Abstract
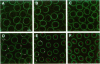
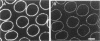
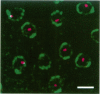
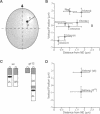
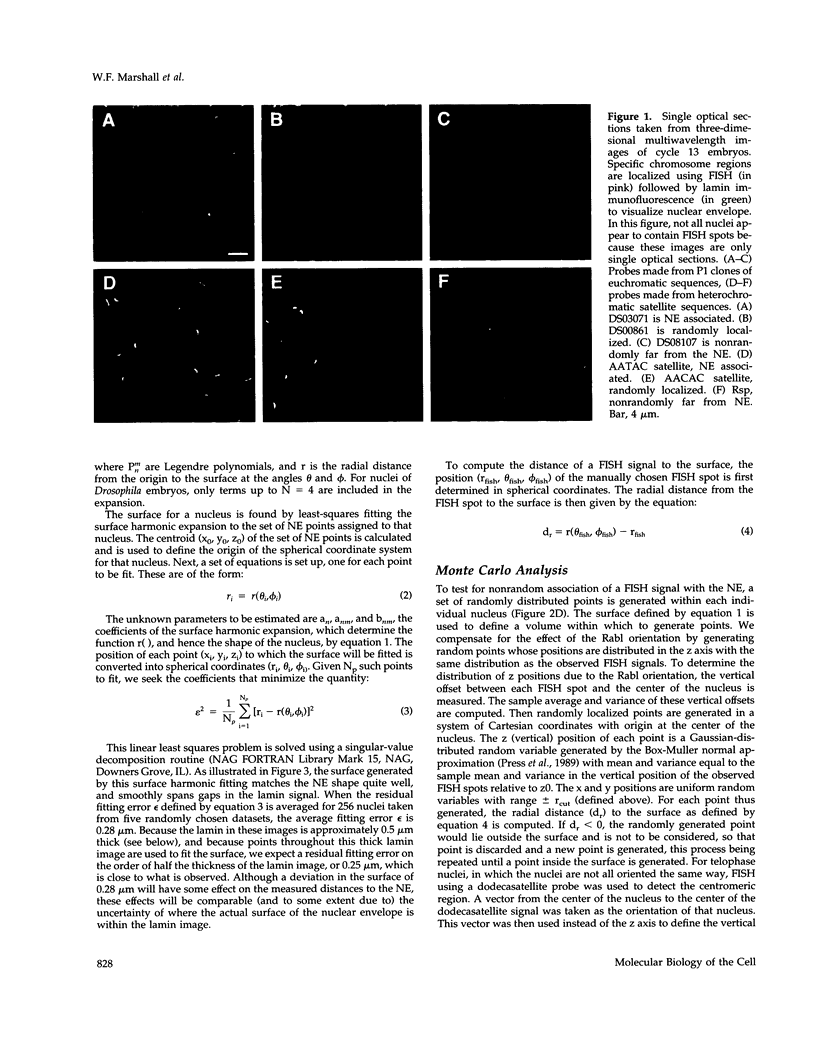
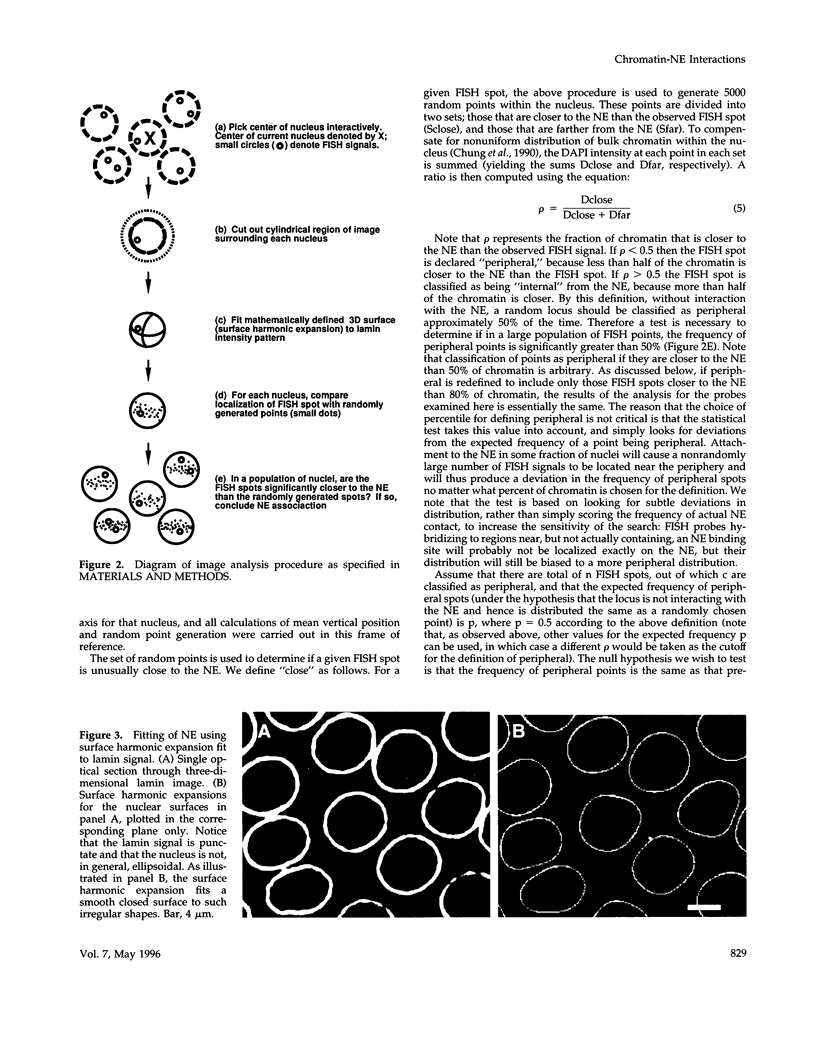
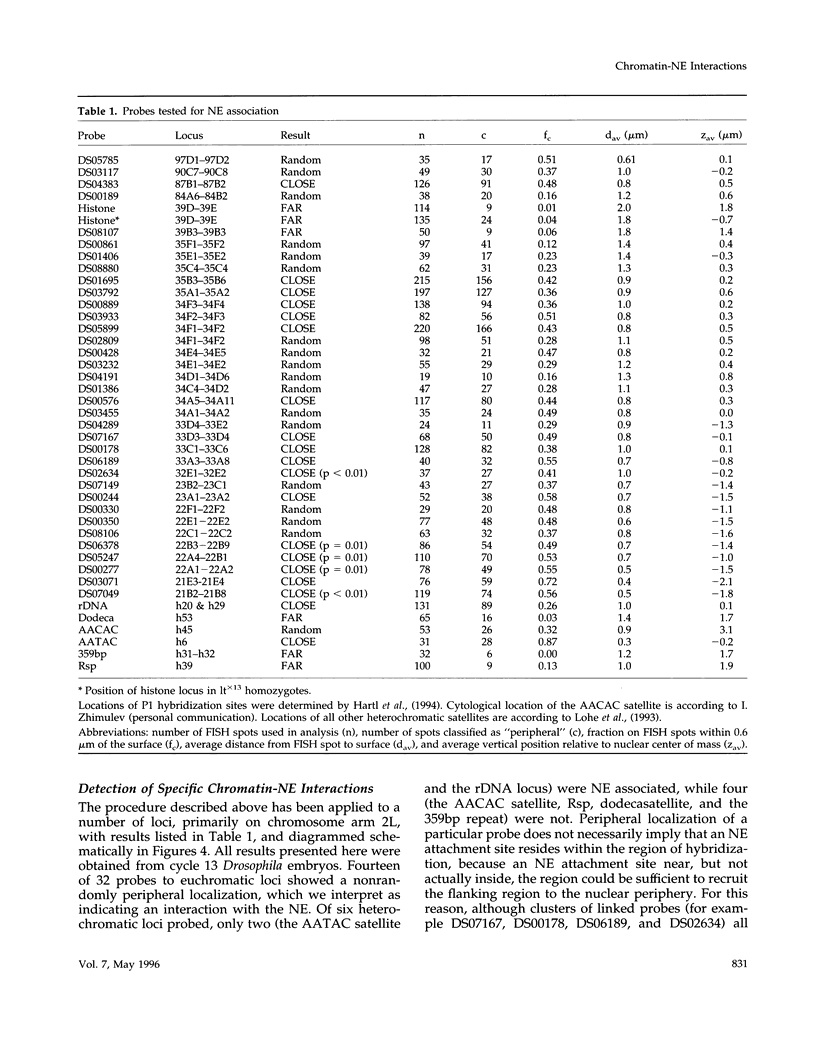
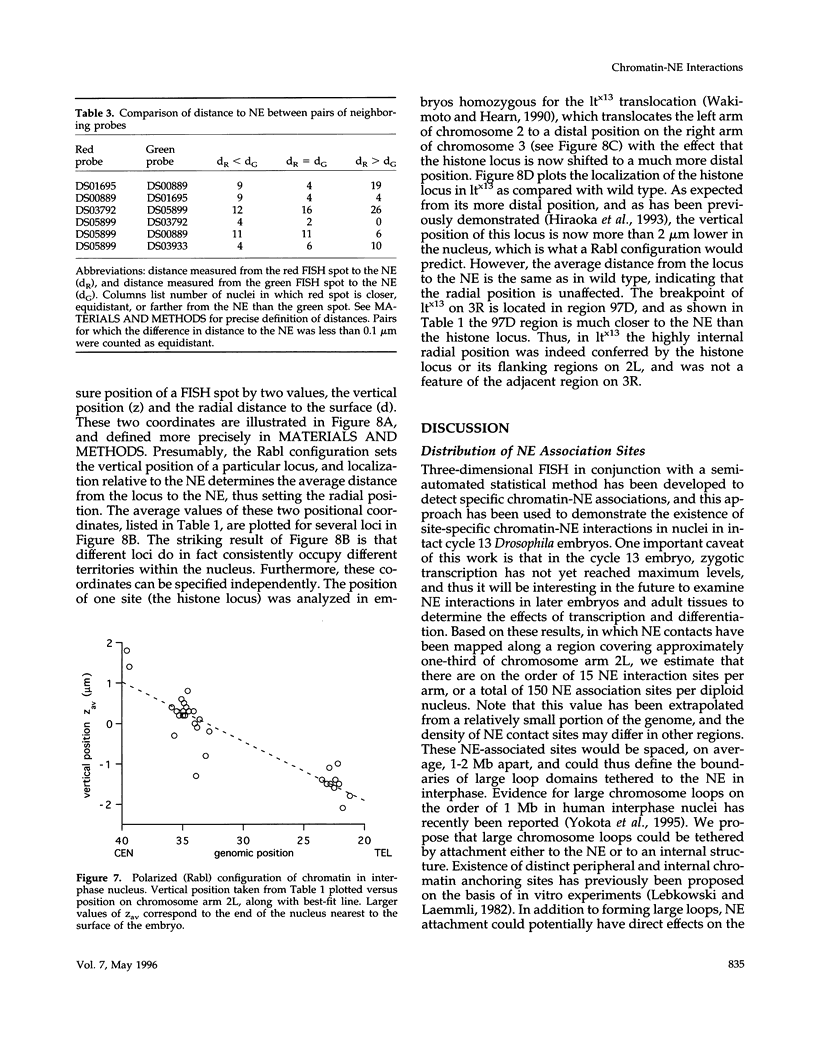
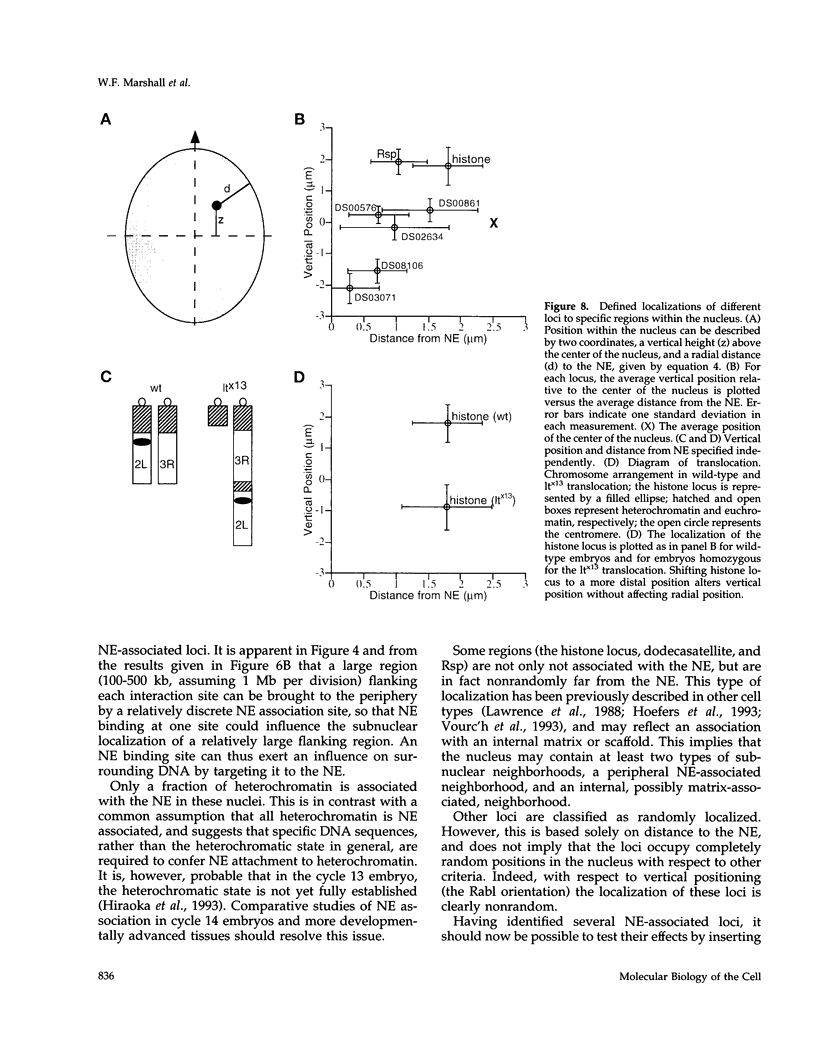
Specific interactions of chromatin with the nuclear envelope (NE) in early embryos of Drosophila melanogaster have been mapped and analyzed. Using fluorescence in situ hybridization, the three-dimensional positions of 42 DNA probes, primarily to chromosome 2L, have been mapped in nuclei of intact Drosophila embryos, revealing five euchromatic and two heterochromatic regions associated with the NE. These results predict that there are approximately 15 NE contacts per chromosome arm, which delimit large chromatin loops of approximately 1-2 Mb. These NE association sites do not strictly correlate with scaffold-attachment regions, heterochromatin, or binding sites of known chromatin proteins. Pairs of neighboring probes surrounding one NE association site were used to delimit the NE association site more precisely, suggesting that peripheral localization of a large stretch of chromatin is likely to result from NE association at a single discrete site. These NE interactions are not established until after telophase, by which time the nuclear envelope has reassembled around the chromosomes, and they are thus unlikely to be involved in binding of NE vesicles to chromosomes following mitosis. Analysis of positions of these probes also reveals that the interphase nucleus is strongly polarized in a Rabl configuration which, together with specific targeting to the NE or to the nuclear interior, results in each locus occupying a highly determined position within the nucleus.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agard D. A., Hiraoka Y., Shaw P., Sedat J. W. Fluorescence microscopy in three dimensions. Methods Cell Biol. 1989;30:353–377. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60986-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belmont A. S., Zhai Y., Thilenius A. Lamin B distribution and association with peripheral chromatin revealed by optical sectioning and electron microscopy tomography. J Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;123(6 Pt 2):1671–1685. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.6.1671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyajati C., Worcel A. Isolation, characterization, and structure of the folded interphase genome of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1976 Nov;9(3):393–407. