Abstract
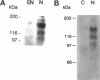
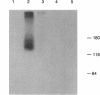
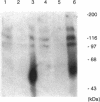
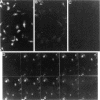
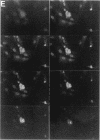
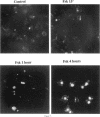
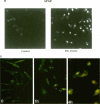
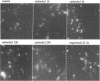
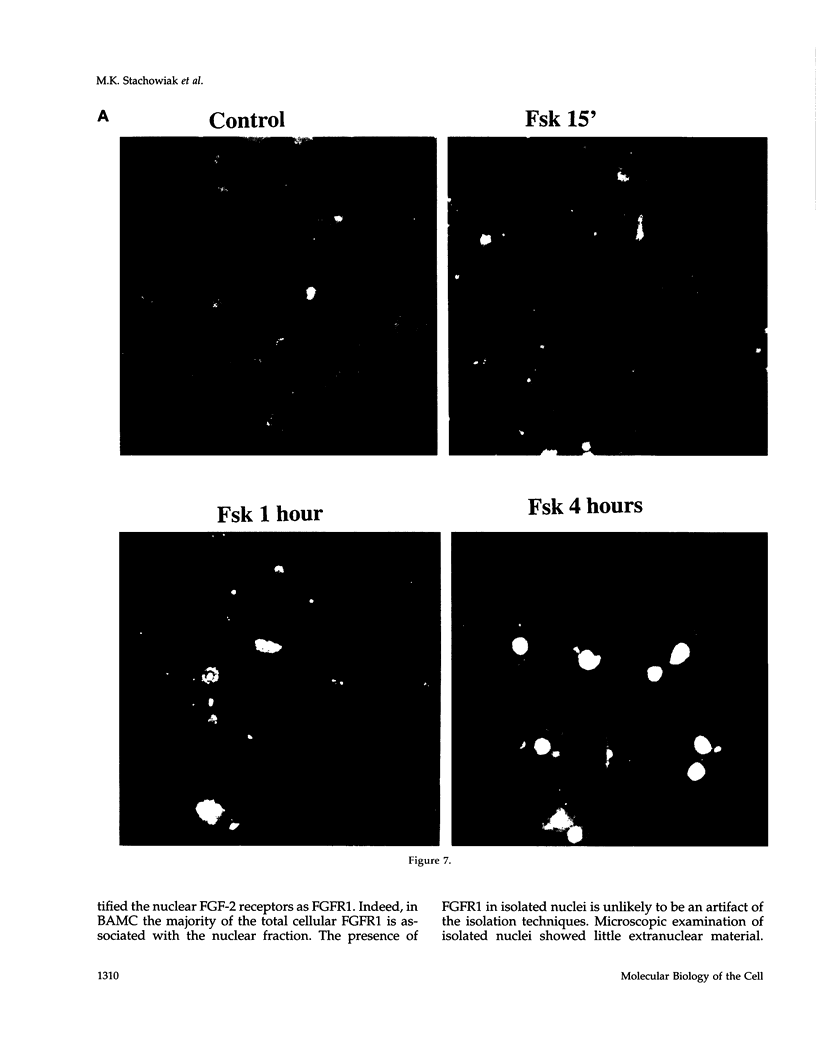
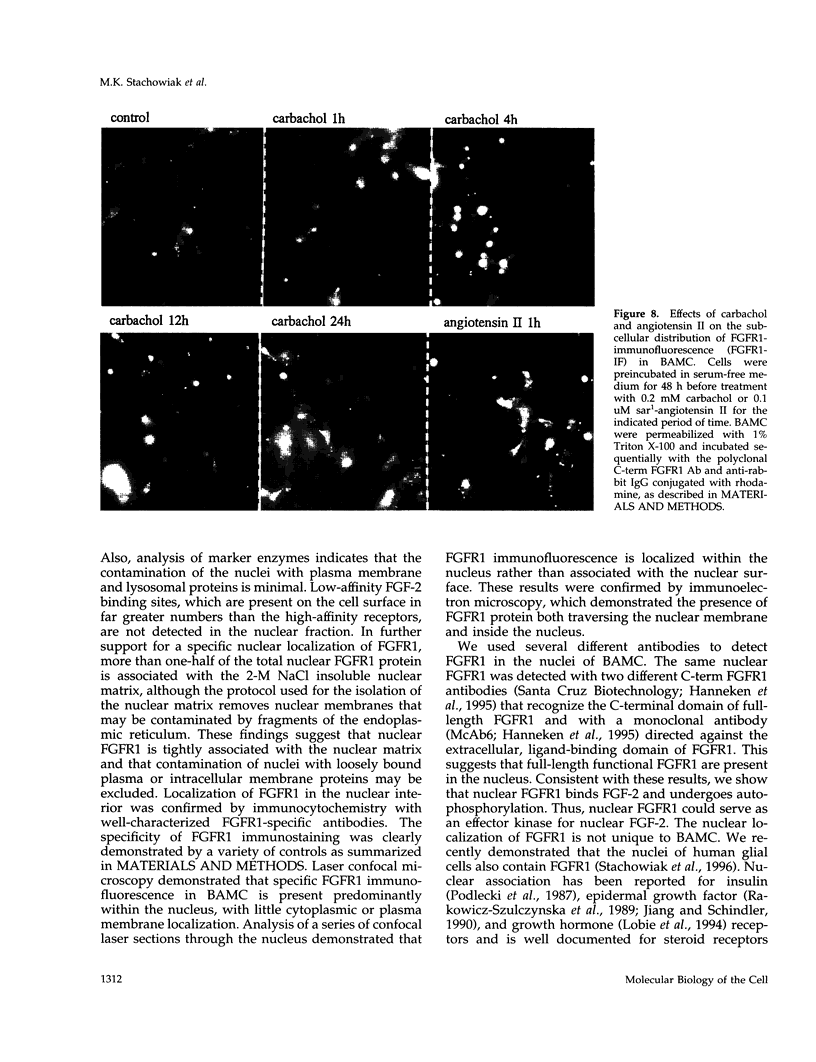
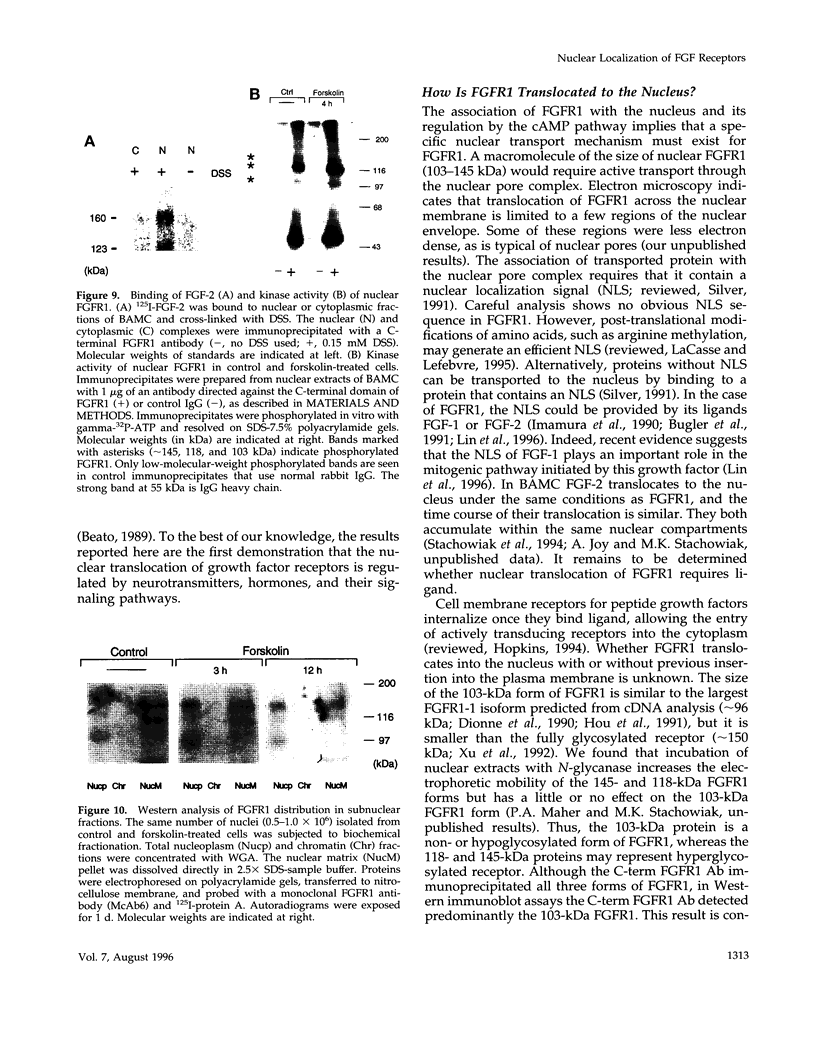
In an effort to determine the localization of fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptors (FGFR) that could mediate the intracellular action of FGF-2, we discovered the presence of high-affinity. FGF-2 binding sites in the nuclei of bovine adrenal medullary cells (BAMC). Western blot analysis demonstrated the presence of 103-, 118-, and 145-kDa forms of FGFR1 in nuclei isolated from BAMC. 125I-FGF-2 cross-linking to nuclear extracts followed by FGFR1 immunoprecipitation showed that FGFR1 can account for the nuclear FGF-2 binding sites. Nuclear FGFR1 has kinase activity and undergoes autophosphorylation. Immunocytochemistry with the use of confocal and electron microscopes demonstrated the presence of FGFR1 within the nuclear interior. Nuclear subfractionation followed by Western blot or immunoelectron microscopic analysis showed that the nuclear FGFR1 is contained in the nuclear matrix and the nucleoplasm. Agents that induce translocation of endogenous FGF-2 to the nucleus (forskolin, carbachol, or angiotensin II) increased the intranuclear accumulation of FGFR1. This accumulation was accompanied by an overall increase in FGF-2-inducible tyrosine kinase activity. Our findings suggest a novel mode for growth factor action whereby growth factor receptors translocate to the nucleus in parallel with their ligand and act as direct mediators of nuclear responses to cell stimulation.
Full text
PDF



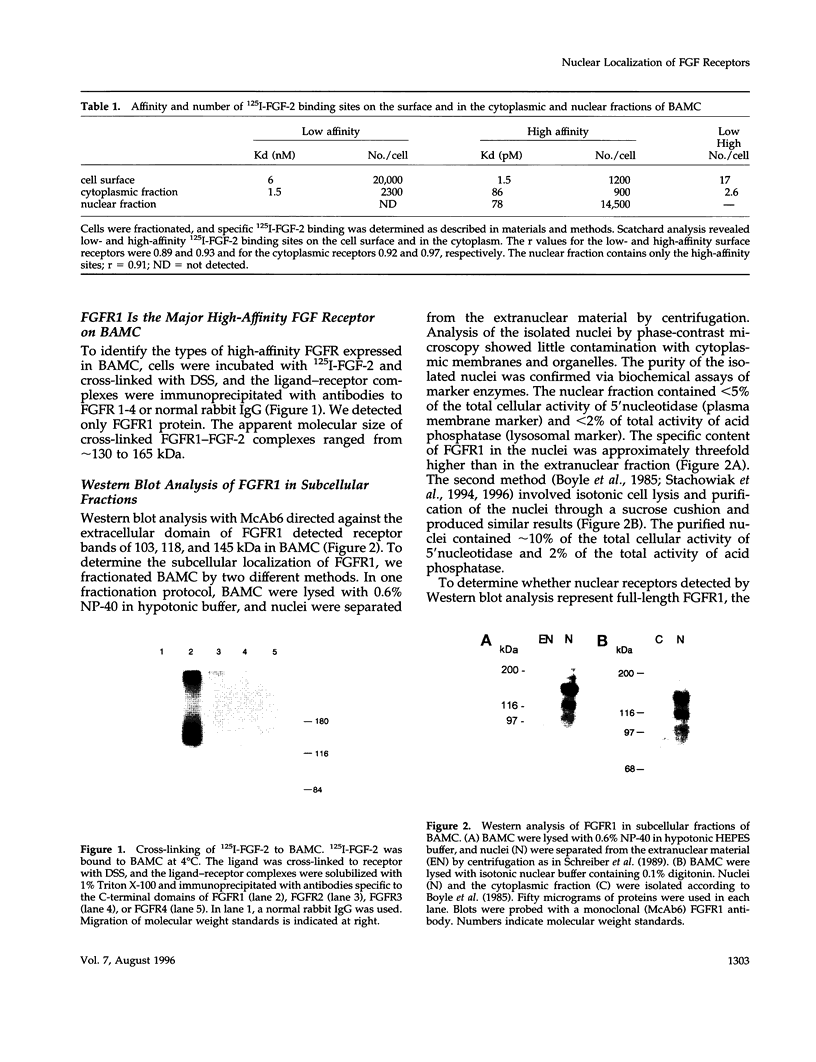




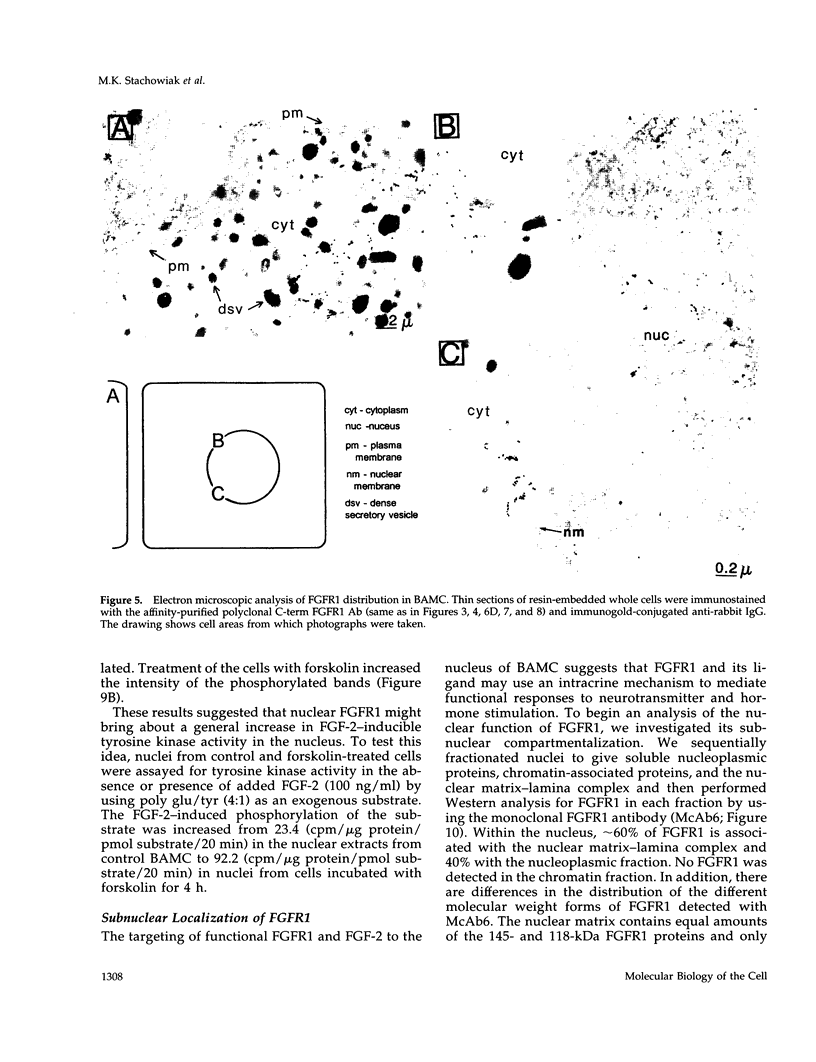
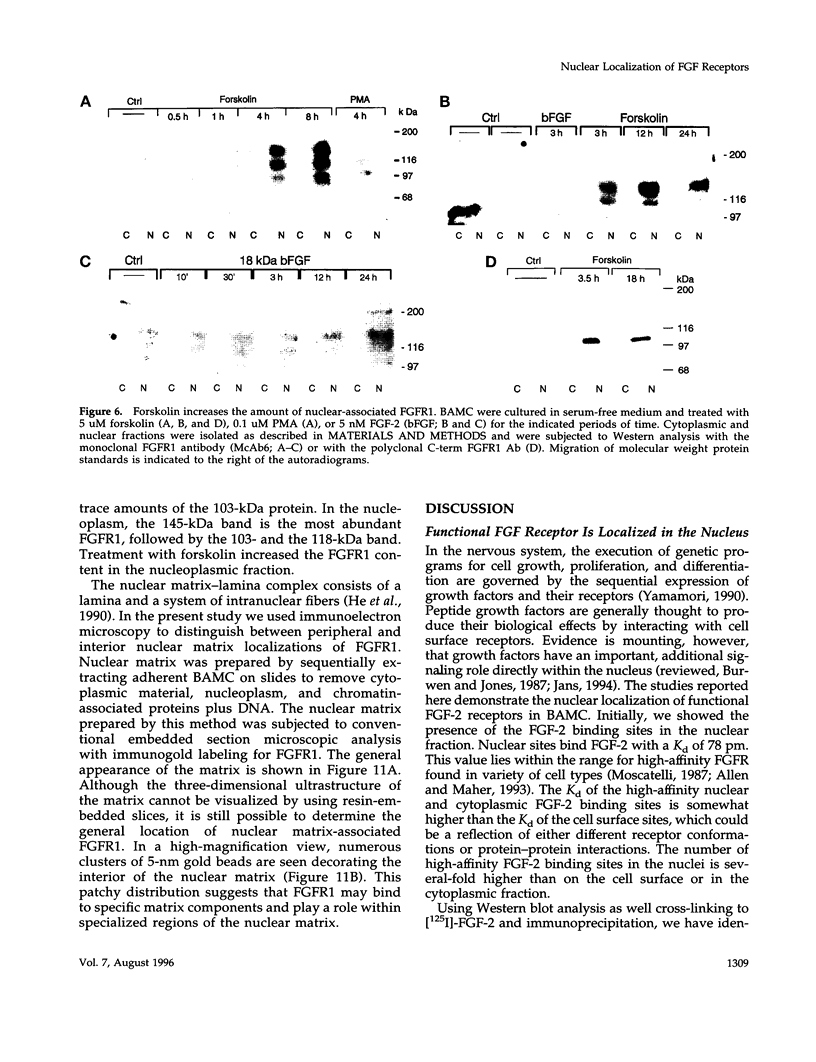





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham J. A., Mergia A., Whang J. L., Tumolo A., Friedman J., Hjerrild K. A., Gospodarowicz D., Fiddes J. C. Nucleotide sequence of a bovine clone encoding the angiogenic protein, basic fibroblast growth factor. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):545–548. doi: 10.1126/science.2425435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham J. A., Whang J. L., Tumolo A., Mergia A., Friedman J., Gospodarowicz D., Fiddes J. C. Human basic fibroblast growth factor: nucleotide sequence and genomic organization. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2523–2528. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04530.