Abstract
The objective of this stimulation study was to evaluate effect of simoidicity of the concentration–effect (C–E) relationship on the efficiency of population parameter estimation from sparse sampling and is a continuation of previous work that addressed the effect of sample size and number of samples on parameters estimation from sparse sampling for drugs with C–E relationship characterized by high sigmoidicity (γ > 5). The findings are based on observed C–E relationships for two drugs, octreotide and remifentanil, characterized by simple Emax and sigmoid Emax models (γ = ~2.5), respectively. For each model, C–E profiles (100 replicates of 100 subjects each) were simulated for several sampling designs, with four or five samples/individual randomly obtained from within sampling windows based on EC50-normalized plasma drug concentrations, PD parameters based on observed population mean values, and inter-individual and residual variability of 30% and 25%, respectively. The C–E profiles were fitted using non-linear mixed effect modeling with the first-order conditional estimation method; variability parameters were described by an exponential error model. The results showed that, for the sigmoid Emax model, designs with four or five samples reliably estimated the PD parameters (EC50, Emax, E0, and γ), whereas the five-sample design, with two samples in the 2–3 Emax region, provided in addition more reliable estimates of inter-individual variability; increasing the information content of the EC50 region was not critical as long as this region was covered by a single sample in the 0.5–1.5 EC50 window. For the simple Emax model, because of the shallower profile, enriching the EC50 region was more important. The impact of enrichment of appropriate regions for the two models can be explained based on the shape (sigmoidicity) of the concentration–effect relationships, with shallower C–E profiles requiring data enrichment in the EC50 region and steeper curves less so; in both cases, the Emax region needs to be adequately delineated, however. The results provide a general framework for population parameter estimation from sparse sampling in clinical trials when the underlying C–E profiles have different degrees of sigmoidicity.
Key words: clinical trials, PK-PD simulations, population PK-PD modeling, sparse sampling
INTRODUCTION
Population pharmacodynamic modeling is useful in assessing quantitative relationships between plasma drug concentrations, drug response, and patient covariates. In the learn and confirm paradigm of drug development, pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic (PK-PD) models can be developed in the early phase (phase 1/2a,b; learning) to gain an understanding of a drug’s behavior in terms of its concentration–effect (C–E) relationship, variability, etc., to make decisions regarding its future development. In the confirming part (i.e., phase 3), it is feasible to obtain only a few samples (sparse samples) from individual patients because of practical constraints.
The decision regarding the number of samples and timing of sample collection depends on the underlying PK and PD properties of a drug, as well as practical aspects related to implementation of PK sampling in clinical trials. We previously showed that, for a drug with a C–E profile characterized by a high Hill coefficient (γ > 5), it is possible to accurately and precisely estimate population PD parameters from sparse sampling (1). The reliability of PD and inter-individual variability parameters were not only dependent on the number of samples collected per individual but also on the sample size (number of individuals sampled) and the underlying variability in the parameters. It was demonstrated that four or five samples per individual, obtained from within pre-defined windows, were sufficient to provide accurate and precise estimates of almost all of the PD and variability parameters.
Because the sensitivity of the C–E profile is characterized by the steepness of the relationship (i.e., sigmoidicity), which can then influence the reliability of parameter estimates when only a few samples are obtained, the objective of the current paper was to evaluate the efficiency of population parameter estimation from sparse sampling for drugs with different degrees of sigmoidicity. This was evaluated by simulations based on observed C–E relationships for two drugs, octreotide (2), and remifentanil (3). The C–E relationship for octreotride was characterized by a simple Emax model and that for remifentanil by a sigmoid Emax model with moderate sigmoidicity (γ = 2.51). This evaluation and that published previously (1) would collectively be applicable for population PD parameter estimation of drugs with C–E profiles with varying degrees of sigmoidicity.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Pharmacodynamic Parameters
The reported population PD parameters of octreotide (2), based on insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) response, were E0 and Emax (expressed as percent of baseline) of 110 and 40, respectively, EC50 = 746 pg/mL, and γ = 1 (Eq. 1).
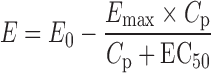 |
1 |
where E is the PD response, E0 is the baseline, Emax is the percentage of maximal decrease in IGF-1 concentration, Cp is octreotide plasma concentration, and EC50 is the plasma concentration of octreotide corresponding to 50% of the maximal effect.
