Abstract
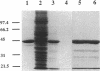
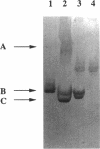
Non-muscle cells contain 15-500 microM actin, a large fraction of which is unpolymerized. Thus, the concentration of unpolymerized actin is well above the critical concentration for polymerization in vitro (0.2 microM). This fraction of actin could be prevented from polymerization by being ADP bound (therefore less favored to polymerize) or by being ATP bound and sequestered by a protein such as thymosin beta 4, or both. We isolated the unpolymerized actin from Xenopus egg extracts using immobilized DNase 1 and assayed the bound nucleotide. High-pressure liquid chromatography analysis showed that the bulk of soluble actin is ATP bound. Analysis of actin-bound nucleotide exchange rates suggested the existence of two pools of unpolymerized actin, one of which exchanges nucleotide relatively rapidly and another that apparently does not exchange. Native gel electrophoresis of Xenopus egg extracts demonstrated that most of the soluble actin exists in complexes with other proteins, one of which might be thymosin beta 4. These results are consistent with actin polymerization being controlled by the sequestration and release of ATP-bound actin, and argue against nucleotide exchange playing a major role in regulating actin polymerization.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balasubramanian M. K., Hirani B. R., Burke J. D., Gould K. L. The Schizosaccharomyces pombe cdc3+ gene encodes a profilin essential for cytokinesis. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;125(6):1289–1301. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.6.1289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss F., Temm-Grove C., Henning S., Jockusch B. M. Distribution of profilin in fibroblasts correlates with the presence of highly dynamic actin filaments. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1992;22(1):51–61. doi: 10.1002/cm.970220106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlier M. F., Jean C., Rieger K. J., Lenfant M., Pantaloni D. Modulation of the interaction between G-actin and thymosin beta 4 by the ATP/ADP ratio: possible implication in the regulation of actin dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5034–5038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson L., Nyström L. E., Sundkvist I., Markey F., Lindberg U. Actin polymerizability is influenced by profilin, a low molecular weight protein in non-muscle cells. J Mol Biol. 1977 Sep 25;115(3):465–483. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90166-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassimeris L., Safer D., Nachmias V. T., Zigmond S. H. Thymosin beta 4 sequesters the majority of G-actin in resting human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(5):1261–1270. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.5.1261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooley L., Verheyen E., Ayers K. chickadee encodes a profilin required for intercellular cytoplasm transport during Drosophila oogenesis. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):173–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90128-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A. The role of actin polymerization in cell motility. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:585–605. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.003101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkel T., Theriot J. A., Dise K. R., Tomaselli G. F., Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J. Dynamic actin structures stabilized by profilin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 15;91(4):1510–1514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.4.1510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Furman M. I., Wachsstock D., Safer D., Nachmias V. T., Pollard T. D. The control of actin nucleotide exchange by thymosin beta 4 and profilin. A potential regulatory mechanism for actin polymerization in cells. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Sep;3(9):1015–1024. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.9.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haarer B. K., Lillie S. H., Adams A. E., Magdolen V., Bandlow W., Brown S. S. Purification of profilin from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and analysis of profilin-deficient cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;110(1):105–114. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto K., Tatsumi N. Regulation of actin polymerization by membrane fraction of platelets. Biochem Int. 1988 Feb;16(2):267–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugwitz M., Noegel A. A., Karakesisoglou J., Schleicher M. Dictyostelium amoebae that lack G-actin-sequestering profilins show defects in F-actin content, cytokinesis, and development. Cell. 1994 Oct 21;79(2):303–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90199-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock S. E. Actin deoxyroboncuclease I interaction. Depolymerization and nucleotide exchange. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5668–5673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holliday L. S., Bubb M. R., Korn E. D. Rabbit skeletal muscle actin behaves differently than Acanthamoeba actin when added to soluble extracts of Acanthamoeba castellanii. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Oct 29;196(2):569–575. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. R., Mitchison T. J., Alberts B. M. Behaviour of microtubules and actin filaments in living Drosophila embryos. Development. 1988 Aug;103(4):675–686. doi: 10.1242/dev.103.4.675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinosian H. J., Selden L. A., Estes J. E., Gershman L. C. Nucleotide binding to actin. Cation dependence of nucleotide dissociation and exchange rates. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):8683–8691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn E. D. Actin polymerization and its regulation by proteins from nonmuscle cells. Physiol Rev. 1982 Apr;62(2):672–737. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.2.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magdolen V., Drubin D. G., Mages G., Bandlow W. High levels of profilin suppress the lethality caused by overproduction of actin in yeast cells. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jan 18;316(1):41–47. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81733-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannherz H. G., Goody R. S., Konrad M., Nowak E. The interaction of bovine pancreatic deoxyribonuclease I and skeletal muscle actin. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Mar;104(2):367–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W. Cell cycle extracts. Methods Cell Biol. 1991;36:581–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki K., Hatano S. Mechanism of regulation of actin polymerization by Physarum profilin. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;98(6):1919–1925. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.6.1919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantaloni D., Carlier M. F. How profilin promotes actin filament assembly in the presence of thymosin beta 4. Cell. 1993 Dec 3;75(5):1007–1014. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90544-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D. Assembly and dynamics of the actin filament system in nonmuscle cells. J Cell Biochem. 1986;31(2):87–95. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240310202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D. Rate constants for the reactions of ATP- and ADP-actin with the ends of actin filaments. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2747–2754. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer D. An electrophoretic procedure for detecting proteins that bind actin monomers. Anal Biochem. 1989 Apr;178(1):32–37. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90351-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer D., Golla R., Nachmias V. T. Isolation of a 5-kilodalton actin-sequestering peptide from human blood platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2536–2540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. C., Goldstein A. L., Wang Y. L. Thymosin beta 4 (Fx peptide) is a potent regulator of actin polymerization in living cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4678–4682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sohn R. H., Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J. Profilin: at the crossroads of signal transduction and the actin cytoskeleton. Bioessays. 1994 Jul;16(7):465–472. doi: 10.1002/bies.950160705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theriot J. A., Mitchison T. J., Tilney L. G., Portnoy D. A. The rate of actin-based motility of intracellular Listeria monocytogenes equals the rate of actin polymerization. Nature. 1992 May 21;357(6375):257–260. doi: 10.1038/357257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theriot J. A., Rosenblatt J., Portnoy D. A., Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Mitchison T. J. Involvement of profilin in the actin-based motility of L. monocytogenes in cells and in cell-free extracts. Cell. 1994 Feb 11;76(3):505–517. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90114-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vojtek A., Haarer B., Field J., Gerst J., Pollard T. D., Brown S., Wigler M. Evidence for a functional link between profilin and CAP in the yeast S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):497–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu F. X., Lin S. C., Morrison-Bogorad M., Atkinson M. A., Yin H. L. Thymosin beta 10 and thymosin beta 4 are both actin monomer sequestering proteins. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):502–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu F. X., Lin S. C., Morrison-Bogorad M., Yin H. L. Effects of thymosin beta 4 and thymosin beta 10 on actin structures in living cells. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1994;27(1):13–25. doi: 10.1002/cm.970270103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]