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen L. E., Maher P. A. Expression of basic fibroblast growth factor and its receptor in an invasive bladder carcinoma cell line. J Cell Physiol. 1993 May;155(2):368–375. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041550218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldin V., Roman A. M., Bosc-Bierne I., Amalric F., Bouche G. Translocation of bFGF to the nucleus is G1 phase cell cycle specific in bovine aortic endothelial cells. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1511–1517. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08269.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berezney R., Coffey D. S. Nuclear protein matrix: association with newly synthesized DNA. Science. 1975 Jul 25;189(4199):291–293. doi: 10.1126/science.1145202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergonzoni L., Caccia P., Cletini O., Sarmientos P., Isacchi A. Characterization of a biologically active extracellular domain of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 expressed in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Dec 15;210(3):823–829. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17485.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bikfalvi A., Klein S., Pintucci G., Quarto N., Mignatti P., Rifkin D. B. Differential modulation of cell phenotype by different molecular weight forms of basic fibroblast growth factor: possible intracellular signaling by the high molecular weight forms. J Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;129(1):233–243. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.1.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boarder M. R., Plevin R., Marriott D. B. Angiotensin II potentiates prostaglandin stimulation of cyclic AMP levels in intact bovine adrenal medulla cells but not adenylate cyclase in permeabilized cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15319–15324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouche G., Gas N., Prats H., Baldin V., Tauber J. P., Teissié J., Amalric F. Basic fibroblast growth factor enters the nucleolus and stimulates the transcription of ribosomal genes in ABAE cells undergoing G0----G1 transition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6770–6774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., Lampert M. A., Li A. C., Baluda M. A. Nuclear compartmentalization of the v-myb oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3017–3023. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugler B., Amalric F., Prats H. Alternative initiation of translation determines cytoplasmic or nuclear localization of basic fibroblast growth factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):573–577. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee P. K., Flint S. J. Partition of E1A proteins between soluble and structural fractions of adenovirus-infected and -transformed cells. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1018–1026. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1018-1026.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deppert W., Von Der Weth A. Functional interaction of nuclear transport-defective simian virus 40 large T antigen with chromatin and nuclear matrix. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):838–846. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.838-846.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionne C. A., Crumley G., Bellot F., Kaplow J. M., Searfoss G., Ruta M., Burgess W. H., Jaye M., Schlessinger J. Cloning and expression of two distinct high-affinity receptors cross-reacting with acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2685–2692. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07454.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman R. N., Tachibana C. Y., Abrams H. D., Hann S. R. V-myc- and c-myc-encoded proteins are associated with the nuclear matrix. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):114–126. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frödin M., Gammeltoft S. Insulin-like growth factors act synergistically with basic fibroblast growth factor and nerve growth factor to promote chromaffin cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 1;91(5):1771–1775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.5.1771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield I., Nickerson J., Penman S., Stanley M. Human papillomavirus 16 E7 protein is associated with the nuclear matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11217–11221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grothe C., Unsicker K. Immunocytochemical mapping of basic fibroblast growth factor in the developing and adult rat adrenal gland. Histochemistry. 1990;94(2):141–147. doi: 10.1007/BF02440180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti A., Costa E. A role for nicotinic receptors in the regulation of the adenylate cyclase of adrenal medulla. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1974 Jun;189(3):665–675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanneken A., Maher P. A., Baird A. High affinity immunoreactive FGF receptors in the extracellular matrix of vascular endothelial cells--implications for the modulation of FGF-2. J Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;128(6):1221–1228. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.6.1221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He D. C., Nickerson J. A., Penman S. Core filaments of the nuclear matrix. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):569–580. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins C. R. Internalization of polypeptide growth factor receptors and the regulation of transcription. Biochem Pharmacol. 1994 Jan 13;47(1):151–154. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(94)90449-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou J. Z., Kan M. K., McKeehan K., McBride G., Adams P., McKeehan W. L. Fibroblast growth factor receptors from liver vary in three structural domains. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):665–668. doi: 10.1126/science.1846977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imamura T., Engleka K., Zhan X., Tokita Y., Forough R., Roeder D., Jackson A., Maier J. A., Hla T., Maciag T. Recovery of mitogenic activity of a growth factor mutant with a nuclear translocation sequence. Science. 1990 Sep 28;249(4976):1567–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.1699274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A., Cook P. R. Transcription occurs at a nucleoskeleton. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):919–925. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03719.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jans D. A. Nuclear signaling pathways for polypeptide ligands and their membrane receptors? FASEB J. 1994 Aug;8(11):841–847. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.11.8070633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaye M., Howk R., Burgess W., Ricca G. A., Chiu I. M., Ravera M. W., O'Brien S. J., Modi W. S., Maciag T., Drohan W. N. Human endothelial cell growth factor: cloning, nucleotide sequence, and chromosome localization. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):541–545. doi: 10.1126/science.3523756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang L. W., Schindler M. Nucleocytoplasmic transport is enhanced concomitant with nuclear accumulation of epidermal growth factor (EGF) binding activity in both 3T3-1 and EGF receptor reconstituted NR-6 fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):559–568. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. E., Williams L. T. Structural and functional diversity in the FGF receptor multigene family. Adv Cancer Res. 1993;60:1–41. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60821-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston C. L., Cox H. C., Gomm J. J., Coombes R. C. Fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs) localize in different cellular compartments. A splice variant of FGFR-3 localizes to the nucleus. J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 22;270(51):30643–30650. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.51.30643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keegan K., Johnson D. E., Williams L. T., Hayman M. J. Isolation of an additional member of the fibroblast growth factor receptor family, FGFR-3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1095–1099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaCasse E. C., Lefebvre Y. A. Nuclear localization signals overlap DNA- or RNA-binding domains in nucleic acid-binding proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 May 25;23(10):1647–1656. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.10.1647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. Z., Yao S. Y., Hawiger J. Role of the nuclear localization sequence in fibroblast growth factor-1-stimulated mitogenic pathways. J Biol Chem. 1996 Mar 8;271(10):5305–5308. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.10.5305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobie P. E., Wood T. J., Chen C. M., Waters M. J., Norstedt G. Nuclear translocation and anchorage of the growth hormone receptor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 16;269(50):31735–31746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher P. A. Tissue-dependent regulation of protein tyrosine kinase activity during embryonic development. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(5):955–963. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.5.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini M. A., Shan B., Nickerson J. A., Penman S., Lee W. H. The retinoblastoma gene product is a cell cycle-dependent, nuclear matrix-associated protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 4;91(1):418–422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason I. J. The ins and outs of fibroblast growth factors. Cell. 1994 Aug 26;78(4):547–552. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90520-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCready S. J., Godwin J., Mason D. W., Brazell I. A., Cook P. R. DNA is replicated at the nuclear cage. J Cell Sci. 1980 Dec;46:365–386. doi: 10.1242/jcs.46.1.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli D. High and low affinity binding sites for basic fibroblast growth factor on cultured cells: absence of a role for low affinity binding in the stimulation of plasminogen activator production by bovine capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Apr;131(1):123–130. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041310118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli D. Metabolism of receptor-bound and matrix-bound basic fibroblast growth factor by bovine capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;107(2):753–759. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.2.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi Y., Kihara K., Mizuno K., Masamune Y., Yoshitake Y., Nishikawa K. Direct effect of basic fibroblast growth factor on gene transcription in a cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5216–5220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partanen J., Mäkelä T. P., Eerola E., Korhonen J., Hirvonen H., Claesson-Welsh L., Alitalo K. FGFR-4, a novel acidic fibroblast growth factor receptor with a distinct expression pattern. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1347–1354. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07654.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podlecki D. A., Smith R. M., Kao M., Tsai P., Huecksteadt T., Brandenburg D., Lasher R. S., Jarett L., Olefsky J. M. Nuclear translocation of the insulin receptor. A possible mediator of insulin's long term effects. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3362–3368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prudovsky I., Savion N., Zhan X., Friesel R., Xu J., Hou J., McKeehan W. L., Maciag T. Intact and functional fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptor-1 trafficks near the nucleus in response to FGF-1. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 16;269(50):31720–31724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puchacz E., Stachowiak E. K., Florkiewicz R. Z., Lukas R. J., Stachowiak M. K. Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) regulates tyrosine hydroxylase and proenkephalin mRNA levels in adrenal chromaffin cells. Brain Res. 1993 Apr 30;610(1):39–52. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91214-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakowicz-Szulczynska E. M., Otwiaska D., Rodeck U., Koprowski H. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) and monoclonal antibody to cell surface EGF receptor bind to the same chromatin receptor. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Feb 1;268(2):456–464. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90313-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray J., Hogg J., Beutler A. S., Takayama H., Baird A., Gage F. H. Expression of biologically active basic fibroblast growth factor by genetically modified rat primary skin fibroblasts. J Neurochem. 1995 Feb;64(2):503–513. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1995.64020503.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruta M., Burgess W., Givol D., Epstein J., Neiger N., Kaplow J., Crumley G., Dionne C., Jaye M., Schlessinger J. Receptor for acidic fibroblast growth factor is related to the tyrosine kinase encoded by the fms-like gene (FLG). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8722–8726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schaffner W. Rapid detection of octamer binding proteins with 'mini-extracts', prepared from a small number of cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6419–6419. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., Ling N., Baird A. Multiple influences of a heparin-binding growth factor on neuronal development. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):635–643. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweigerer L., Neufeld G., Mergia A., Abraham J. A., Fiddes J. C., Gospodarowicz D. Basic fibroblast growth factor in human rhabdomyosarcoma cells: implications for the proliferation and neovascularization of myoblast-derived tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):842–846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman L., Stocker K. M., Morrison R., Ciment G. Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) acts intracellularly to cause the transdifferentiation of avian neural crest-derived Schwann cell precursors into melanocytes. Development. 1993 Aug;118(4):1313–1326. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.4.1313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P. A. How proteins enter the nucleus. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):489–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90233-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachowiak M. K., Hong J. S., Viveros O. H. Coordinate and differential regulation of phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase, tyrosine hydroxylase and proenkephalin mRNAs by neural and hormonal mechanisms in cultured bovine adrenal medullary cells. Brain Res. 1990 Mar 5;510(2):277–288. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91378-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachowiak M. K., Maher P. A., Joy A., Mordechai E., Stachowiak E. K. Nuclear localization of functional FGF receptor 1 in human astrocytes suggests a novel mechanism for growth factor action. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1996 May;38(1):161–165. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(96)00010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachowiak M. K., Moffett J., Joy A., Puchacz E., Florkiewicz R., Stachowiak E. K. Regulation of bFGF gene expression and subcellular distribution of bFGF protein in adrenal medullary cells. J Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;127(1):203–223. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.1.