For remifentanil (3), the reported PD parameters were (using electroencephalogram to measure the drug effect) E0 = 20 Hz, Emax = 5.62 Hz, EC50 = 11.2 ng/mL, and γ = 2.51 (Eq. 2).
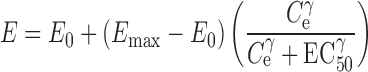 |
2 |
where E is the PD response. E0 is the measured baseline, Emax is the maximum measured effect, Ce is the apparent effect site concentration, EC50 is the concentration that produces 50% of the maximum effect, and γ is the steepness of the concentration–response relationship (sigmoidicity constant).
Plasma concentrations of octreotide and remifentanil were normalized to their EC50 (by using EC50 as the unit of concentration, viz., the concentration is a fraction or multiple of the EC50). Therefore, the findings can be generalized to other drugs with comparable concentration–response characteristics.
Sampling Designs
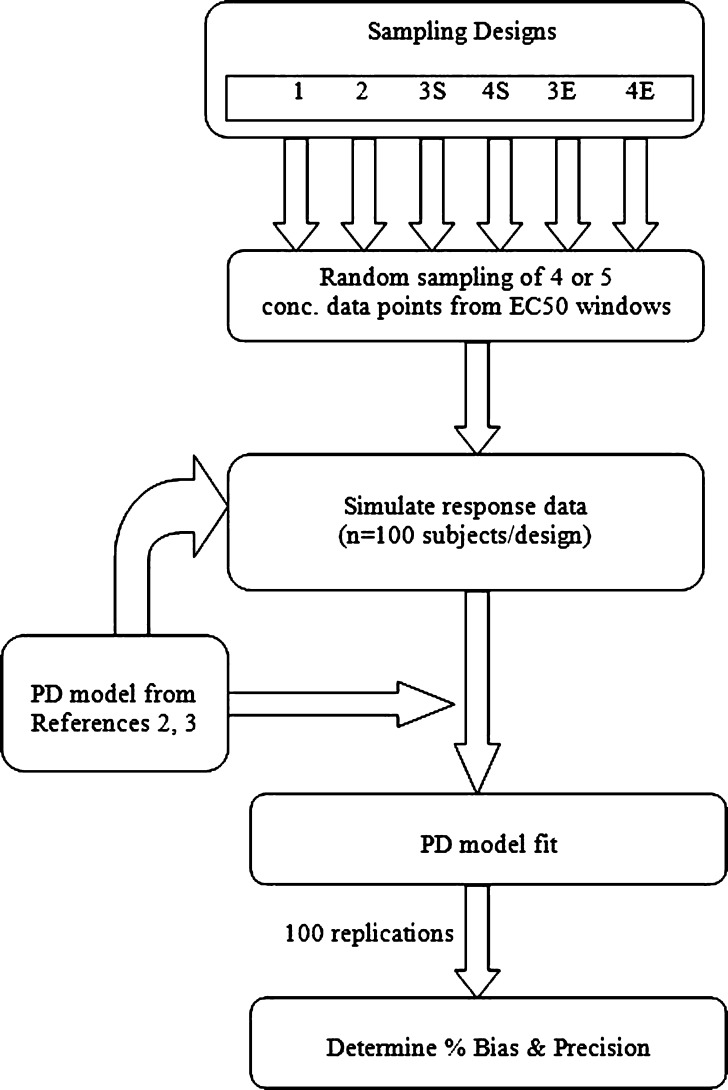
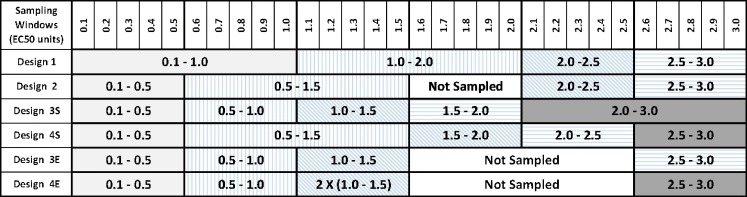
As shown in the schematic in Fig. 1, for each PD model, four sampling designs each with four or five concentration samples per individual obtained from sampling windows that were based on EC50 concentration units (Table I and Fig. 2) were evaluated. The concentration samples were randomly obtained from each sampling window using the random number generator in Excel. Design 1 was previously found to reliably estimate PD parameters from sparse sampling for a drug with a high hill coefficient (γ = 6.22) (1). Designs 1 and 2 were common to both drugs and encompassed concentrations that were threefold higher than the EC50 (i.e., in the Emax region), with four samples per individual (four sampling windows). Designs 3S and 4S, with five samples per individual (five sampling windows), were applied to the sigmoid Emax model, whereas designs 3E and 4E, with four and five samples per individual, respectively, were applied to the simple Emax model. For each design, 100 subjects were simulated, and this was repeated 100 times; therefore, evaluation of each of the designs was based on 40,000 or 50,000 concentration–effect pairs (i.e., four samples × 100 subjects × 100 replicates or five samples × 100 subjects × 100 replicates).
