Abstract
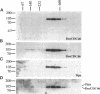
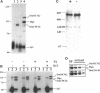
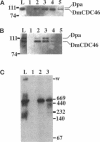
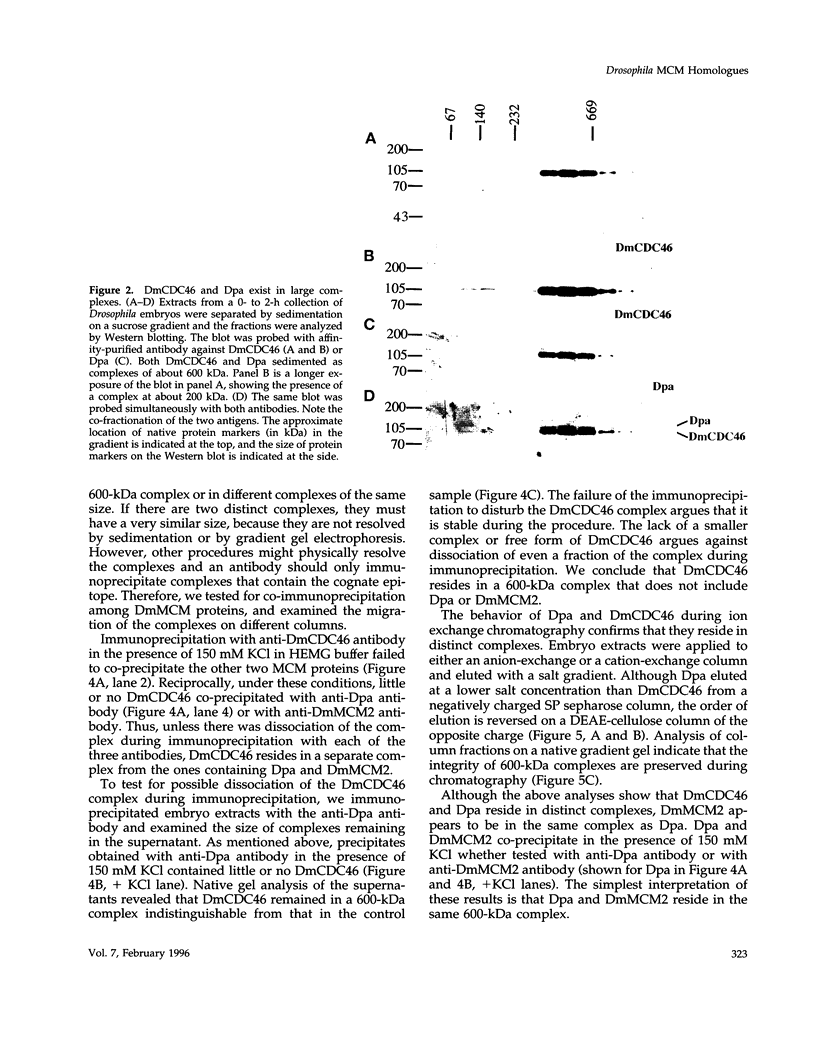
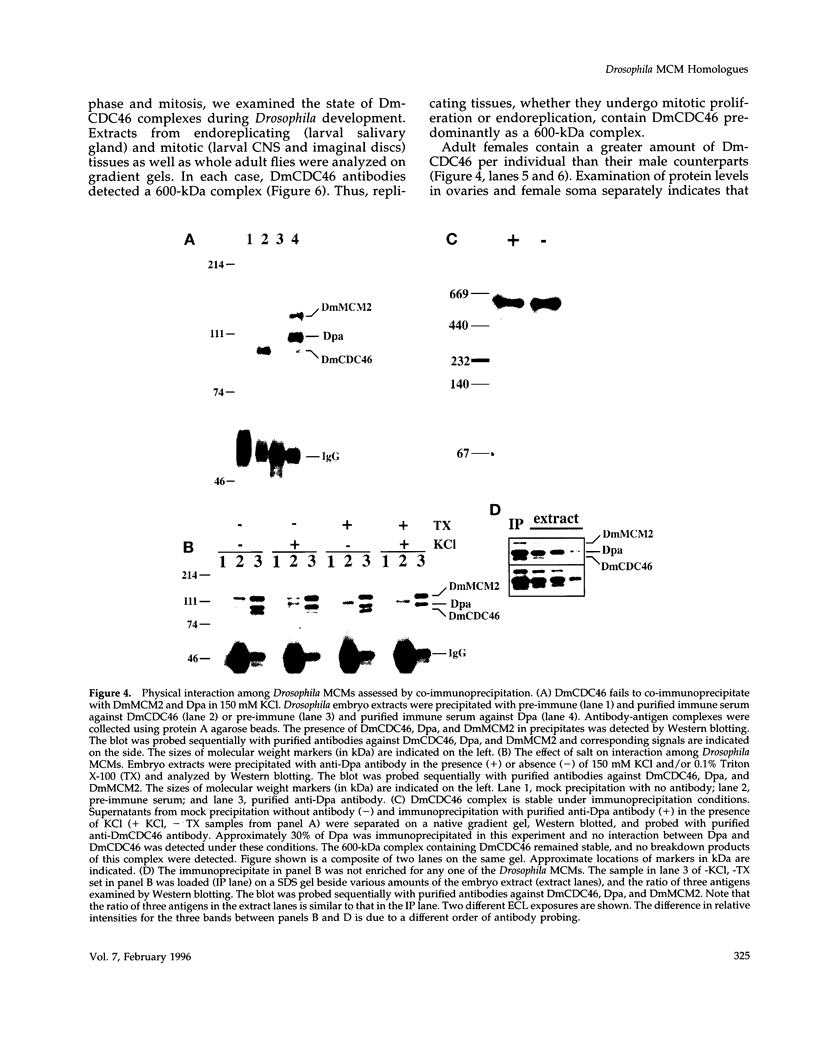
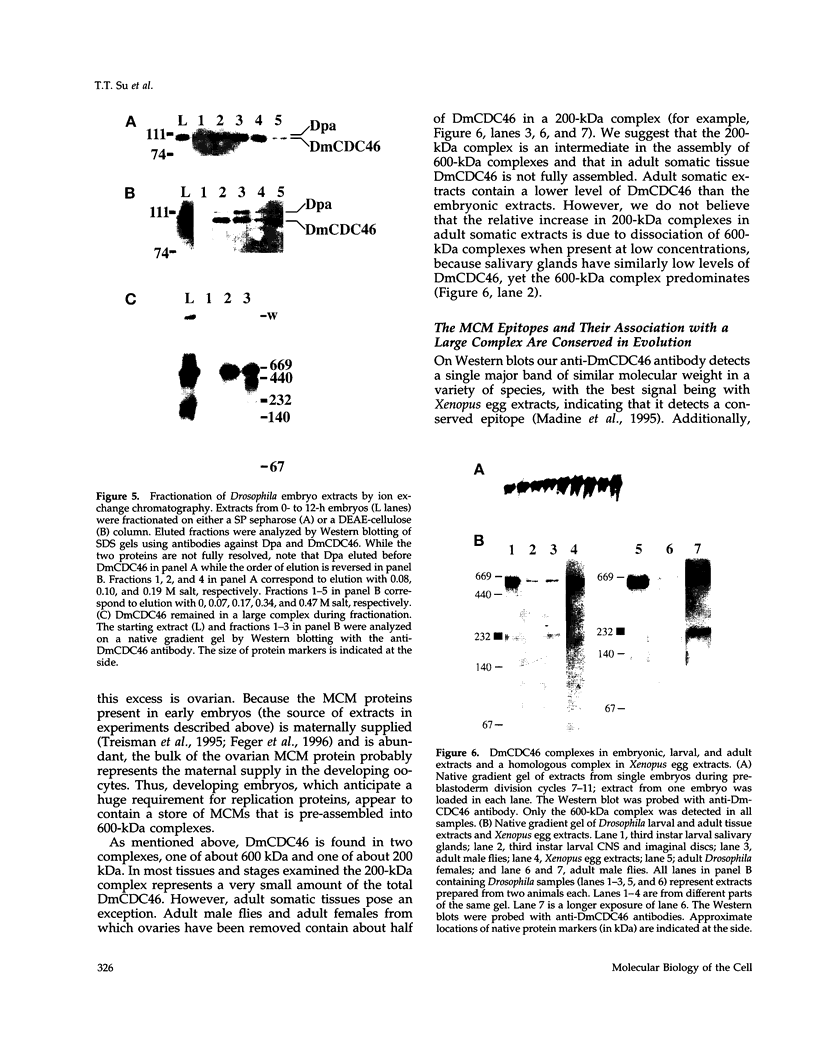
MCM genes encode a family of evolutionarily conserved proteins required for DNA replication. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, where they were first identified, MCM genes interact genetically with each other. Allele specificity in these interactions suggests that MCM proteins physically associate with one another and that this association is essential for function. We describe here an analysis of physical interactions among three Drosophila MCM proteins. Using specific antibodies we detect Drosophila MCMs almost exclusively in 600-kDa protein complexes. Co-immunoprecipitation data demonstrate the existence of at least two distinct types of 600-kDa complexes, one that contains DmCDC46 and one that appears to contain both DmMCM2 and Dpa (a CDC54 homologue). These complexes are stable throughout embryonic division cycles, are resistant to treatments with salt and detergent, and are present during development in tissues undergoing mitotic DNA replication as well as endoreplication. When extracts are prepared under low salt conditions all three MCM proteins co-immunoprecipitate. Consequently, we suggest that the 600-kDa complexes interact in a higher order complex.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell S. P., Stillman B. ATP-dependent recognition of eukaryotic origins of DNA replication by a multiprotein complex. Nature. 1992 May 14;357(6374):128–134. doi: 10.1038/357128a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blow J. J., Laskey R. A. A role for the nuclear envelope in controlling DNA replication within the cell cycle. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):546–548. doi: 10.1038/332546a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhart R., Schulte D., Hu D., Musahl C., Göhring F., Knippers R. Interactions of human nuclear proteins P1Mcm3 and P1Cdc46. Eur J Biochem. 1995 Mar 1;228(2):431–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Hennessy K. M., Botstein D., Tye B. K. CDC46/MCM5, a yeast protein whose subcellular localization is cell cycle-regulated, is involved in DNA replication at autonomously replicating sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10459–10463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong J. P., Mahbubani H. M., Khoo C. Y., Blow J. J. Purification of an MCM-containing complex as a component of the DNA replication licensing system. Nature. 