N. Dual regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor bioavailability by genetic and proteolytic mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):26031–26037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakeman L. B., Armanini M., Phillips H. S., Ferrara N. Developmental expression of binding sites and messenger ribonucleic acid for vascular endothelial growth factor suggests a role for this protein in vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. Endocrinology. 1993 Aug;133(2):848–859. doi: 10.1210/endo.133.2.7688292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakeman L. B., Winer J., Bennett G. L., Altar C. A., Ferrara N. Binding sites for vascular endothelial growth factor are localized on endothelial cells in adult rat tissues. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jan;89(1):244–253. doi: 10.1172/JCI115568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandel J., Bossy-Wetzel E., Radvanyi F., Klagsbrun M., Folkman J., Hanahan D. Neovascularization is associated with a switch to the export of bFGF in the multistep development of fibrosarcoma. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1095–1104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90033-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. J., Li B., Houck K., Winer J., Ferrara N. The vascular endothelial growth factor proteins: identification of biologically relevant regions by neutralizing monoclonal antibodies. Growth Factors. 1992;7(1):53–64. doi: 10.3109/08977199209023937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. J., Li B., Winer J., Armanini M., Gillett N., Phillips H. S., Ferrara N. Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis suppresses tumour growth in vivo. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):841–844. doi: 10.1038/362841a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leto G., Gebbia N., Rausa L., Tumminello F. M. Cathepsin D in the malignant progression of neoplastic diseases (review). Anticancer Res. 1992 Jan-Feb;12(1):235–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. W., Cachianes G., Kuang W. J., Goeddel D. V., Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a secreted angiogenic mitogen. Science. 1989 Dec 8;246(4935):1306–1309. doi: 10.1126/science.2479986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Casillas F., Cheifetz S., Doody J., Andres J. L., Lane W. S., Massagué J. Structure and expression of the membrane proteoglycan betaglycan, a component of the TGF-beta receptor system. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):785–795. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J. Transforming growth factor-alpha. A model for membrane-anchored growth factors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21393–21396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Hogan B. L. Growth factor-regulated proteases and extracellular matrix remodeling during mammalian development. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1990;24:219–259. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60089-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean I. W., Nakane P. K. Periodate-lysine-paraformaldehyde fixative. A new fixation for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1077–1083. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignatti P., Tsuboi R., Robbins E., Rifkin D. B. In vitro angiogenesis on the human amniotic membrane: requirement for basic fibroblast growth factor-induced proteinases. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):671–682. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepper M. S., Ferrara N., Orci L., Montesano R. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) induces plasminogen activators and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in microvascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Dec 16;181(2):902–906. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91276-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peretz T., Antebi S. U., Beller U., Horowitz A. T., Fuks Z., Vlodavsky I. Maintenance on extracellular matrix and expression of heparanase activity by human ovarian carcinoma cells from biopsy specimens. Int J Cancer. 1990 Jun 15;45(6):1054–1060. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910450613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez C., Albert I., DeFay K., Zachariades N., Gooding L., Kriegler M. A nonsecretable cell surface mutant of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) kills by cell-to-cell contact. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):251–258. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90158-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips H. S., Hains J., Leung D. W., Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor is expressed in rat corpus luteum. Endocrinology. 1990 Aug;127(2):965–967. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-2-965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plouët J., Schilling J., Gospodarowicz D. Isolation and characterization of a newly identified endothelial cell mitogen produced by AtT-20 cells. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3801–3806. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08557.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raines E. W., Ross R. Compartmentalization of PDGF on extracellular binding sites dependent on exon-6-encoded sequences. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(2):533–543. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.2.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rathjen P. D., Toth S., Willis A., Heath J. K., Smith A. G. Differentiation inhibiting activity is produced in matrix-associated and diffusible forms that are generated by alternate promoter usage. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1105–1114. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90387-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkin D. B., Moscatelli D., Bizik J., Quarto N., Blei F., Dennis P., Flaumenhaft R., Mignatti P. Growth factor control of extracellular proteolysis. Cell Differ Dev. 1990 Dec 2;32(3):313–318. doi: 10.1016/0922-3371(90)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela O., Rifkin D. B. Release of basic fibroblast growth factor-heparan sulfate complexes from endothelial cells by plasminogen activator-mediated proteolytic activity. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):767–775. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreenath T., Matrisian L. M., Stetler-Stevenson W., Gattoni-Celli S., Pozzatti R. O. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase genes in transformed rat cell lines of high and low metastatic potential. Cancer Res. 1992 Sep 15;52(18):4942–4947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J., Borzillo G. V., Rettenmier C. W. Direct stimulation of cells expressing receptors for macrophage colony-stimulating factor (CSF-1) by a plasma membrane-bound precursor of human CSF-1. Blood. 1990 Oct 1;76(7):1308–1314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischer E., Mitchell R., Hartman T., Silva M., Gospodarowicz D., Fiddes J. C., Abraham J. A. The human gene for vascular endothelial growth factor. Multiple protein forms are encoded through alternative exon splicing. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):11947–11954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I., Eldor A., Haimovitz-Friedman A., Matzner Y., Ishai-Michaeli R., Lider O., Naparstek Y., Cohen I. R., Fuks Z. Expression of heparanase by platelets and circulating cells of the immune system: possible involvement in diapedesis and extravasation. Invasion Metastasis. 1992;12(2):112–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I., Folkman J., Sullivan R., Fridman R., Ishai-Michaeli R., Sasse J., Klagsbrun M. Endothelial cell-derived basic fibroblast growth factor: synthesis and deposition into subendothelial extracellular matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2292–2296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yayon A., Klagsbrun M., Esko J. D., Leder P., Ornitz D. M. Cell surface, heparin-like molecules are required for binding of basic fibroblast growth factor to its high affinity receptor. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):841–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90512-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]