Fig. 1.
Simulation strategy for the evaluation of the designs for accuracy and precision
Table I.
Sampling Designs Evaluated for Estimation of Parameter Accuracy and Precision
| Design | Model | Model drug | Sampling windows (EC50 units)a | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |||
| 1 | Sigmoid E max | Remifentanil | 0.1–1 | 1–2 | 2–2.5 | 2.5–3 | NS |
| E max | Octreotide | ||||||
| 2 | Sigmoid E max | Remifentanil | 0.1–0.5 | 0.5–1.5 | 2–2.5 | 2.5–3 | NS |
| E max | Octreotide | ||||||
| 3S | Sigmoid E max | Remifentanil | 0.1–0.5 | 0.5–1 | 1–1.5 | 1.5–2 | 2–3 |
| 4S | Sigmoid E max | Remifentanil | 0.1–0.5 | 0.5–1.5 | 1.5–2 | 2–2.5 | 2.5–3 |
| 3E | E max | Octreotide | 0.1–0.5 | 0.5–1 | 1–1.5 | 2.5–3 | NS |
| 4E | E max | Octreotide | 0.1–0.5 | 0.5–1 | 1–1.5 | 1–1.5 | 2.5–3 |
NS not sampled
aRepresents sampling intervals in terms of EC50 units; for each design a single sample was obtained within each window
Fig. 2.
Sampling windows used for various investigated designs based on EC50 units. Designs 1, 2, 3S, and 4S were applied to the sigmoid E max model, and designs 1, 2, 3E, and 4E were applied to the E max model
Pharmacodynamic and Statistical Models
In the simulation experiments, a simple Emax model was used to describe the C–E relationship of octreotide, and a sigmoid Emax model was used for remifentanil; for both drugs, inter- and intra-individual variability were described by exponential error models, as described previously (1). For each drug, using the appropriate PD model and associated parameters summarized above, C–E profiles were simulated in individual subjects for the sampling designs summarized in Table I and Fig. 2. In these simulations, for each of the drugs, the PK model was not fitted separately. The individual response was calculated using PD parameters generated from a normal distribution with population mean values summarized above and coefficient of variation for inter-individual variability set at 30% (for all parameters). The coefficient of variation of the residual error (added to the response) was set at a moderate level of 25% (4). The concentration–effect profiles were simulated by nonlinear mixed effect modeling using NONMEM (Version V) (5), taking variability into consideration. A PRED subroutine (5) was used for the simulations. The first-order conditional estimation (without interaction) method in NONMEM was used to estimate the PD and variability parameters. This method provides more accurate and precise estimates of the variability parameters using the exponential error model than the first order method (5,6). The estimated parameters were EC50, Emax, E0 and γ (for the sigmoid Emax model), with their respective inter-individual variability, ωEC50, ωEmax, ωE0 and  (for the sigmoid Emax model), and residual error σ.
(for the sigmoid Emax model), and residual error σ.
Bias and Precision of Parameter Estimates
Each replicate of 100 individuals provided the population estimates of the PD and variability parameters, and the values from 100 replicates were used to estimate the accuracy (bias) and precision of the estimates using the percent prediction error (%PE), as follows (7):
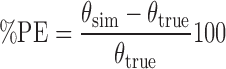 |
3 |
where θsim is the estimated population value of the parameter from one simulated data set and θtrue is the true population value for the parameter. The %PE was calculated for the 100 simulated data sets for each design. The mean and standard deviation of %PE were used to measure bias and precision of parameter estimates, respectively. A mean of %PE for a parameter estimate ≤15% was accepted as being unbiased, and standard deviation of% PE of ≤35% was accepted as being precise (7).
