Abstract
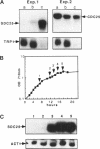
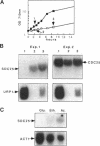
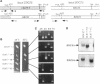
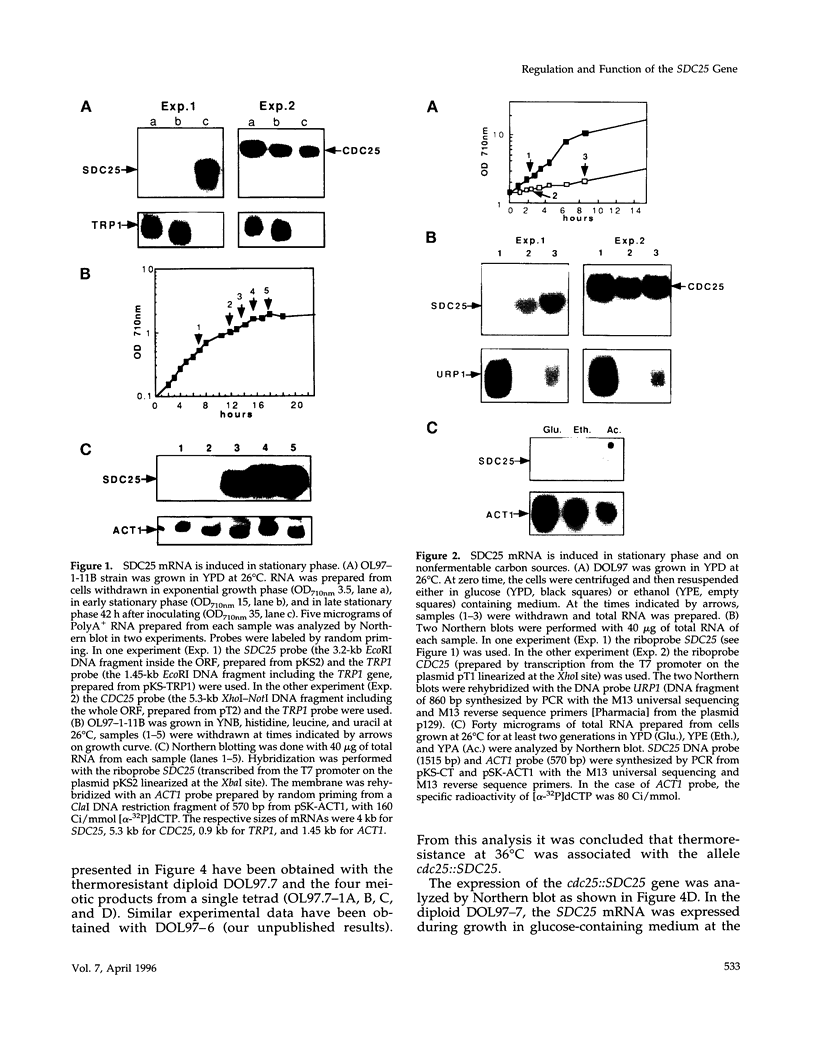
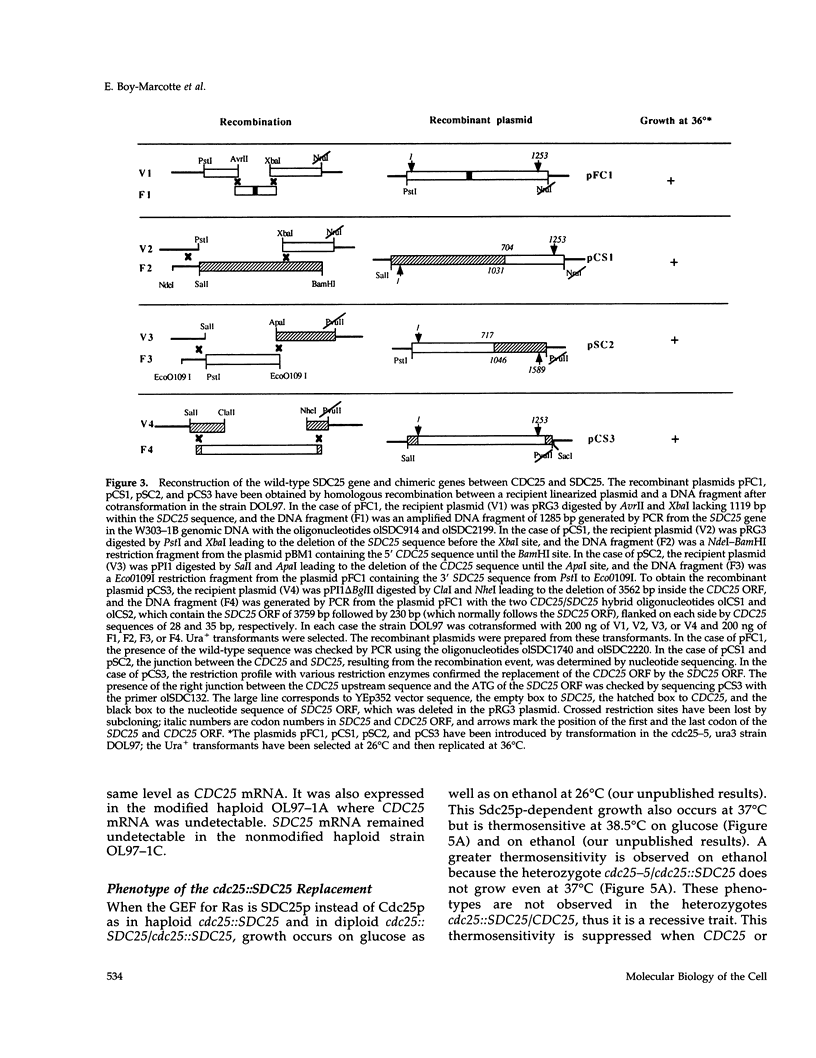
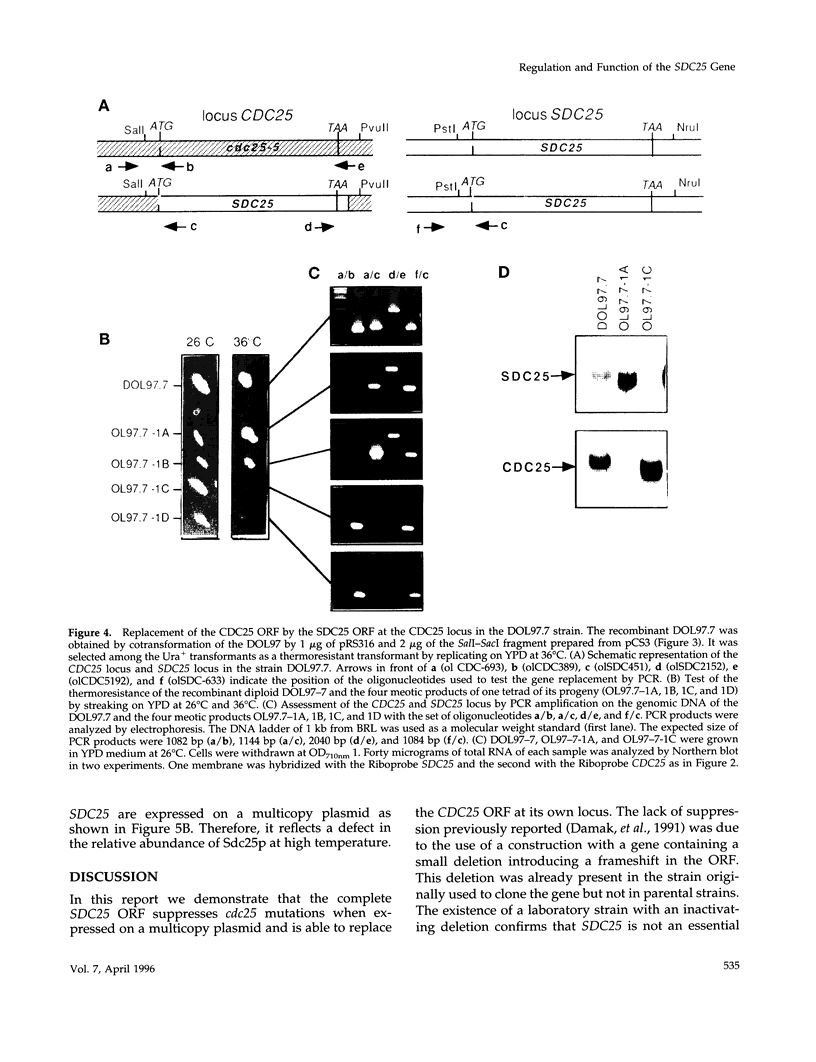
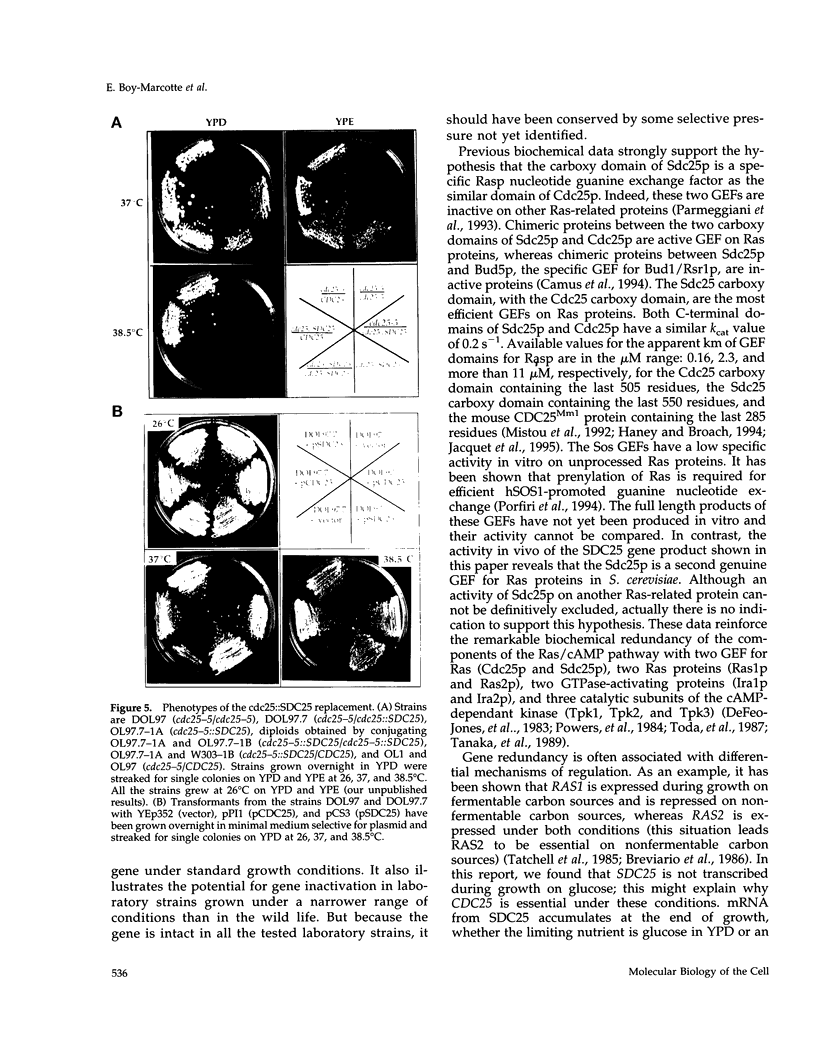
The SDC25 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is homologous to CDC25. Its 3' domain encodes a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for Ras. Nevertheless, the GEF encoded by CDC24 is determinant for the Ras/cAMP pathway activation in growth. We demonstrate that the SDC25 gene product is a functional GEF for Ras: the complete SDC25 gene functionally replaces CDC25 when overexpressed or when transcribed under CDC25 transcriptional control at the CDC25 locus. Chimeric proteins between Sdc25p and Cdc25p are also functional GEFs for Ras. We also show that the two genes are differentially regulated: SDC25 is not transcribed at a detectable level in growth conditions when glucose is the carbon source. It is transcribed at the end of growth when nutrients are depleted and in cells grown on nonfermentable carbon sources. In contrast, CDC25 accumulation is slightly reduced when glucose is replaced by a nonfermentable carbon source.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barlat I., Schweighoffer F., Chevallier-Multon M. C., Duchesne M., Fath I., Landais D., Jacquet M., Tocque B. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene product SDC25 C-domain functions as an oncoprotein in NIH3T3 cells. Oncogene. 1993 Jan;8(1):215–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boguski M. S., McCormick F. Proteins regulating Ras and its relatives. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):643–654. doi: 10.1038/366643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowtell D., Fu P., Simon M., Senior P. Identification of murine homologues of the Drosophila son of sevenless gene: potential activators of ras. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6511–6515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boy-Marcotte E., Buu A., Soustelle C., Poullet P., Parmeggiani A., Jacquet M. The C-terminal part of the CDC25 gene product has Ras-nucleotide exchange activity when present in a chimeric SDC25-CDC25 protein. Curr Genet. 1993 May-Jun;23(5-6):397–401. doi: 10.1007/BF00312625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boy-Marcotte E., Damak F., Camonis J., Garreau H., Jacquet M. The C-terminal part of a gene partially homologous to CDC 25 gene suppresses the cdc25-5 mutation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90355-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breviario D., Hinnebusch A., Cannon J., Tatchell K., Dhar R. Carbon source regulation of RAS1 expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the phenotypes of ras2- cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4152–4156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camonis J. H., Jacquet M. A new RAS mutation that suppresses the CDC25 gene requirement for growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2980–2983. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camus C., Boy-Marcotte E., Jacquet M. Two subclasses of guanine exchange factor (GEF) domains revealed by comparison of activities of chimeric genes constructed from CDC25, SDC25 and BUD5 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1994 Oct 28;245(2):167–176. doi: 10.1007/BF00283264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chardin P., Camonis J. H., Gale N. W., van Aelst L., Schlessinger J., Wigler M. H., Bar-Sagi D. Human Sos1: a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Ras that binds to GRB2. Science. 1993 May 28;260(5112):1338–1343. doi: 10.1126/science.8493579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Créchet J. B., Poullet P., Mistou M. Y., Parmeggiani A., Camonis J., Boy-Marcotte E., Damak F., Jacquet M. Enhancement of the GDP-GTP exchange of RAS proteins by the carboxyl-terminal domain of SCD25. Science. 1990 May 18;248(4957):866–868. doi: 10.1126/science.2188363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damak F., Boy-Marcotte E., Le-Roscouet D., Guilbaud R., Jacquet M. SDC25, a CDC25-like gene which contains a RAS-activating domain and is a dispensable gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):202–212. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFeo-Jones D., Scolnick E. M., Koller R., Dhar R. ras-Related gene sequences identified and isolated from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):707–709. doi: 10.1038/306707a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Démolis N., Mallet L., Bussereau F., Jacquet M. RIM2, MSI1 and PGI1 are located within an 8 kb segment of Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome II, which also contains the putative ribosomal gene L21 and a new putative essential gene with a leucine zipper motif. Yeast. 1993 Jun;9(6):645–659. doi: 10.1002/yea.320090611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Démolis N., Mallet L., Jacquet M. A 12.5 kb fragment of the yeast chromosome II contains two adjacent genes encoding ribosomal proteins and six putative new genes, one of which encodes a putative transcriptional factor. Yeast. 1994 Nov;10(11):1511–1525. doi: 10.1002/yea.320101116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnsworth C. L., Freshney N. W., Rosen L. B., Ghosh A., Greenberg M. E., Feig L. A. Calcium activation of Ras mediated by neuronal exchange factor Ras-GRF. Nature. 1995 Aug 10;376(6540):524–527. doi: 10.1038/376524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haney S. A., Broach J. R. Cdc25p, the guanine nucleotide exchange factor for the Ras proteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, promotes exchange by stabilizing Ras in a nucleotide-free state. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 17;269(24):16541–16548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., Mortimer R. K., Culotti J., Culotti M. Genetic Control of the Cell Division Cycle in Yeast: V. Genetic Analysis of cdc Mutants. Genetics. 1973 Jun;74(2):267–286. doi: 10.1093/genetics/74.2.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. E., Myers A. M., Koerner T. J., Tzagoloff A. Yeast/E. coli shuttle vectors with multiple unique restriction sites. Yeast. 1986 Sep;2(3):163–167. doi: 10.1002/yea.320020304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman C. S., Winston F. A ten-minute DNA preparation from yeast efficiently releases autonomous plasmids for transformation of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquet E., Baouz S., Parmeggiani A. Characterization of mammalian C-CDC25Mm exchange factor and kinetic properties of the exchange reaction intermediate p21.C-CDC25Mm. Biochemistry. 1995 Sep 26;34(38):12347–12354. doi: 10.1021/bi00038a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplon T., Jacquet M. The cellular content of Cdc25p, the Ras exchange factor in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is regulated by destabilization through a cyclin destruction box. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 1;270(35):20742–20747. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.35.20742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li N., Batzer A., Daly R., Yajnik V., Skolnik E., Chardin P., Bar-Sagi D., Margolis B., Schlessinger J. Guanine-nucleotide-releasing factor hSos1 binds to Grb2 and links receptor tyrosine kinases to Ras signalling. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):85–88. doi: 10.1038/363085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mager W. H., De Kruijff A. J. Stress-induced transcriptional activation. Microbiol Rev. 1995 Sep;59(3):506–531. doi: 10.1128/mr.59.3.506-531.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martegani E., Vanoni M., Zippel R., Coccetti P., Brambilla R., Ferrari C., Sturani E., Alberghina L. Cloning by functional complementation of a mouse cDNA encoding a homologue of CDC25, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAS activator. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2151–2157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05274.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mistou M. Y., Jacquet E., Poullet P., Rensland H., Gideon P., Schlichting I., Wittinghofer A., Parmeggiani A. Mutations of Ha-ras p21 that define important regions for the molecular mechanism of the SDC25 C-domain, a guanine nucleotide dissociation stimulator. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2391–2397. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05303.