Abstract
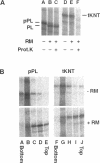
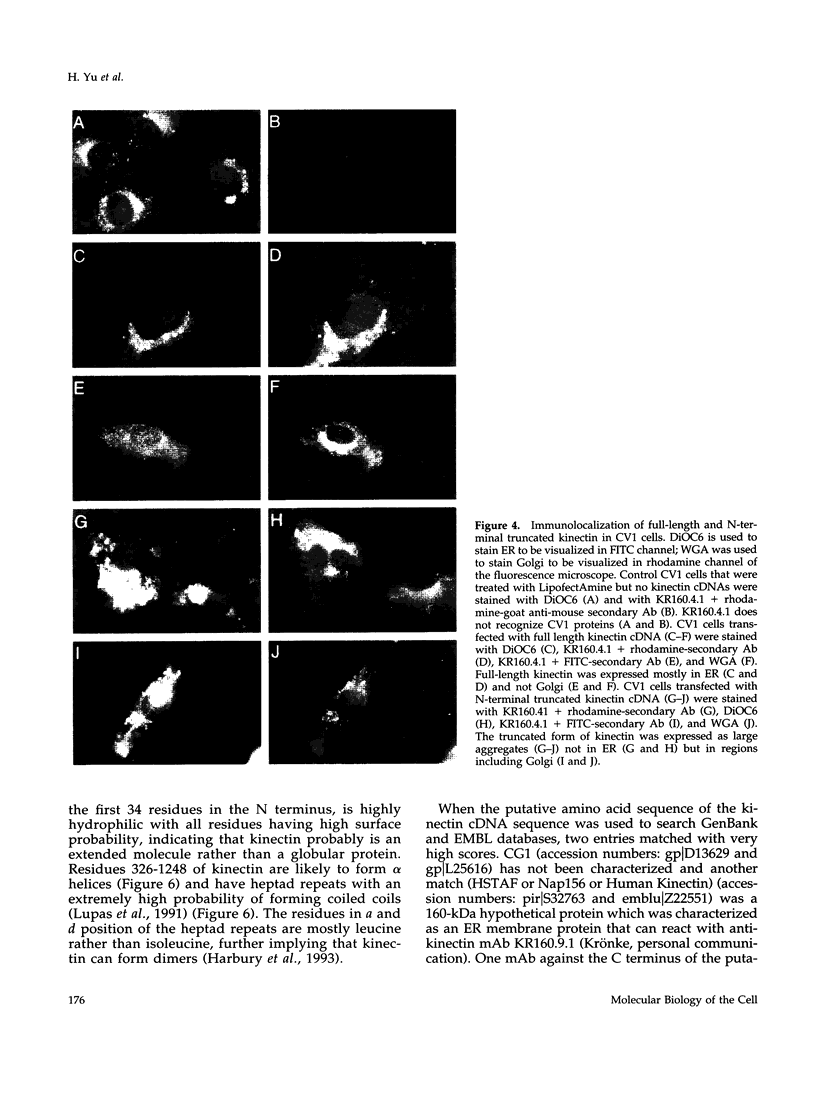
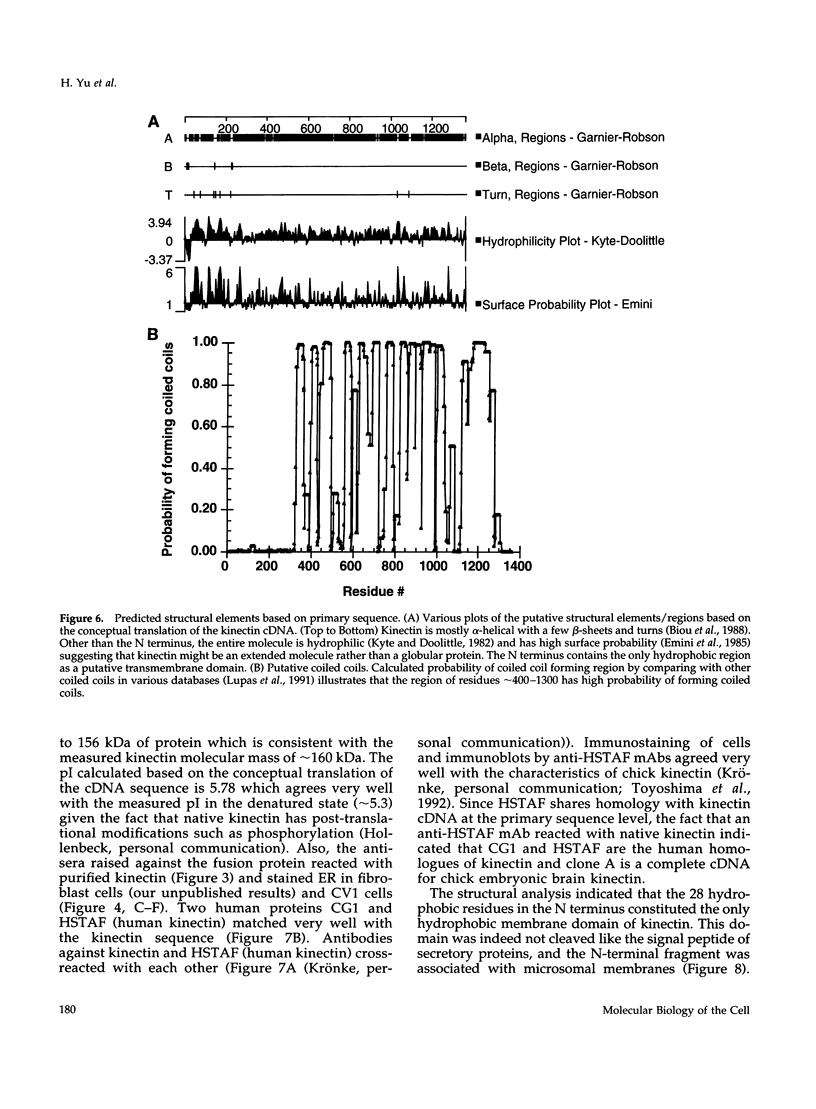
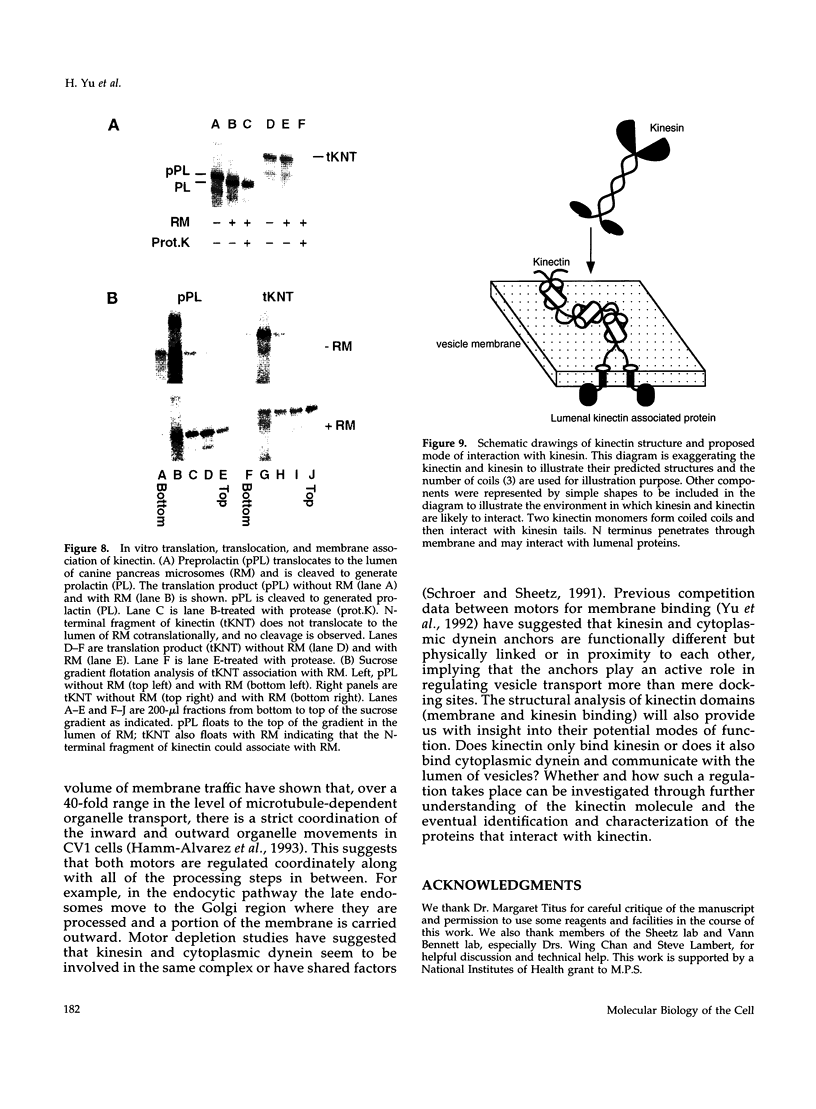
Kinectin is a kinesin-binding protein (Toyoshima et al., 1992) that is required for kinesin-based motility (Kumar et al., 1995). A kinectin cDNA clone containing a 4.7-kilobase insert was isolated from an embryonic chick brain cDNA library by immunoscreening with a panel of monoclonal antibodies. The cDNA contained an open reading frame of 1364 amino acids encoding a protein of 156 kDa. A bacterially expressed product of the full length cDNA bound purified kinesin. Transient expression in CV-1 cells gave an endoplasmic reticulum distribution that depended upon the N-terminal domain. Analysis of the predicted amino acid sequence indicated a highly hydrophobic near N-terminal stretch of 28 amino acids and a large portion (326-1248) of predicted alpha helical coiled coils. The 30-kDa fragment containing the N-terminal hydrophobic region was produced by cell-free in vitro translation and found to assemble with canine pancreas rough microsomes. Cleavage of the N terminus was not observed confirming its role as a potential transmembrane domain. Thus, the kinectin cDNA encodes a cytoplasmic-oriented integral membrane protein that binds kinesin and is likely to be a coiled-coil dimer.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews D. W., Lauffer L., Walter P., Lingappa V. R. Evidence for a two-step mechanism involved in assembly of functional signal recognition particle receptor. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):797–810. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bairoch A. PROSITE: a dictionary of sites and patterns in proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19 (Suppl):2241–2245. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.suppl.2241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biou V., Gibrat J. F., Levin J. M., Robson B., Garnier J. Secondary structure prediction: combination of three different methods. Protein Eng. 1988 Sep;2(3):185–191. doi: 10.1093/protein/2.3.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhardt J. K., McIlvain J. M., Jr, Sheetz M. P., Argon Y. Lytic granules from cytotoxic T cells exhibit kinesin-dependent motility on microtubules in vitro. J Cell Sci. 1993 Jan;104(Pt 1):151–162. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104.1.