RESULTS
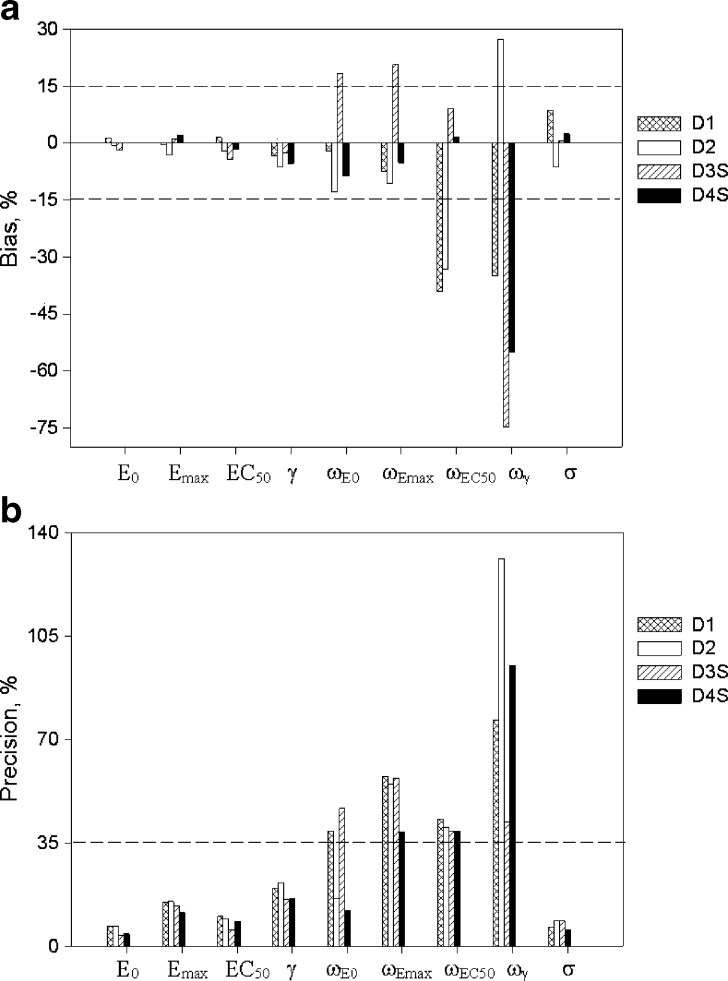
For the sigmoid Emax model, in regard to parameter accuracy (Fig. 3a), design 1 (four samples per individual) with concentrations ranging from one tenth to three times the EC50 yielded unbiased population estimates of EC50, Emax, E0, γ, ωEmax, and ωE0; however, inter-individual variability of EC50 and γ (i.e., ωEC50 and 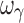 ) were biased. In regard to precision, all PD parameters were precisely estimated (Fig. 3b), whereas ωEmax and
) were biased. In regard to precision, all PD parameters were precisely estimated (Fig. 3b), whereas ωEmax and 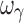 estimates were imprecise and estimates of ωE0 and ωEC50 were marginally imprecise (%PE, 39 and 43, respectively). Design 2, also with four samples per individual, yielded unbiased estimates of all PD and variability parameters, except ωEC50 and
estimates were imprecise and estimates of ωE0 and ωEC50 were marginally imprecise (%PE, 39 and 43, respectively). Design 2, also with four samples per individual, yielded unbiased estimates of all PD and variability parameters, except ωEC50 and 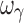 , which were biased. In regard to precision, all PD parameters and ωE0 were estimated with good precision; however, ωEmax, and
, which were biased. In regard to precision, all PD parameters and ωE0 were estimated with good precision; however, ωEmax, and 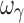 were imprecise and ωEC50 was marginally imprecise (%PE, 40).
were imprecise and ωEC50 was marginally imprecise (%PE, 40).
Fig. 3.