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mézard C., Pompon D., Nicolas A. Recombination between similar but not identical DNA sequences during yeast transformation occurs within short stretches of identity. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):659–670. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90434-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. At least 1400 base pairs of 5'-flanking DNA is required for the correct expression of the HO gene in yeast. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):213–223. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80117-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nugent J. H., Alfa C. E., Young T., Hyams J. S. Conserved structural motifs in cyclins identified by sequence analysis. J Cell Sci. 1991 Jul;99(Pt 3):669–674. doi: 10.1242/jcs.99.3.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porfiri E., Evans T., Chardin P., Hancock J. F. Prenylation of Ras proteins is required for efficient hSOS1-promoted guanine nucleotide exchange. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 9;269(36):22672–22677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers S., Kataoka T., Fasano O., Goldfarb M., Strathern J., Broach J., Wigler M. Genes in S. cerevisiae encoding proteins with domains homologous to the mammalian ras proteins. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):607–612. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90340-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rey I., Schweighoffer F., Barlat I., Camonis J., Boy-Marcotte E., Guilbaud R., Jacquet M., Tocque B. The COOH-domain of the product of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae SCD25 gene elicits activation of p21-ras proteins in mammalian cells. Oncogene. 1991 Feb;6(2):347–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronne H. Glucose repression in fungi. Trends Genet. 1995 Jan;11(1):12–17. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(00)88980-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M., Bradshaw-Rouse J., Markwardt D., Heideman W. Changes in gene expression in the Ras/adenylate cyclase system of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: correlation with cAMP levels and growth arrest. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Jul;4(7):757–765. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.7.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M. E., Brown T. A., Trumpower B. L. A rapid and simple method for preparation of RNA from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):3091–3092. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.3091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweighoffer F., Cai H., Chevallier-Multon M. C., Fath I., Cooper G., Tocque B. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae SDC25 C-domain gene product overcomes the dominant inhibitory activity of Ha-Ras Asn-17. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):39–43. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweighoffer F., Faure M., Fath I., Chevallier-Multon M. C., Apiou F., Dutrillaux B., Sturani E., Jacquet M., Tocque B. Identification of a human guanine nucleotide-releasing factor (H-GRF55) specific for Ras proteins. Oncogene. 1993 Jun;8(6):1477–1485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shou C., Farnsworth C. L., Neel B. G., Feig L. A. Molecular cloning of cDNAs encoding a guanine-nucleotide-releasing factor for Ras p21. Nature. 1992 Jul 23;358(6384):351–354. doi: 10.1038/358351a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Nakafuku M., Satoh T., Marshall M. S., Gibbs J. B., Matsumoto K., Kaziro Y., Toh-e A. S. cerevisiae genes IRA1 and IRA2 encode proteins that may be functionally equivalent to mammalian ras GTPase activating protein. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):803–807. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90094-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Morishita T., Hashimoto Y., Hattori S., Nakamura S., Shibuya M., Matuoka K., Takenawa T., Kurata T., Nagashima K. C3G, a guanine nucleotide-releasing protein expressed ubiquitously, binds to the Src homology 3 domains of CRK and GRB2/ASH proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):3443–3447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatchell K., Robinson L. C., Breitenbach M. RAS2 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is required for gluconeogenic growth and proper response to nutrient limitation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3785–3789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thierry A., Gaillon L., Galibert F., Dujon B. Construction of a complete genomic library of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and physical mapping of chromosome XI at 3.7 kb resolution. Yeast. 1995 Feb;11(2):121–135. doi: 10.1002/yea.320110204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Cameron S., Sass P., Zoller M., Wigler M. Three different genes in S. cerevisiae encode the catalytic subunits of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90223-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschumper G., Carbon J. Sequence of a yeast DNA fragment containing a chromosomal replicator and the TRP1 gene. Gene. 1980 Jul;10(2):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90133-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Aelst L., Boy-Marcotte E., Camonis J. H., Thevelein J. M., Jacquet M. The C-terminal part of the CDC25 gene product plays a key role in signal transduction in the glucose-induced modulation of cAMP level in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 13;193(3):675–680. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19386.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]