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly T., Gilmore R. Formation of a functional ribosome-membrane junction during translocation requires the participation of a GTP-binding protein. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2253–2261. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cyr J. L., Pfister K. K., Bloom G. S., Slaughter C. A., Brady S. T. Molecular genetics of kinesin light chains: generation of isoforms by alternative splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10114–10118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Hughes J. V., Perlow D. S., Boger J. Induction of hepatitis A virus-neutralizing antibody by a virus-specific synthetic peptide. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):836–839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.836-839.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endow S. A. The emerging kinesin family of microtubule motor proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jun;16(6):221–225. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90089-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed B. M., Lempert N., Lawrence D. A. The inhibitory effects of N-ethylmaleimide, colchicine and cytochalasins on human T-cell functions. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1989;11(5):459–465. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(89)90174-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauger A. K., Goldstein L. S. The Drosophila kinesin light chain. Primary structure and interaction with kinesin heavy chain. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 25;268(18):13657–13666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg S., Chang P., Silverstein S. C. Tyrosine phosphorylation is required for Fc receptor-mediated phagocytosis in mouse macrophages. J Exp Med. 1993 Feb 1;177(2):529–534. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm-Alvarez S. F., Kim P. Y., Sheetz M. P. Regulation of vesicle transport in CV-1 cells and extracts. J Cell Sci. 1993 Nov;106(Pt 3):955–966. doi: 10.1242/jcs.106.3.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbury P. B., Zhang T., Kim P. S., Alber T. A switch between two-, three-, and four-stranded coiled coils in GCN4 leucine zipper mutants. Science. 1993 Nov 26;262(5138):1401–1407. doi: 10.1126/science.8248779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hein J. Unified approach to alignment and phylogenies. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:626–645. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho W. C., Allan V. J., van Meer G., Berger E. G., Kreis T. E. Reclustering of scattered Golgi elements occurs along microtubules. Eur J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;48(2):250–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hortsch M., Labeit S., Meyer D. I. Complete cDNA sequence coding for human docking protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):361–362. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingold A. L., Cohn S. A., Scholey J. M. Inhibition of kinesin-driven microtubule motility by monoclonal antibodies to kinesin heavy chains. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 2):2657–2667. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Structural features in eukaryotic mRNAs that modulate the initiation of translation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):19867–19870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C., Ferguson M., Chen L. B. Construction of the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2045–2055. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Donaldson J. G., Schweizer A., Berger E. G., Hauri H. P., Yuan L. C., Klausner R. D. Microtubule-dependent retrograde transport of proteins into the ER in the presence of brefeldin A suggests an ER recycling pathway. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):821–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90096-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupas A., Van Dyke M., Stock J. Predicting coiled coils from protein sequences. Science. 1991 May 24;252(5009):1162–1164. doi: 10.1126/science.252.5009.1162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekori Y. A., Baram D., Goldberg A., Klajman A. Inhibition of delayed hypersensitivity reactions in mice by colchicine. I. Mechanism of inhibition of contact sensitivity in vivo. Cell Immunol. 1989 May;120(2):330–340. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90201-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicchitta C. V., Blobel G. Nascent secretory chain binding and translocation are distinct processes: differentiation by chemical alkylation. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):789–795. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroer T. A., Schnapp B. J., Reese T. S., Sheetz M. P. The role of kinesin and other soluble factors in organelle movement along microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1785–1792. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroer T. A., Sheetz M. P. Functions of microtubule-based motors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:629–652. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.003213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroer T. A., Sheetz M. P. Two activators of microtubule-based vesicle transport. J Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;115(5):1309–1318. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.5.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz M. P., Vale R., Schnapp B., Schroer T., Reese T. Vesicle movements and microtubule-based motors. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1986;5:181–188. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1986.supplement_5.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Bushnell A., Silverstein S. C. Tubular lysosome morphology and distribution within macrophages depend on the integrity of cytoplasmic microtubules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1921–1925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima I., Yu H., Steuer E. R., Sheetz M. P. Kinectin, a major kinesin-binding protein on ER. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(5):1121–1131. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.5.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale R. D., Goldstein L. S. One motor, many tails: an expanding repertoire of force-generating enzymes. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):883–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90334-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee R. B., Shpetner H. S. Motor proteins of cytoplasmic microtubules. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:909–932. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Gilmore R., Blobel G. Protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90520-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedaman K. P., Knight A. E., Kendrick-Jones J., Scholey J. M. Sequences of sea urchin kinesin light chain isoforms. J Mol Biol. 1993 May 5;231(1):155–158. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu H., Toyoshima I., Steuer E. R., Sheetz M. P. Kinesin and cytoplasmic dynein binding to brain microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):20457–20464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]