Accuracy (top) and precision (bottom) of parameter estimates for the sigmoid E max model. The horizontal line represents the 15% cut-off for accuracy and 35% cut-off for precision
For the sigmoid Emax model, design 3S, with five samples per individual (with the additional sample in the 0.5–1.5 EC50 region), yielded unbiased and precise estimates of all PD parameters; however the inter-individual variability parameters were biased and imprecise with the exception of ωEC50, which was unbiased and marginally imprecise (%PE, 39). Design 4S, also with five samples per individual (with the additional sample in the Emax region), yielded unbiased and precise estimates of all PD and variability parameters except ωEmax, ωEC50 that were marginally imprecise and 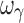 , which was biased and imprecise. The residual error was unbiased and precise for the four designs with either four or five samples. Overall, design 4S was the most satisfactory design in terms of accuracy and precision of both PD and variability parameters (with the exception of
, which was biased and imprecise. The residual error was unbiased and precise for the four designs with either four or five samples. Overall, design 4S was the most satisfactory design in terms of accuracy and precision of both PD and variability parameters (with the exception of 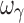 ) for a drug with a hill coefficient of ~2.5.
) for a drug with a hill coefficient of ~2.5.
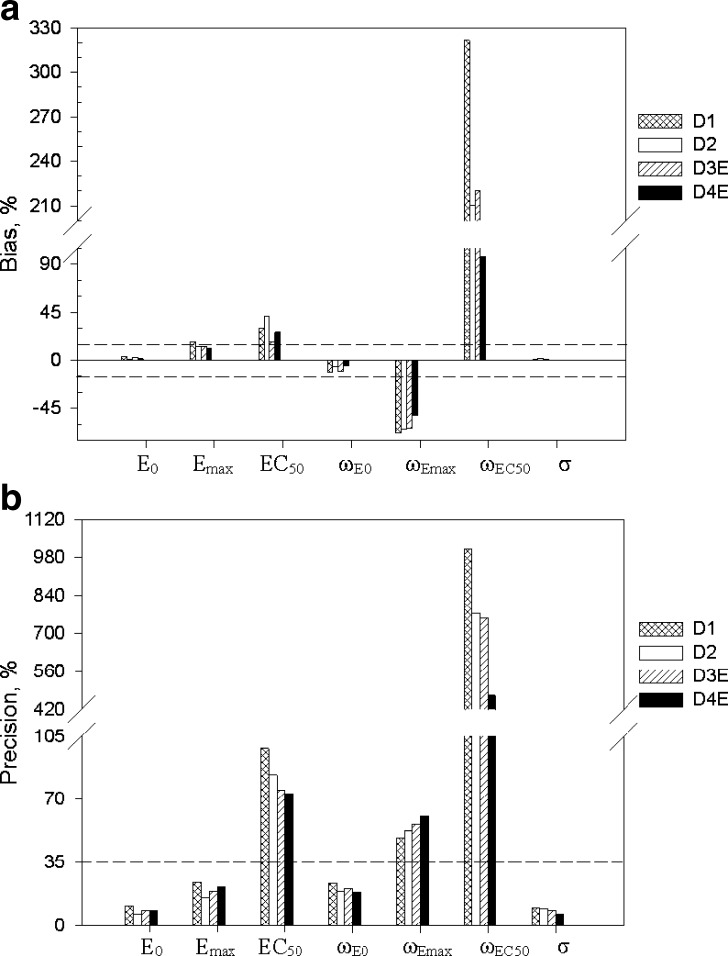
For the Emax model, in regard to the accuracy of the parameter estimates (Fig. 4a), designs D1 and D2 gave unbiased estimates of PD parameters E0 and Emax; EC50 was biased. In regard to inter-individual variability, ωE0 was unbiased, whereas ωEC50 and ωEmax were biased. In regard to precision, E0 and Emax were precisely estimated, EC50 was imprecise, and inter-individual variability parameters, with the exception of ωE0, were imprecise. With designs 3E and 4E, with samples in the 0.5–1.5 EC50 window, the PD parameters E0 and Emax were unbiased (as with D1 and D2, Fig. 2a). In regard to EC50, this parameter was marginally biased (%PE, 18) with design 3E and biased with 4E. In regard to inter-individual variability in the PD parameters (Fig. 4b), ωE0 was unbiased, and ωEC50 and ωEmax were biased. In regard to precision, E0 and Emax were precisely estimated, EC50 was imprecise, and inter-individual variability parameters, with the exception of ωE0, were imprecise. The residual error was unbiased and precise for all four designs.
Fig. 4.
