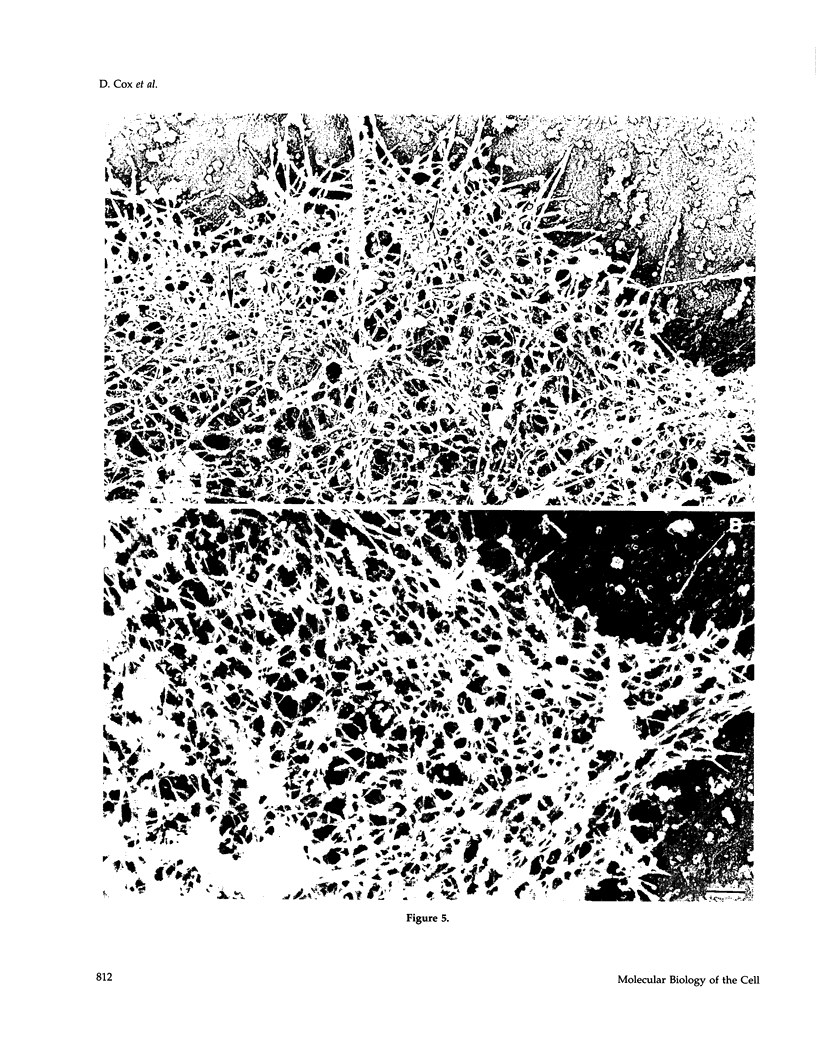
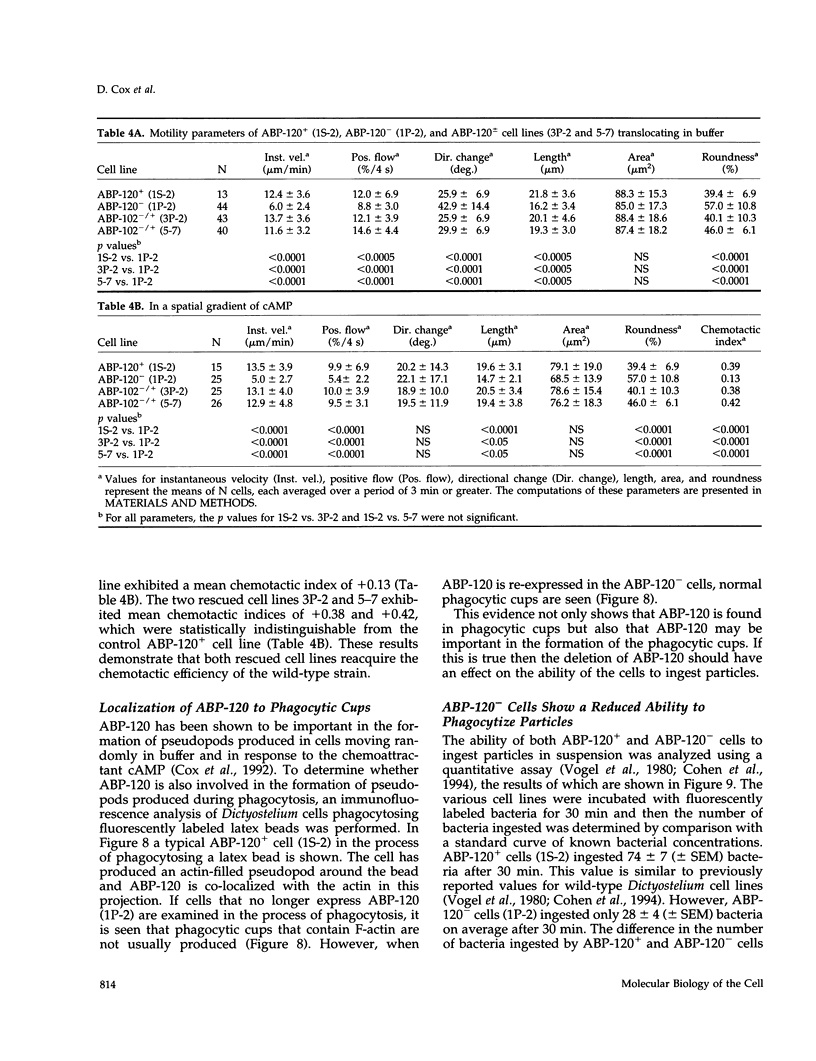
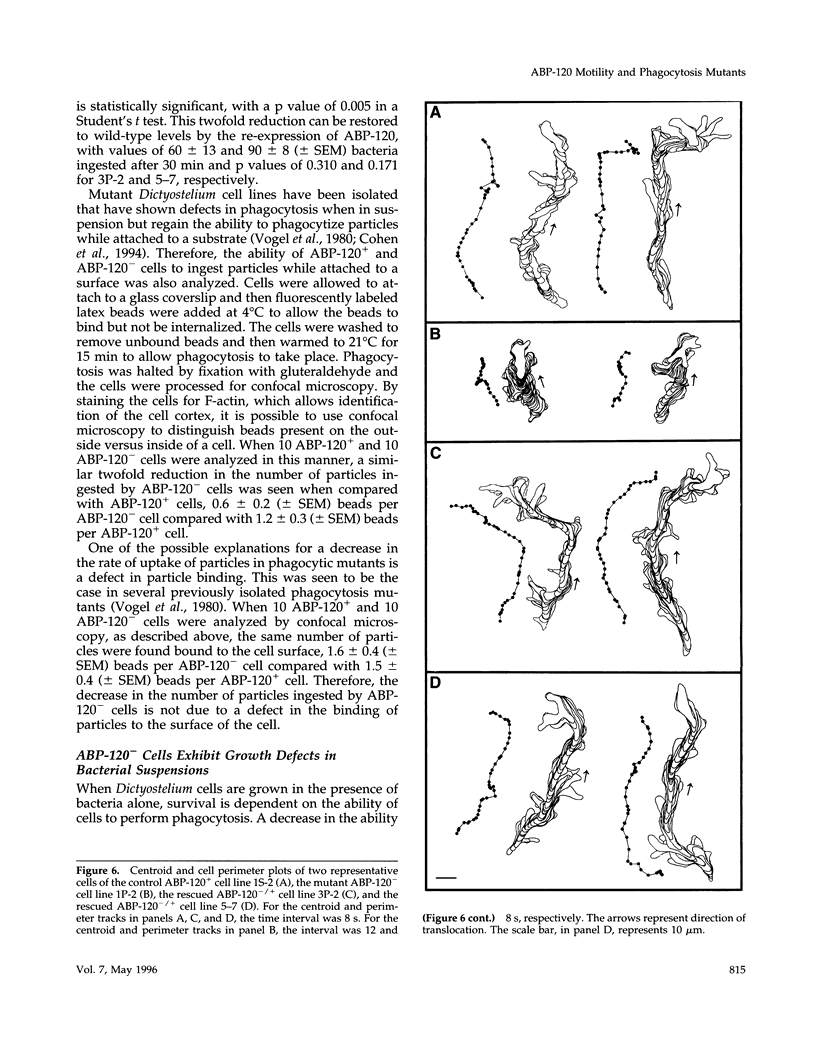
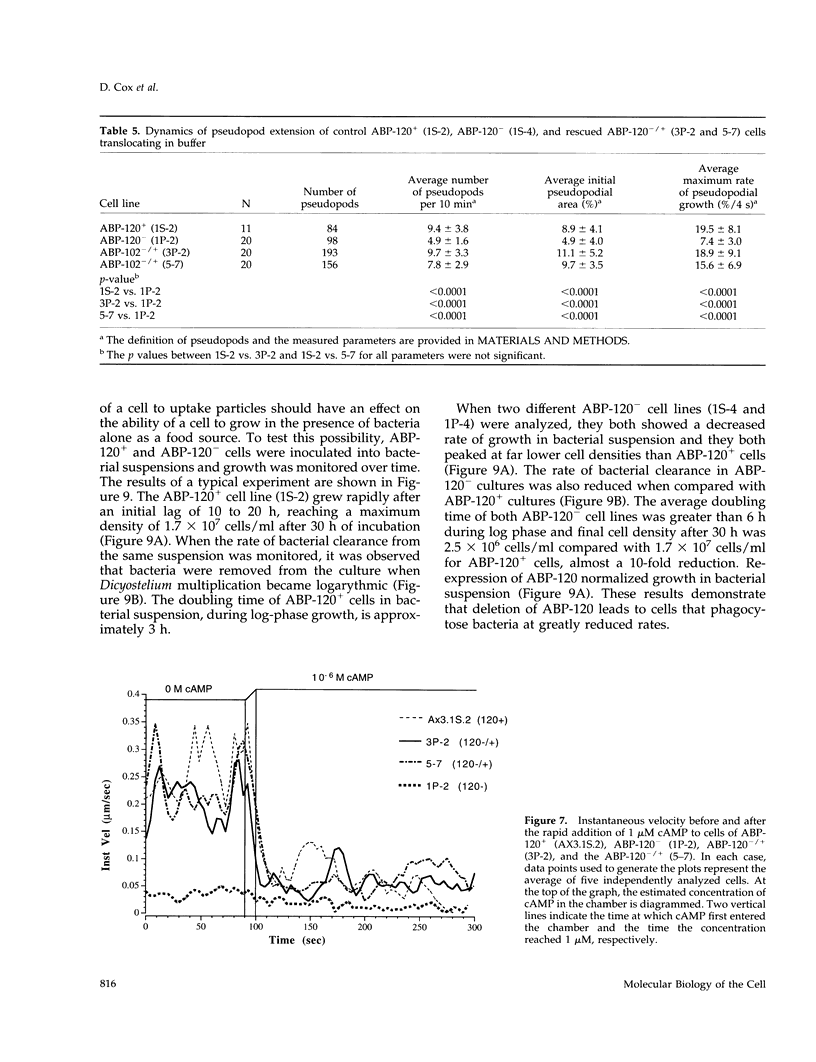
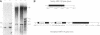Abstract
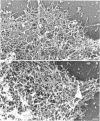
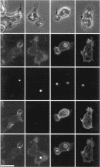
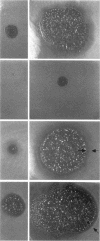
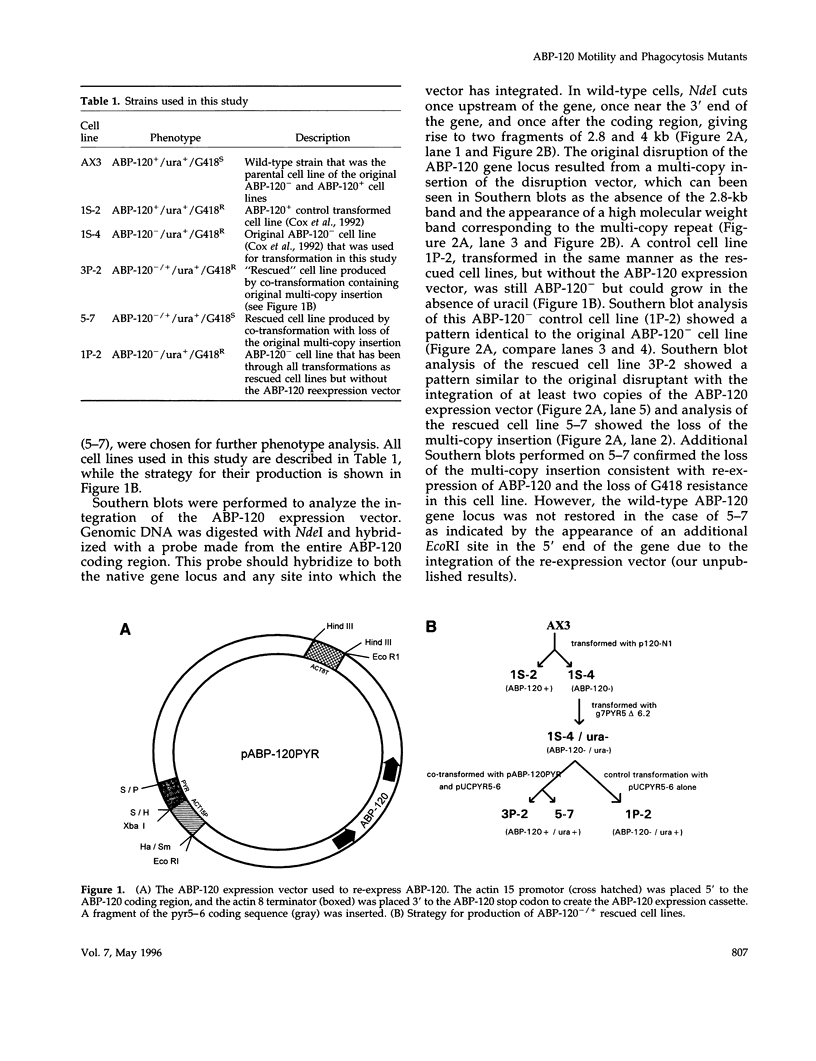
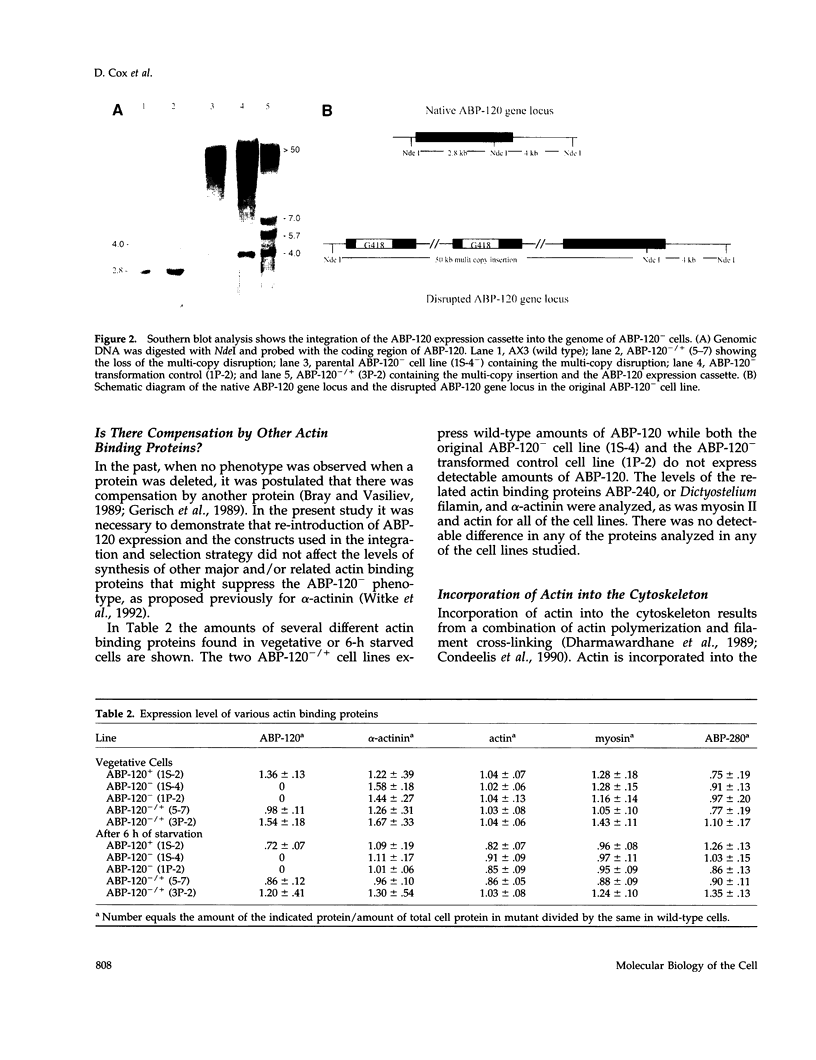
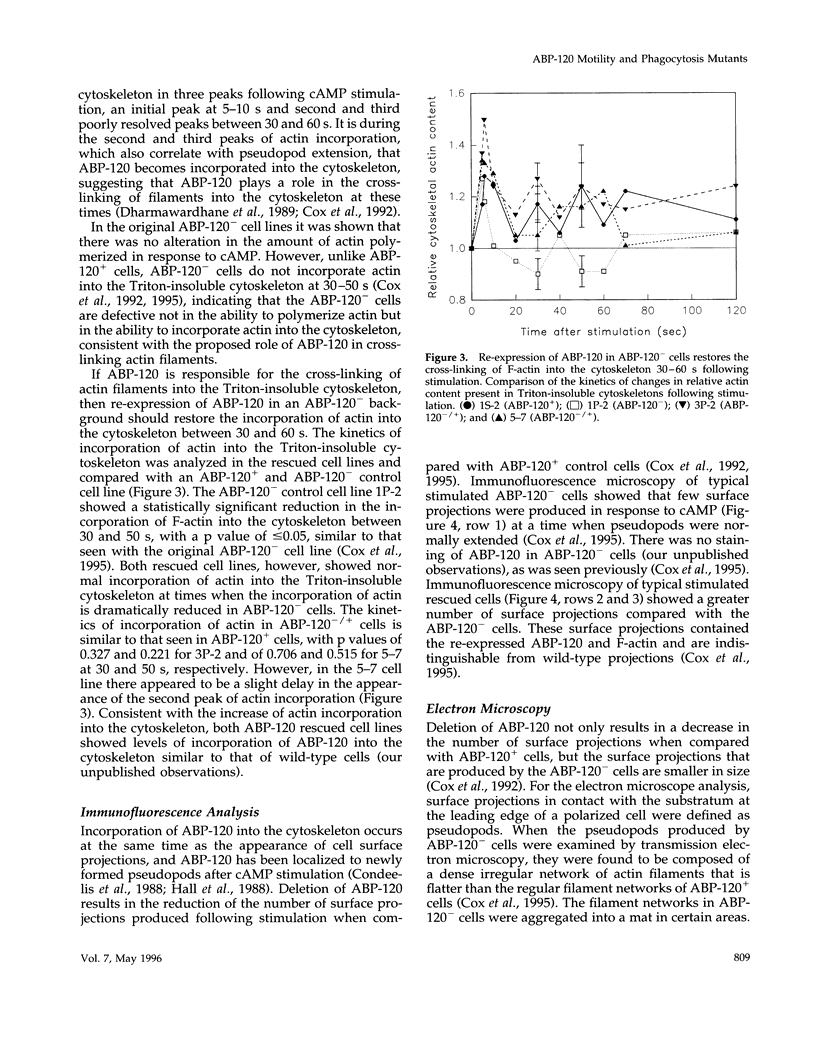
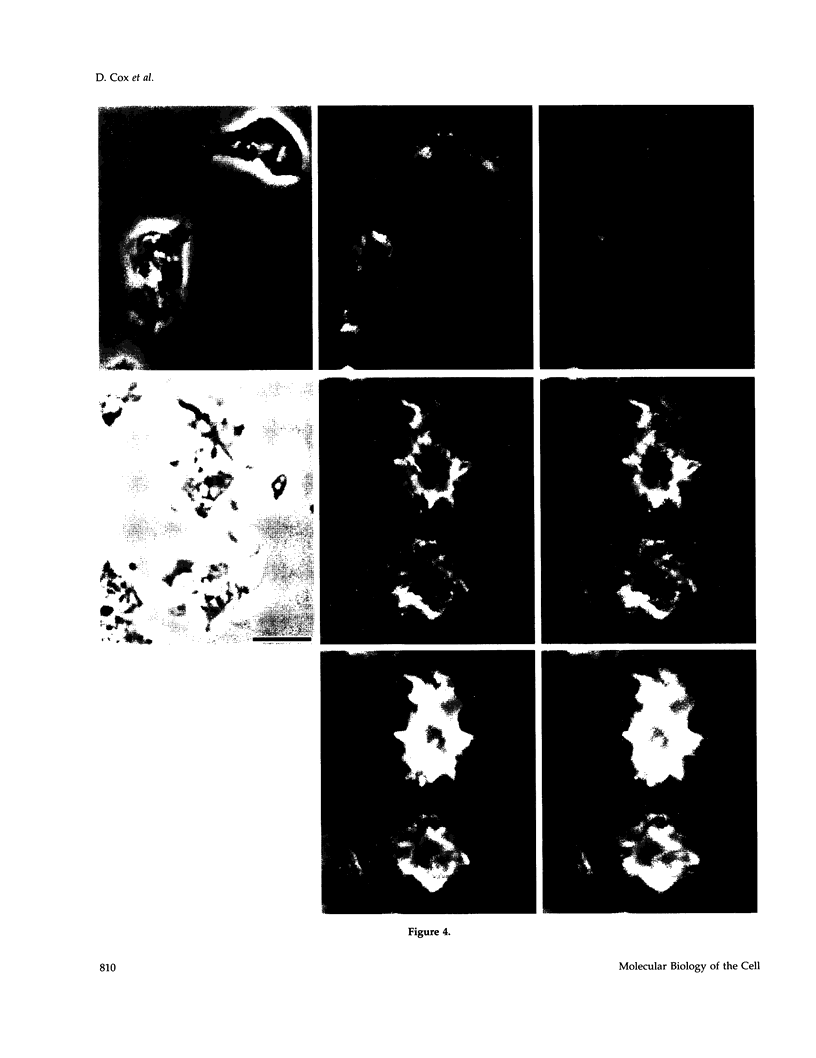
The actin binding protein ABP-120 has been proposed to cross-link actin filaments in nascent pseudopods, in a step required for normal pseudopod extension in motile Dictyostelium amoebae. To test this hypothesis, cell lines that lack ABP-120 were created independently either by chemical mutagenesis or homologous recombination. Different phenotypes were reported in these two studies. The chemical mutant shows only a subtle defect in actin cross-linking, while the homologous recombinant mutants show profound defects in actin cross-linking, cytoskeletal structure, pseudopod number and size, cell motility and chemotaxis and, as shown here, phagocytosis. To resolve the controversy as to what the ABP-120- phenotype is, ABP-120 was re-expressed in an ABP-120- cell line created by homologous recombination. Two independently "rescued" cell lines that express wild-type levels of ABP-120 were analyzed. In both rescued cell lines, actin incorporation into the cytoskeleton, pseudopod formation, cell morphology, instantaneous velocity, phagocytosis, and chemotaxis were restored to wild-type levels. There is no alteration in the expression levels of several related actin binding proteins in either the original ABP-120- cell line or in the rescued cell lines, leading to the conclusion that neither the aberrant phenotype observed in ABP-120- cells nor the normal phenotype reasserted in rescued cells can be attributed to alterations in the levels of other abundant and related actin binding proteins. Re-expression of ABP-120 in ABP-120- cells reestablishes normal structural and behavioral parameters, demonstrating that the severity and properties of the structural and behavioral defects of ABP-120- cell lines produced by homologous recombination are the direct result of the absence of ABP-120.