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berezney R., Coffey D. S. Identification of a nuclear protein matrix. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Oct 23;60(4):1410–1417. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90355-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billia F., de Boni U. Localization of centromeric satellite and telomeric DNA sequences in dorsal root ganglion neurons, in vitro. J Cell Sci. 1991 Sep;100(Pt 1):219–226. doi: 10.1242/jcs.100.1.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G. Gene gating: a hypothesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8527–8529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmena M., Abad J. P., Villasante A., Gonzalez C. The Drosophila melanogaster dodecasatellite sequence is closely linked to the centromere and can form connections between sister chromatids during mitosis. J Cell Sci. 1993 May;105(Pt 1):41–50. doi: 10.1242/jcs.105.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung H. M., Shea C., Fields S., Taub R. N., Van der Ploeg L. H., Tse D. B. Architectural organization in the interphase nucleus of the protozoan Trypanosoma brucei: location of telomeres and mini-chromosomes. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2611–2619. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07443.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comings D. E. Arrangement of chromatin in the nucleus. Hum Genet. 1980 Feb;53(2):131–143. doi: 10.1007/BF00273484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer T., Kurz A., Zirbel R., Dietzel S., Rinke B., Schröck E., Speicher M. R., Mathieu U., Jauch A., Emmerich P. Role of chromosome territories in the functional compartmentalization of the cell nucleus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1993;58:777–792. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1993.058.01.085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupraw E. J. THE ORGANIZATION OF NUCLEI AND CHROMOSOMES IN HONEYBEE EMBRYONIC CELLS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jan;53(1):161–168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.1.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison J. R., Howard G. C. Non-random position of the A-T rich DNA sequences in early embryos of Drosophila virilis. Chromosoma. 1981;83(4):555–561. doi: 10.1007/BF00328279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foe V. E., Alberts B. M. Reversible chromosome condensation induced in Drosophila embryos by anoxia: visualization of interphase nuclear organization. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1623–1636. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foisner R., Gerace L. Integral membrane proteins of the nuclear envelope interact with lamins and chromosomes, and binding is modulated by mitotic phosphorylation. Cell. 1993 Jul 2;73(7):1267–1279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90355-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Laemmli U. K. Cohabitation of scaffold binding regions with upstream/enhancer elements of three developmentally regulated genes of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):521–530. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90877-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. A., Glass J. R., Taniura H., Hasel K. W., Blevitt J. M., Gerace L. The alpha-helical rod domain of human lamins A and C contains a chromatin binding site. EMBO J. 1993 Nov;12(11):4413–4424. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06126.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass J. R., Gerace L. Lamins A and C bind and assemble at the surface of mitotic chromosomes. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1047–1057. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl D. L., Nurminsky D. I., Jones R. W., Lozovskaya E. R. Genome structure and evolution in Drosophila: applications of the framework P1 map. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):6824–6829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.6824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan A. B., Errington R. J., White N. S., Jackson D. A., Cook P. R. Replication and transcription sites are colocalized in human cells. J Cell Sci. 1994 Feb;107(Pt 2):425–434. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.2.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilliker A. J., Appels R. The arrangement of interphase chromosomes: structural and functional aspects. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Dec;185(2):267–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90301-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraoka Y., Agard D. A., Sedat J. W. Temporal and spatial coordination of chromosome movement, spindle formation, and nuclear envelope breakdown during prometaphase in Drosophila melanogaster embryos. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):2815–2828. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraoka Y., Dernburg A. F., Parmelee S. J., Rykowski M. C., Agard D. A., Sedat J. W. The onset of homologous chromosome pairing during Drosophila melanogaster embryogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;120(3):591–600. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.3.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraoka Y., Minden J. S., Swedlow J. R., Sedat J. W., Agard D. A. Focal points for chromosome condensation and decondensation revealed by three-dimensional in vivo time-lapse microscopy. Nature. 