Accuracy (top) and precision (bottom) of parameter estimates for the E max model. The horizontal line represents the 15% cut-off for accuracy and 35% cut-off for precision
In general, for the sigmoid Emax model, the four evaluated designs with four or five samples performed well in terms of accuracy and precision of the PD parameters (EC50, Emax, E0, and γ). The five-sample design, with two samples in the 2–3 Emax region (design 4S), provided estimates of inter-individual variability that were in general markedly more accurate and precise than with the other designs. Thus, placement of the additional fifth sample in the Emax region was important as evidenced by the better performance of design 4S versus 3S. For the Emax model, design 3E with sampling in the 0.5–1.5 EC50 window (EC50 region) performed better than designs D1 and D2 in regard to EC50 bias but not precision of this parameter. For design 4E, addition of the fifth sample in the 1–1.5 window (i.e., two samples in the same window) did not further improve the accuracy and precision of the PD and inter-individual variability parameters.
DISCUSSION
As a continuation of our previous work (1) that addressed the effect of sample size and number of samples on population PD parameters from sparse sampling for drugs with a high hill coefficient (γ > 5), the objective of the present work was to generalize the utility of sparse sampling to estimate population PD parameters for drugs with lower hill coefficients.
The results showed that, for the sigmoid Emax model, enriching the data with an additional (fifth) sample in an appropriate region of the profile resulted in more reliable parameter estimates. The impact of data enrichment on the efficiency of parameter estimates is in agreement with the results of Al-Banna et al. (8) and Ette et al. (9) where increasing the number of samples, respectively, from two to three and three to four (i.e., increasing the information content) resulted in improved efficiency of parameter estimates for a simple one-compartment PK model with IV bolus administration; the point of location of the additional sample on the IV profile did not markedly affect the estimates. However, in the current evaluation, placement of the additional sample in an appropriate region of the C–E profile, rather than just its presence within the profile, markedly influenced the efficiency of parameter estimation. This is evidenced for the sigmoid Emax model, by improved parameter accuracy and precision for design 4S (versus 3S) in which the additional fifth sample was obtained in the Emax region (rather than the EC50 region), i.e., Emax was better delineated by obtaining one sample in each of the 2–2.5 and 2.5–3 EC50 windows versus 3S where a single sample was obtained in the 2–3 EC50 window. It is well recognized that reliable delineation of Emax of the concentration–effect profile dictates the reliability of parameter estimates (10). For the simple Emax model, while the Emax coverage window was the same (i.e., 2.5–3 EC50 units) for all the four designs, the importance of sample placement was also evidenced for this model, where providing better coverage of the EC50 region (compared to designs D1 and D2) by obtaining two samples in the 0.5–1.5 EC50 region (i.e., one sample in each of the 0.5–1 and 1–1.5 EC50 windows, design 3E) resulted in improved accuracy of EC50. The lack of agreement between the two evaluations regarding the effect of sample placement is due solely to the more complex nature of C–E profile compared to the simple one-compartment IV bolus model evaluated in Al-Banna et al. (8) and Ette et al. (9)
For the sigmoid Emax model, both the four- and five-sample designs yielded accurate and precise estimates of the PD parameters (EC50, Emax, E0, and γ). The five sample designs (4S), with the additional sample in the Emax region of the profile (vide supra), in addition to accurate PD parameters, also yielded inter-individual variability parameters (except 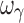 ) that were more accurate and more precise than with the other designs. The estimation problem with the inter-individual variability of γ (sigmoidicity factor) may be related to the general problem of parameter estimation when the dependent variable (e.g., response) changes steeply within a narrow range of the independent variable. The sigmoidicity factor only reflects the degree of sensitivity of the C–E relationship, with a larger value of the exponent resulting in a steeper curve, and is devoid of any biological meaning. While accurate and precise estimates of γ were obtained in these simulations, the poor estimates of inter-individual variability of this parameter are apparently an inherent estimation problem. A proposed approach that may overcome this problem is to estimate inter-individual variability in γ after all the other parameters have been estimated (11).
) that were more accurate and more precise than with the other designs. The estimation problem with the inter-individual variability of γ (sigmoidicity factor) may be related to the general problem of parameter estimation when the dependent variable (e.g., response) changes steeply within a narrow range of the independent variable. The sigmoidicity factor only reflects the degree of sensitivity of the C–E relationship, with a larger value of the exponent resulting in a steeper curve, and is devoid of any biological meaning. While accurate and precise estimates of γ were obtained in these simulations, the poor estimates of inter-individual variability of this parameter are apparently an inherent estimation problem. A proposed approach that may overcome this problem is to estimate inter-individual variability in γ after all the other parameters have been estimated (11).