Full text
PDF





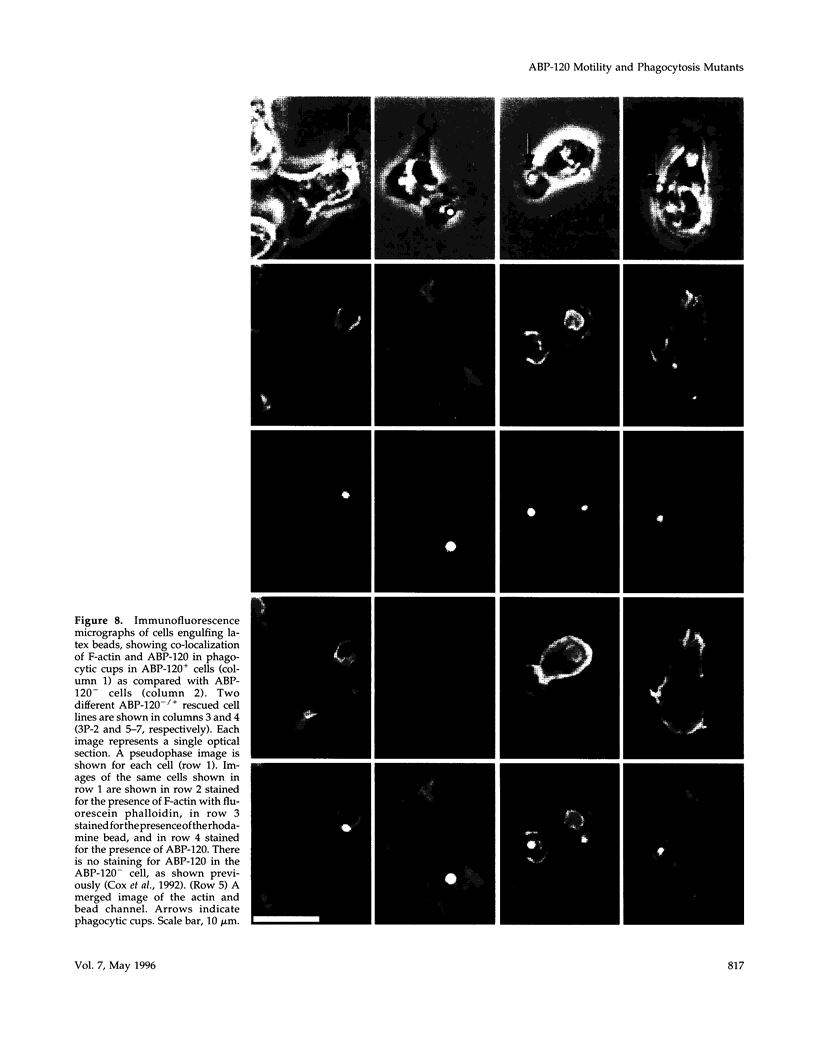
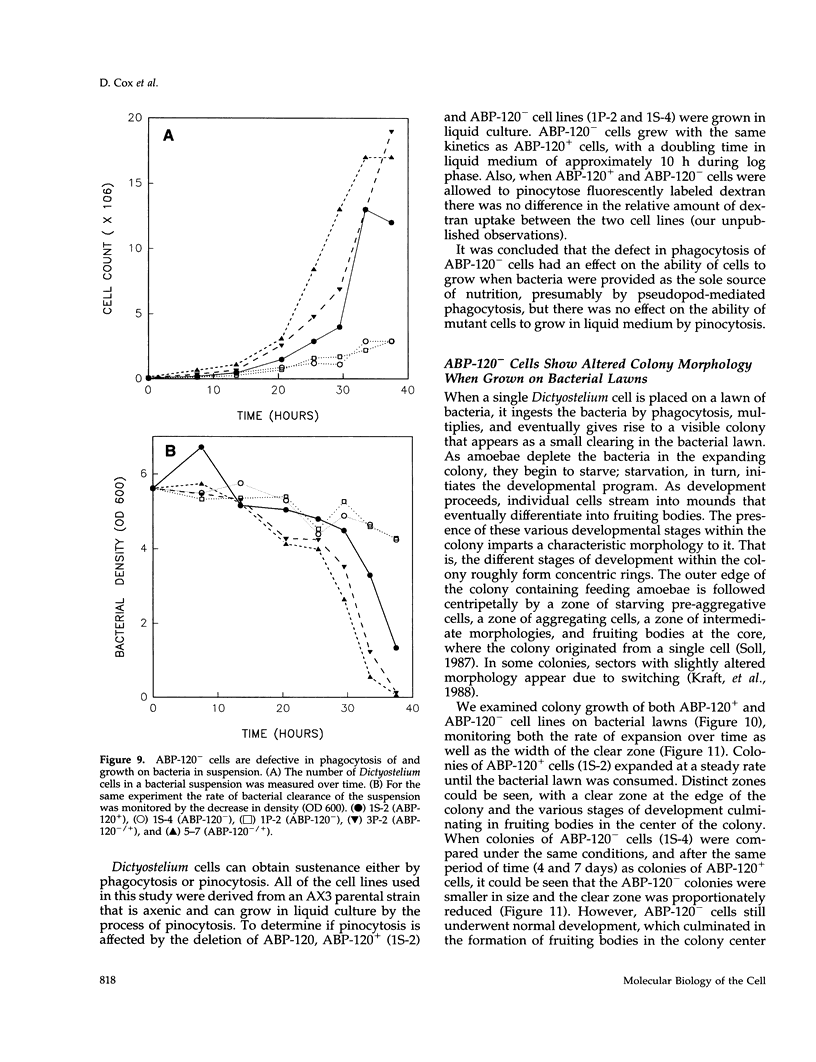
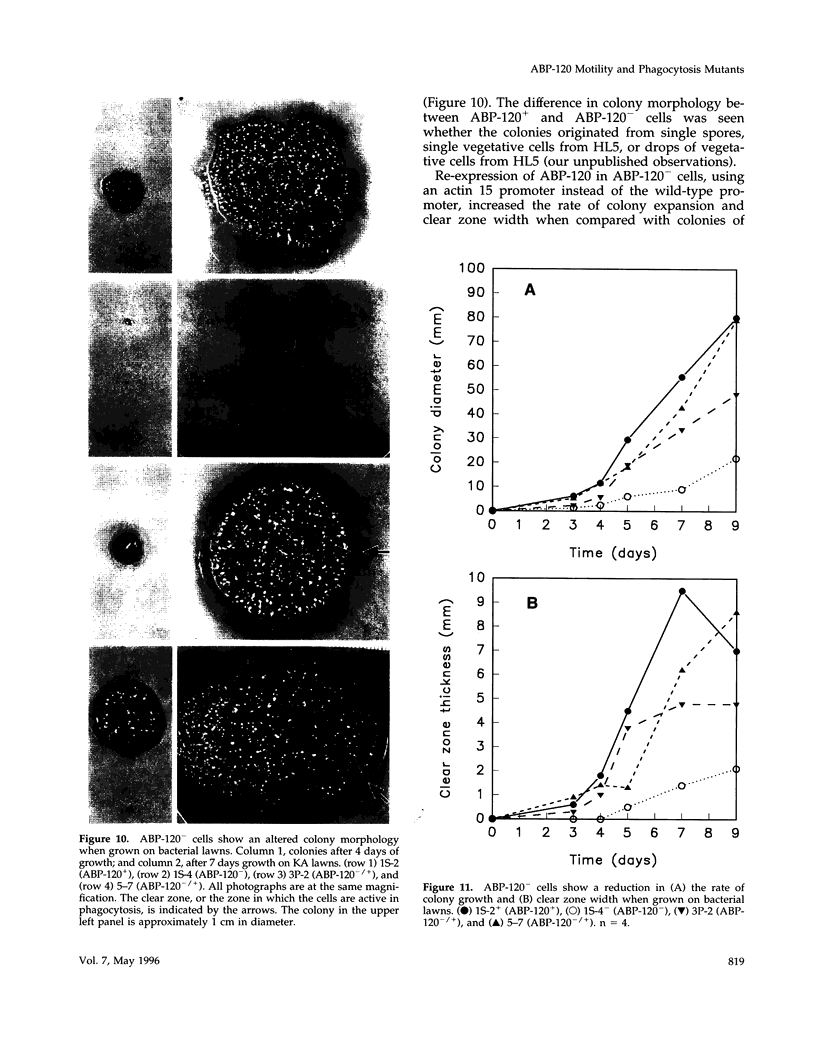




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bray D., Vasiliev J. Cell motility. Networks from mutants. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):203–204. doi: 10.1038/338203a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brink M., Gerisch G., Isenberg G., Noegel A. A., Segall J. E., Wallraff E., Schleicher M. A Dictyostelium mutant lacking an F-actin cross-linking protein, the 120-kD gelation factor. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1477–1489. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carboni J. M., Condeelis J. S. Ligand-induced changes in the location of actin, myosin, 95K (alpha-actinin), and 120K protein in amebae of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;100(6):1884–1893. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.6.1884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C. J., Bacon R., Clarke M., Joiner K., Mellman I. Dictyostelium discoideum mutants with conditional defects in phagocytosis. J Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;126(4):955–966. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.4.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. M., Knecht D., Lodish H. F., Loomis W. F. DNA sequences required for expression of a Dictyostelium actin gene. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3361–3366. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04651.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condeelis J., Bresnick A., Demma M., Dharmawardhane S., Eddy R., Hall A. L., Sauterer R., Warren V. Mechanisms of amoeboid chemotaxis: an evaluation of the cortical expansion model. Dev Genet. 1990;11(5-6):333–340. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020110504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condeelis J. Life at the leading edge: the formation of cell protrusions. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:411–444. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.09.110193.002211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condeelis J. Understanding the cortex of crawling cells: insights from Dictyostelium. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;3(11):371–376. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90085-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condeelis J., Vahey M., Carboni J. M., DeMey J., Ogihara S. Properties of the 120,000- and 95,000-dalton actin-binding proteins from Dictyostelium discoideum and their possible functions in assembling the cytoplasmic matrix. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 2):119s–126s. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.119s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D., Condeelis J., Wessels D., Soll D., Kern H., Knecht D. A. Targeted disruption of the ABP-120 gene leads to cells with altered motility. J Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;116(4):943–955. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.4.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D., Ridsdale J. A., Condeelis J., Hartwig J. Genetic deletion of ABP-120 alters the three-dimensional organization of actin filaments in Dictyostelium pseudopods. J Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;128(5):819–835. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.5.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmawardhane S., Warren V., Hall A. L., Condeelis J. Changes in the association of actin-binding proteins with the actin cytoskeleton during chemotactic stimulation of Dictyostelium discoideum. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1989;13(1):57–63. doi: 10.1002/cm.970130107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynes J. L., Firtel R. A. Molecular complementation of a genetic marker in Dictyostelium using a genomic DNA library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7966–7970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke J., Kessin R. A defined minimal medium for axenic strains of Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2157–2161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., Lynch T. J., Brzeska H., Korn E. D. Myosin I is located at the leading edges of locomoting Dictyostelium amoebae. Nature. 1989 Sep 28;341(6240):328–331. doi: 10.1038/341328a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerisch G., Segall J. E., Wallraff E. Isolation and behavioral analysis of mutants defective in cytoskeletal proteins. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1989;14(1):75–79. doi: 10.1002/cm.970140115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg S., el Khoury J., di Virgilio F., Kaplan E. M., Silverstein S. C. Ca(2+)-independent F-actin assembly and disassembly during Fc receptor-mediated phagocytosis in mouse macrophages. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(4):757–767. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.4.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. L., Schlein A., Condeelis J. Relationship of pseudopod extension to chemotactic hormone-induced actin polymerization in amoeboid cells. J Cell Biochem. 1988 Jul;37(3):285–299. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240370304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwig J. H., Kwiatkowski D. J. Actin-binding proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;3(1):87–97. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90170-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwig J. H., Shevlin P. The architecture of actin filaments and the ultrastructural location of actin-binding protein in the periphery of lung macrophages. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):1007–1020. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.1007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvath L. Regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis: correlations with actin polymerization. Cancer Invest. 