1989 Nov 16;342(6247):293–296. doi: 10.1038/342293a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraoka Y., Swedlow J. R., Paddy M. R., Agard D. A., Sedat J. W. Three-dimensional multiple-wavelength fluorescence microscopy for the structural analysis of biological phenomena. Semin Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;2(3):153–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstrasser M., Mathog D., Gruenbaum Y., Saumweber H., Sedat J. W. Spatial organization of chromosomes in the salivary gland nuclei of Drosophila melanogaster. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;102(1):112–123. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.1.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstrasser M., Sedat J. W. Three-dimensional organization of Drosophila melanogaster interphase nuclei. II. Chromosome spatial organization and gene regulation. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;104(6):1471–1483. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.6.1471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison N., Weintraub H. Localization of DNAase I-sensitive sequences to specific regions of interphase nuclei. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):471–482. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90177-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izaurralde E., Mirkovitch J., Laemmli U. K. Interaction of DNA with nuclear scaffolds in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1988 Mar 5;200(1):111–125. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90337-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A., Dickinson P., Cook P. R. Attachment of DNA to the nucleoskeleton of HeLa cells examined using physiological conditions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 11;18(15):4385–4393. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.15.4385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James T. C., Eissenberg J. C., Craig C., Dietrich V., Hobson A., Elgin S. C. Distribution patterns of HP1, a heterochromatin-associated nonhistone chromosomal protein of Drosophila. Eur J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;50(1):170–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellum R., Schedl P. A group of scs elements function as domain boundaries in an enhancer-blocking assay. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2424–2431. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. B., Villnave C. A., Singer R. H. Sensitive, high-resolution chromatin and chromosome mapping in situ: presence and orientation of two closely integrated copies of EBV in a lymphoma line. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):51–61. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90530-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebkowski J. S., Laemmli U. K. Non-histone proteins and long-range organization of HeLa interphase DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 5;156(2):325–344. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90332-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohe A. R., Hilliker A. J., Roberts P. A. Mapping simple repeated DNA sequences in heterochromatin of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1993 Aug;134(4):1149–1174. doi: 10.1093/genetics/134.4.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loidl J. The initiation of meiotic chromosome pairing: the cytological view. Genome. 1990 Dec;33(6):759–778. doi: 10.1139/g90-115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludérus M. E., de Graaf A., Mattia E., den Blaauwen J. L., Grande M. A., de Jong L., van Driel R. Binding of matrix attachment regions to lamin B1. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):949–959. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90245-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludérus M. E., den Blaauwen J. L., de Smit O. J., Compton D. A., van Driel R. Binding of matrix attachment regions to lamin polymers involves single-stranded regions and the minor groove. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;14(9):6297–6305. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.9.6297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Borden J. Reproducible compartmentalization of individual chromosome domains in human CNS cells revealed by in situ hybridization and three-dimensional reconstruction. Chromosoma. 1988;96(6):397–410. doi: 10.1007/BF00303033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathog D., Hochstrasser M., Gruenbaum Y., Saumweber H., Sedat J. Characteristic folding pattern of polytene chromosomes in Drosophila salivary gland nuclei. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):414–421. doi: 10.1038/308414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. B., Davies H. G. Three-dimensional reconstruction of the chromatin bodies in the nuclei of mature erythrocytes from the newt Triturus cristatus: the number of nuclear envelope-attachment sites. J Cell Sci. 1979 Feb;35:59–66. doi: 10.1242/jcs.35.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paddy M. R., Belmont A. S., Saumweber H., Agard D. A., Sedat J. W. Interphase nuclear envelope lamins form a discontinuous network that interacts with only a fraction of the chromatin in the nuclear periphery. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):89–106. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90243-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palladino F., Laroche T., Gilson E., Axelrod A., Pillus L., Gasser S. M. SIR3 and SIR4 proteins are required for the positioning and integrity of yeast telomeres. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):543–555. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90388-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pimpinelli S., Dimitri P. Cytogenetic analysis of segregation distortion in Drosophila melanogaster: the cytological organization of the Responder (Rsp) locus. Genetics. 1989 Apr;121(4):765–772. doi: 10.1093/genetics/121.4.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell C., Mashiko T., Odaka K., Ueno K. Describing head shape with surface harmonic expansions. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1991 Mar;38(3):303–306. doi: 10.1109/10.133214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rastelli L., Chan C. S., Pirrotta V. Related chromosome binding sites for zeste, suppressors of zeste and Polycomb group proteins in Drosophila and their dependence on Enhancer of zeste function. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1513–1522. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05795.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. L. Macromolecular domains within the cell nucleus. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:265–315. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.09.110193.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukegawa J., Blobel G. A nuclear pore complex protein that contains zinc finger motifs, binds DNA, and faces the nucleoplasm. Cell. 1993 Jan 15;72(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90047-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telenius H., Carter N. P., Bebb C. E., Nordenskjöld M., Ponder B. A., Tunnacliffe A. Degenerate oligonucleotide-primed PCR: general amplification of target DNA by a single degenerate primer. Genomics. 1992 Jul;13(3):718–725. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90147-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udvardy A., Maine E., Schedl P. The 87A7 chromomere. Identification of novel chromatin structures flanking the heat shock locus that may define the boundaries of higher order domains. J Mol Biol. 1985 Sep 20;185(2):341–358. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90408-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vourc'h C., Taruscio D., Boyle A. L., Ward D. C. Cell cycle-dependent distribution of telomeres, centromeres, and chromosome-specific subsatellite domains in the interphase nucleus of mouse lymphocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1993 Mar;205(1):142–151. doi: 10.1006/excr.1993.1068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakimoto B. T., Hearn M. G. The effects of chromosome rearrangements on the expression of heterochromatic genes in chromosome 2L of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1990 May;125(1):141–154. doi: 10.1093/genetics/125.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiese C., Wilson K. L. Nuclear membrane dynamics. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;5(3):387–394. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worman H. J., Evans C. D., Blobel G. The lamin B receptor of the nuclear envelope inner membrane: a polytopic protein with eight potential transmembrane domains. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1535–1542. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. I., Lyttle T. W., Wu M. L., Lin G. F. Association between a satellite DNA sequence and the Responder of Segregation Distorter in D. melanogaster. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):179–189. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90550-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota H., van den Engh G., Hearst J. E., Sachs R. K., Trask B. J. Evidence for the organization of chromatin in megabase pair-sized loops arranged along a random walk path in the human G0/G1 interphase nucleus. J Cell Biol. 1995 Sep;130(6):1239–1249. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.6.1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan J., Simos G., Blobel G., Georgatos S. D. Binding of lamin A to polynucleosomes. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9211–9215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalensky A. O., Allen M. J., Kobayashi A., Zalenskaya I. A., Balhórn R., Bradbury E. M. Well-defined genome architecture in the human sperm nucleus. Chromosoma. 1995 May;103(9):577–590. doi: 10.1007/BF00357684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dekken H., Pinkel D., Mullikin J., Trask B., van den Engh G., Gray J. Three-dimensional analysis of the organization of human chromosome domains in human and human-hamster hybrid interphase nuclei. J Cell Sci. 1989 Oct;94(Pt 2):299–306. doi: 10.1242/jcs.94.2.299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dekken H., van Rotterdam A., Jonker R., van der Voort H. T., Brakenhoff G. J., Bauman J. G. Confocal microscopy as a tool for the study of the intranuclear topography of chromosomes. J Microsc. 1990 May;158(Pt 2):207–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1990.tb02994.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]