For the simple Emax model, design 3E with one sample each in the 0.5–1 and 1–1.5 EC50 windows performed better than D1 and D2 in regard to EC50 bias; precision of this parameter was not affected. Including an additional sample in an adjacent window (e.g., 1.5–2 EC50) may also have further improved EC50 precision. Collectively, the results of the simple and sigmoid Emax models show that appropriate coverage of the EC50 region is necessary for shallower C–E profiles. Inclusion of the additional fifth sample (design 4E) in the same 1–1.5 window did not further improve the accuracy and precision of the PD and inter-individual variability parameters, demonstrating that obtaining replicate samples within the same window did not increase the information content. Currie (12) and Endrenyi (13), using Monte Carlo simulation and D-optimal designs, respectively, showed that the best designs for estimating the parameters of the Michaelis–Menton equation was to place half the concentrations at the EC50 (i.e., to provide for appropriate coverage of the EC50) and the other half at a concentration as high as possible. The results of the current series of simulations are in agreement with this finding, as evidenced by the better performance of designs 3E over D1 and D2.
Thus, the results of these simulation experiments show that for, both the sigmoid and simple Emax models, as few as four samples obtained in appropriate regions of the concentration–effect profile yields reliable estimates of the majority of the parameters of interest. For the sigmoid Emax model, because of the steeper C–E relationship, better delineation of the Emax region by the addition of the fifth sample in this region yielded reliable estimates of all PD and inter-individual variability parameters (except inter-individual variability of γ); increasing the information content of the EC50 region was not critical, as long as this region was covered by a single sample in the 0.5–1.5 EC50 window. For the simple Emax model, because of the shallower profile, enriching the EC50 region by obtaining one sample each in the 0.5–1 and 1–1.5 EC50 windows was important.
The impact of enrichment of appropriate regions for the two models is intuitively clear based solely on the steepness (sigmoidicity) of the concentration–effect relationships, with shallower C–E curves requiring data enrichment in the EC50 region and steeper curves less so. In this regard, the results of these simulation experiments and those previously described (1) are in agreement and provide a general framework for sparse sampling for C–E profiles with varying degrees of sigmoidicity. Thus, depending on the sigmoidicity, sparse sampling in the following EC50 windows is recommended: for C–E profiles with no sigmoidicity (γ = 1), 0.1–0.5, 0.5–1, 1–1.5, and 2.5–3 EC50 units; for C–E profiles with moderate sigmoidicity (γ = ~2.5), 0.1–0.5, 0.5–1.5, 1.5–2, 2–2.5 and 2.5–3 EC50 units; and as previously published, for C–E profiles with marked sigmoidicity (γ > 5) (1), 0.1–1, 1–2, 2–2.5, and 2.5–3 EC50 units.
The efficiency of parameter estimation depends on an interplay between the sample size, the number of samples per individual, and the underlying variability (1). To facilitate meaningful cross-design comparisons of parameter estimation efficiency, we used a common sample size (100 subjects), inter-individual variability (30%), and residual variability (25%) across the various designs. Regarding the sample size, 100 subjects were used based on our previous work (1), where population sizes of 25, 50, and 100 individuals were evaluated. For PD design with four samples per individual, a reduction in sample size from 100 to 25 individuals did not affect the accuracy and precision of PD parameters estimates; however, it affected the accuracy (at N = 25) and precision (at N = 25 or 50) of the variability parameters that were accurate at samples size of 50 or 100 and both accurate and precise at N = 100. For PD design with five samples per individual, the accuracy of parameter estimates were not affected by a reduction of sample size from 100 to 25 individuals; however, it affected the precision of variability parameters at N = 25 and 50 individuals. From the standpoint of implementation in clinical trials, four or five samples per individual are routinely obtained in phase 2a/b trials, and a sample size of 100 subjects represents only a small fraction of the total sample size utilized in the pivotal (phase 3) trials, with PK/PD sampling performed during (routine) clinic visits for other evaluations (e.g., clinical chemistry and safety).