1990;8(6):651–654. doi: 10.3109/07357909009018937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard T. H., Oresajo C. O. A method for quantifying F-actin in chemotactic peptide activated neutrophils: study of the effect of tBOC peptide. Cell Motil. 1985;5(6):545–557. doi: 10.1002/cm.970050609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knecht D. A., Jung J., Matthews L. Quantification of transformation efficiency using a new method for clonal growth and selection of axenic Dictyostelium cells. Dev Genet. 1990;11(5-6):403–409. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020110513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knecht D. A., Loomis W. F. Antisense RNA inactivation of myosin heavy chain gene expression in Dictyostelium discoideum. Science. 1987 May 29;236(4805):1081–1086. doi: 10.1126/science.3576221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft B., Steinbrech D., Yang M., Soll D. R. High-frequency switching in Dictyostelium. Dev Biol. 1988 Nov;130(1):198–208. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90426-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Modular organization of actin crosslinking proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Mar;16(3):87–92. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogihara S., Carboni J., Condeelis J. Electron microscopic localization of myosin II and ABP-120 in the cortical actin matrix of Dictyostelium amoebae using IgG-gold conjugates. Dev Genet. 1988;9(4-5):505–520. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020090427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven E. P., Axline S. G. Subplasmalemmal microfilaments and microtubules in resting and phagocytizing cultivated macrophages. J Cell Biol. 1973 Oct;59(1):12–27. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.1.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz M. P., Wayne D. B., Pearlman A. L. Extension of filopodia by motor-dependent actin assembly. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1992;22(3):160–169. doi: 10.1002/cm.970220303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelden E., Knecht D. A. Mutants lacking myosin II cannot resist forces generated during multicellular morphogenesis. J Cell Sci. 1995 Mar;108(Pt 3):1105–1115. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.3.1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shutt D. C., Wessels D., Wagenknecht K., Chandrasekhar A., Hitt A. L., Luna E. J., Soll D. R. Ponticulin plays a role in the positional stabilization of pseudopods. J Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;131(6 Pt 1):1495–1506. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.6.1495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll D. R. "DMS," a computer-assisted system for quantitating motility, the dynamics of cytoplasmic flow, and pseudopod formation: its application to Dictyostelium chemotaxis. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1988;10(1-2):91–106. doi: 10.1002/cm.970100114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll D. R. Methods for manipulating and investigating developmental timing in Dictyostelium discoideum. Methods Cell Biol. 1987;28:413–431. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61660-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll D. R. The use of computers in understanding how animal cells crawl. Int Rev Cytol. 1995;163:43–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll D. R., Voss E., Varnum-Finney B., Wessels D. "Dynamic Morphology System": a method for quantitating changes in shape, pseudopod formation, and motion in normal and mutant amoebae of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Cell Biochem. 1988 Jun;37(2):177–192. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240370205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stendahl O. I., Hartwig J. H., Brotschi E. A., Stossel T. P. Distribution of actin-binding protein and myosin in macrophages during spreading and phagocytosis. J Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;84(2):215–224. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.2.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens C. G., Snyderman R. Cyclic nucleotides regulate the morphologic alterations required for chemotaxis in monocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1192–1197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylwester A., Wessels D., Anderson S. A., Warren R. Q., Shutt D. C., Kennedy R. C., Soll D. R. HIV-induced syncytia of a T cell line form single giant pseudopods and are motile. J Cell Sci. 1993 Nov;106(Pt 3):941–953. doi: 10.1242/jcs.106.3.941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titus M. A., Wessels D., Spudich J. A., Soll D. The unconventional myosin encoded by the myoA gene plays a role in Dictyostelium motility. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Feb;4(2):233–246. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.2.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varnum-Finney B. J., Voss E., Soll D. R. Frequency and orientation of pseudopod formation of Dictyostelium discoideum amebae chemotaxing in a spatial gradient: further evidence for a temporal mechanism. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1987;8(1):18–26. doi: 10.1002/cm.970080104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varnum B., Soll D. R. Effects of cAMP on single cell motility in Dictyostelium. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):1151–1155. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.1151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel G., Thilo L., Schwarz H., Steinhart R. Mechanism of phagocytosis in Dictyostelium discoideum: phagocytosis is mediated by different recognition sites as disclosed by mutants with altered phagocytotic properties. J Cell Biol. 1980 Aug;86(2):456–465. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.2.456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessels D., Murray J., Jung G., Hammer J. A., 3rd, Soll D. R. Myosin IB null mutants of Dictyostelium exhibit abnormalities in motility. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1991;20(4):301–315. doi: 10.1002/cm.970200406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessels D., Schroeder N. A., Voss E., Hall A. L., Condeelis J., Soll D. R. cAMP-mediated inhibition of intracellular particle movement and actin reorganization in Dictyostelium. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2841–2851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessels D., Titus M., Soll D. R. A Dictyostelium myosin I plays a crucial role in regulating the frequency of pseudopods formed on the substratum. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1996;33(1):64–79. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0169(1996)33:1<64::AID-CM7>3.0.CO;2-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witke W., Nellen W., Noegel A. Homologous recombination in the Dictyostelium alpha-actinin gene leads to an altered mRNA and lack of the protein. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4143–4148. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02760.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witke W., Schleicher M., Noegel A. A. Redundancy in the microfilament system: abnormal development of Dictyostelium cells lacking two F-actin cross-linking proteins. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):53–62. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90205-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolosewick J. J., Condeelis J. Fine structure of gels prepared from an actin-binding protein and actin: comparison to cytoplasmic extracts and cortical cytoplasm in amoeboid cells of cortical cytoplasm in amoeboid cells of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Cell Biochem. 1986;30(3):227–243. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240300305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H., Sullivan S. J. Sensory adaptation of leukocytes to chemotactic peptides. J Cell Biol. 1979 Aug;82(2):517–527. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.2.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]