1995 Jun 1;375(6530):418–421. doi: 10.1038/375418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coxon A., Maundrell K., Kearsey S. E. Fission yeast cdc21+ belongs to a family of proteins involved in an early step of chromosome replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 11;20(21):5571–5577. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.21.5571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton S., Whitbread L. Cell cycle-regulated nuclear import and export of Cdc47, a protein essential for initiation of DNA replication in budding yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 28;92(7):2514–2518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.7.2514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley J. F., Cocker J. H., Dowell S. J., Rowley A. Two steps in the assembly of complexes at yeast replication origins in vivo. Cell. 1994 Jul 29;78(2):303–316. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90299-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar B. A., Sprenger F., Duronio R. J., Leopold P., O'Farrell P. H. Distinct molecular mechanism regulate cell cycle timing at successive stages of Drosophila embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 1994 Feb 15;8(4):440–452. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.4.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feger G., Vaessin H., Su T. T., Wolff E., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. dpa, a member of the MCM family, is required for mitotic DNA replication but not endoreplication in Drosophila. EMBO J. 1995 Nov 1;14(21):5387–5398. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00223.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann H., Aigle M., Aljinovic G., André B., Baclet M. C., Barthe C., Baur A., Bécam A. M., Biteau N., Boles E. Complete DNA sequence of yeast chromosome II. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 15;13(24):5795–5809. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06923.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsburg S. L., Nurse P. The fission yeast cdc19+ gene encodes a member of the MCM family of replication proteins. J Cell Sci. 1994 Oct;107(Pt 10):2779–2788. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.10.2779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K. M., Clark C. D., Botstein D. Subcellular localization of yeast CDC46 varies with the cell cycle. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2252–2263. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K. M., Lee A., Chen E., Botstein D. A group of interacting yeast DNA replication genes. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):958–969. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A. Cell cycle. A licence to replicate. Nature. 1995 Jun 1;375(6530):360–361. doi: 10.1038/375360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T. Assembly and disassembly of the Drosophila RNA polymerase II complex during transcription. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2624–2631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamakaka R. T., Tyree C. M., Kadonaga J. T. Accurate and efficient RNA polymerase II transcription with a soluble nuclear fraction derived from Drosophila embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):1024–1028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.1024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura H., Nozaki N., Sugimoto K. DNA polymerase alpha associated protein P1, a murine homolog of yeast MCM3, changes its intranuclear distribution during the DNA synthetic period. EMBO J. 1994 Sep 15;13(18):4311–4320. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06751.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubota Y., Mimura S., Nishimoto S., Takisawa H., Nojima H. Identification of the yeast MCM3-related protein as a component of Xenopus DNA replication licensing factor. Cell. 1995 May 19;81(4):601–609. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90081-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. J., Herskowitz I. Isolation of ORC6, a component of the yeast origin recognition complex by a one-hybrid system. Science. 1993 Dec 17;262(5141):1870–1874. doi: 10.1126/science.8266075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madine M. A., Khoo C. Y., Mills A. D., Laskey R. A. MCM3 complex required for cell cycle regulation of DNA replication in vertebrate cells. Nature. 1995 Jun 1;375(6530):421–424. doi: 10.1038/375421a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake S., Okishio N., Samejima I., Hiraoka Y., Toda T., Saitoh I., Yanagida M. Fission yeast genes nda1+ and nda4+, mutations of which lead to S-phase block, chromatin alteration and Ca2+ suppression, are members of the CDC46/MCM2 family. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Oct;4(10):1003–1015. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.10.1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musahl C., Schulte D., Burkhart R., Knippers R. A human homologue of the yeast replication protein Cdc21. Interactions with other Mcm proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1995 Jun 15;230(3):1096–1101. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.tb20660.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A., Orr-Weaver T. Regulation of DNA replication during Drosophila development. Annu Rev Genet. 1987;21:373–403. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.21.120187.002105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su T. T., Follette P. J., O'Farrell P. H. Qualifying for the license to replicate. Cell. 1995 Jun 16;81(6):825–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90000-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman J. E., Follette P. J., O'Farrell P. H., Rubin G. M. Cell proliferation and DNA replication defects in a Drosophila MCM2 mutant. Genes Dev. 1995 Jul 15;9(14):1709–1715. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.14.1709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tye B. K. The MCM2-3-5 proteins: are they replication licensing factors? Trends Cell Biol. 1994 May;4(5):160–166. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitebread L. A., Dalton S. Cdc54 belongs to the Cdc46/Mcm3 family of proteins which are essential for initiation of eukaryotic DNA replication. Gene. 1995 Mar 21;155(1):113–117. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)00925-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan H., Gibson S., Tye B. K. Mcm2 and Mcm3, two proteins important for ARS activity, are related in structure and function. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):944–957. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan H., Merchant A. M., Tye B. K. Cell cycle-regulated nuclear localization of MCM2 and MCM3, which are required for the initiation of DNA synthesis at chromosomal replication origins in yeast. Genes Dev. 1993 Nov;7(11):2149–2160. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.11.2149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]