The inter-individual variability (30%) that was utilized, while moderate and may indeed vary among parameters, nevertheless shows the effect of sigmoidicity on population PK/PD parameter estimation using the sparse sampling paradigm. The observed residual variability for octreotide (2) and remifenatil (3) was low (15.6% and 15%, respectively) and likely a result of the controlled conditions and intensive (serial) sampling used to obtain the underlying observational data. The relatively more practical 25% residual variability used in these evaluations provides additional confidence regarding parameter estimation efficiency under sparse sampling conditions. It is recognized that the levels of inter-individual and residual variability may preclude broader generalizations for situations in which the variability is significantly larger. Prior to initiation of the pivotal phase 3 trials, however, the PK/PD variability characteristics of a drug is usually known from early phase clinical pharmacology studies and/or phase 2a/b; indeed, biomarkers/surrogate endpoints are increasingly being used in such trials (even as perhaps as early as the multiple ascending dose study) to make go/no-go decisions as early as possible. Based on this a priori information, sampling points can be optimized and implemented in the pivotal human trials.
Population PD parameters (typical values), in general, are more accurately and precisely estimated than the variability parameters (8,9). The desire to estimate all PD and variability parameters versus the need to do so should be tempered with practical (and cost) constraints of obtaining a large number of samples. Obtaining a reasonable number of samples (four or five samples) from a subset of subjects in out-patient trails is both feasible and practical. Implicit in these evaluations is the need to drive the concentrations as high as possible to reliably delineate Emax, as is often done (within the constraints of the maximum tolerated dose) to maximize the probability of a successful outcome. If this cannot be achieved because of unanticipated safety concerns, then parameter estimation will be severely compromised regardless of the number of samples collected.
Abbreviations
- C–E
Concentration–effect
- E0
Baseline response
- EC50
Drug concentration at 50% of the Emax
- Emax
Drug efficacy
- γ
The sigmoidicity constant
- Hz
Hertz
- mL
Milliliter
- N
Sample size
- ng
Nanogram
- NONMEM
Non-linear mixed effect modeling
- PD
Pharmacodynamic
- pg
Picogram
- PK
Pharmacokinetic
References
- 1.Girgis S, Pai SM, Girgis IG, Batra VK. Pharmacodynamic parameter estimation: population size versus number of samples. AAPS J. 2005;7(2):E461–E466. doi: 10.1208/aapsj070246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zhou H, Chen TL, Lau H, Kalafsky G, Mcleod JF. Population PK and PK/PD modeling of microencapsulated octreotide acetate in healthy subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2000;50:543–552. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.2000.00297.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Minto CF, Schnider TW, Egan TD, et al. Influence of age and gender on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of remifentanil: I. Model development. Anesthesiology. 1997;86(1):10–23. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199701000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.White DB, Walawander CA, Tung Y, Grasela TH. An evaluation of point and interval estimates in population pharmacokinetics using NONMEM analysis. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1991;19:87–112. doi: 10.1007/BF01062194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Beal SL, Sheiner LB. NONMEM user’s guide parts I–VIII. San Francisco: University of California; 1998. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Jonsson EN, Wade JR, Karlsson MO. Comparison of some practical sampling strategies for population pharmacokinetic studies. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1996;24:245–263. doi: 10.1007/BF02353491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sun H, Ette EI, Ludden TM. On the recording of sample times and parameter estimation from repeated measures pharmacokinetic data. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1996;24:637–650. doi: 10.1007/BF02353484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Al-Banna MK, Kelman AW, Whiting B. Experimental design and efficient parameter estimation in population pharmacokinetics. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1990;18:347–360. doi: 10.1007/BF01062273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ette EI, Howie CA, Kelman AW, Whiting B. Experimental design and efficient parameter estimation in preclinical pharmacokinetic studies. Pharm Res. 1995;12(5):729–737. doi: 10.1023/A:1016267811074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dutta S, Ebling WF. Parameter estimability of biphasic response models. J Pharm Sci. 1997;86(1):44–51. doi: 10.1021/js960248f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic analysis with NONMEM. D. Fisher and S. Shafer, March 2007. http://www.sivauk.org/PreviousMeetings/Cambridge/Shafer%20NONMEM.pdf.
- 12.Currie DJ. Estimating Michaelis–Menten parameters: bias, variance and experimental designs. Biometrics. 1982;38:907–919. doi: 10.2307/2529871. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Endrenyi L, Chan FY. Optimal designs of experiments for the estimation of precise hyperbolic kinetics and binding parameters. J Theor Biol. 1981;90:241–263. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(81)90045-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]