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stemple D. L., Mahanthappa N. K., Anderson D. J. Basic FGF induces neuronal differentiation, cell division, and NGF dependence in chromaffin cells: a sequence of events in sympathetic development. Neuron. 1988 Aug;1(6):517–525. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90182-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischler A. S., Riseberg J. C., Hardenbrook M. A., Cherington V. Nerve growth factor is a potent inducer of proliferation and neuronal differentiation for adult rat chromaffin cells in vitro. J Neurosci. 1993 Apr;13(4):1533–1542. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-04-01533.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsicker K., Westermann R. Basic fibroblast growth factor promotes transmitter storage and synthesis in cultured chromaffin cells. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1992 Feb 21;65(2):211–216. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(92)90181-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I., Bar-Shavit R., Ishai-Michaeli R., Bashkin P., Fuks Z. Extracellular sequestration and release of fibroblast growth factor: a regulatory mechanism? Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jul;16(7):268–271. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waitz W., Loidl P. Cell cycle dependent association of c-myc protein with the nuclear matrix. Oncogene. 1991 Jan;6(1):29–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedłocha A., Falnes P. O., Madshus I. H., Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Dual mode of signal transduction by externally added acidic fibroblast growth factor. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):1039–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie A. O., Morriss-Kay G. M., Jones E. Y., Heath J. K. Functions of fibroblast growth factors and their receptors. Curr Biol. 1995 May 1;5(5):500–507. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00102-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu J., Nakahara M., Crabb J. W., Shi E., Matuo Y., Fraser M., Kan M., Hou J., McKeehan W. L. Expression and immunochemical analysis of rat and human fibroblast growth factor receptor (flg) isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17792–17803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamori T. Molecular mechanisms for generation of neural diversity and specificity: roles of polypeptide factors in development of postmitotic neurons. Neurosci Res. 1992 Jan;12(5):545–582. doi: 10.1016/0168-0102(92)90064-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeitlin S., Parent A., Silverstein S., Efstratiadis A. Pre-mRNA splicing and the nuclear matrix. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):111–120. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]