Abstract
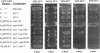
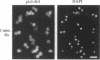
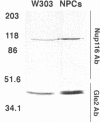
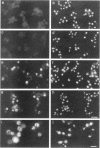
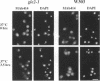
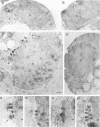
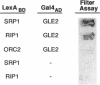
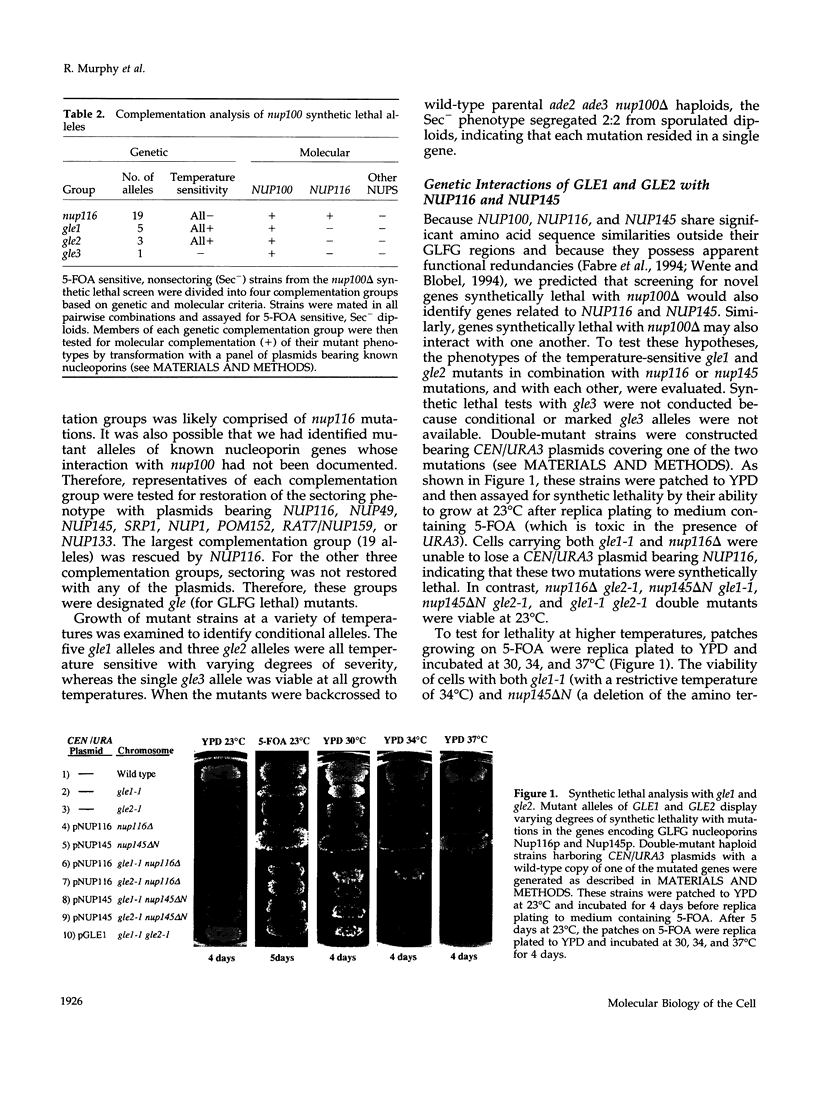
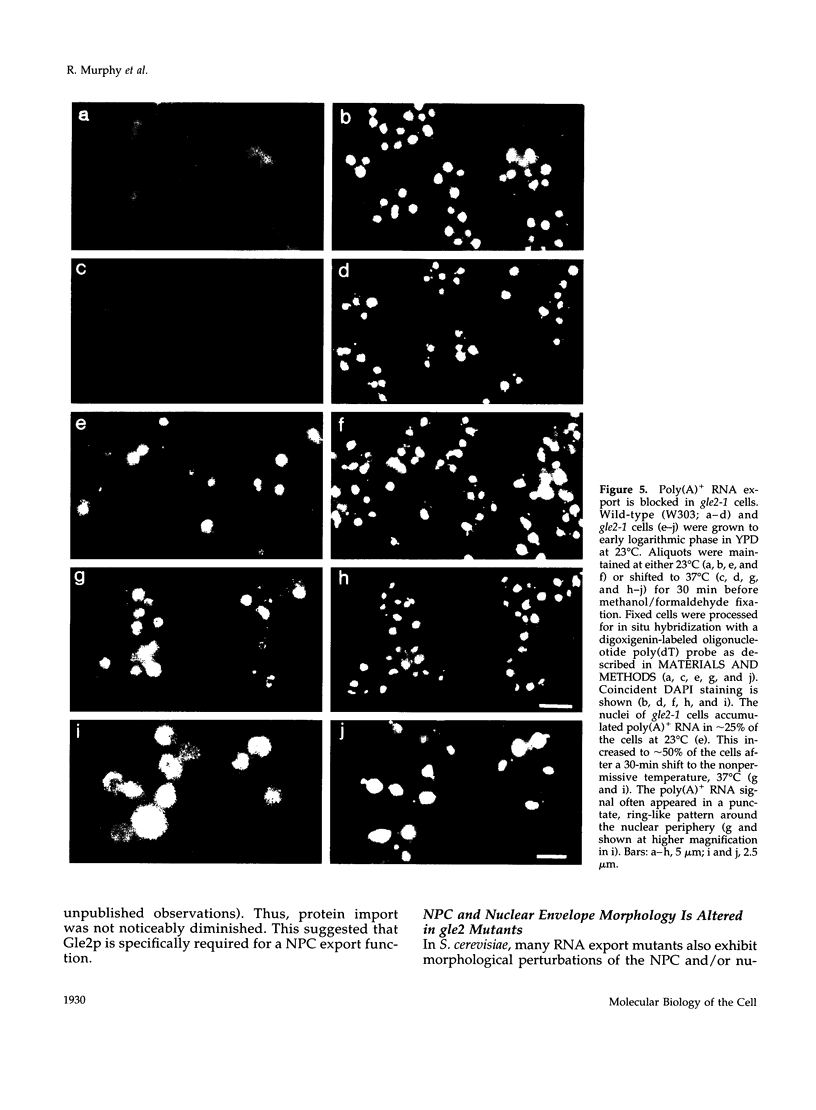
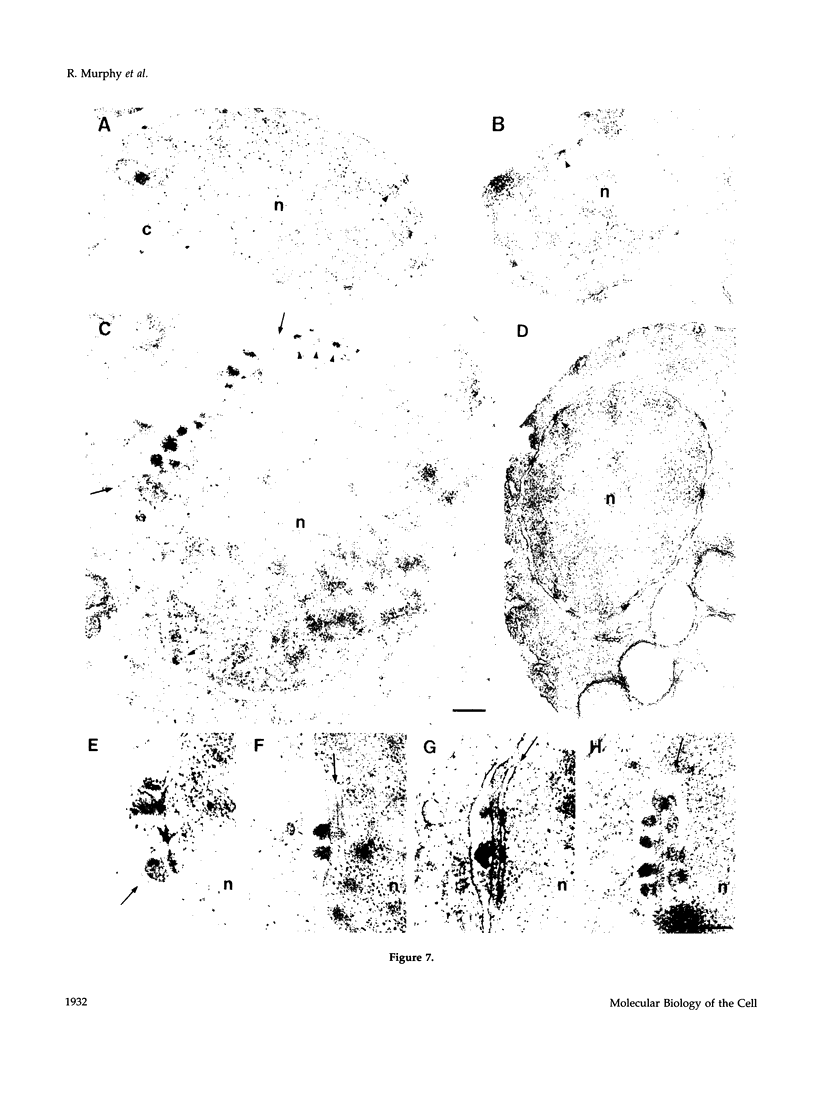
To identify and characterize novel factors required for nuclear transport, a genetic screen was conducted in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mutations that were lethal in combination with a null allele of the gene encoding the nucleoporin Nup100p were isolated using a colony-sectoring assay. Three complementation groups of gle (for GLFG lethal) mutants were identified. In this report, the characterization of GLE2 is detailed. GLE2 encodes a 40.5-kDa polypeptide with striking similarity to that of Schizosaccharomyces pombe RAE1. In indirect immunofluorescence and nuclear pore complex fractionation experiments, Gle2p was associated with nuclear pore complexes. Mutated alleles of GLE2 displayed blockage of polyadenylated RNA export; however, nuclear protein import was not apparently diminished. Immunofluorescence and thin-section electron microscopic analysis revealed that the nuclear pore complex and nuclear envelope structure was grossly perturbed in gle2 mutants. Because the clusters of herniated pore complexes appeared subsequent to the export block, the structural perturbations were likely indirect consequences of the export phenotype. Interestingly, a two-hybrid interaction was detected between Gle2p and Srp1p, the nuclear localization signal receptor, as well as Rip1p, a nuclear export signal-interacting protein. We propose that Gle2p has a novel role in mediating nuclear transport.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam E. J., Adam S. A. Identification of cytosolic factors required for nuclear location sequence-mediated binding to the nuclear envelope. J Cell Biol. 1994 May;125(3):547–555. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.3.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adam S. A. The importance of importin. Trends Cell Biol. 1995 May;5(5):189–191. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(00)88991-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aebi M., Clark M. W., Vijayraghavan U., Abelson J. A yeast mutant, PRP20, altered in mRNA metabolism and maintenance of the nuclear structure, is defective in a gene homologous to the human gene RCC1 which is involved in the control of chromosome condensation. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Oct;224(1):72–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00259453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aitchison J. D., Blobel G., Rout M. P. Nup120p: a yeast nucleoporin required for NPC distribution and mRNA transport. J Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;131(6 Pt 2):1659–1675. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.6.1659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aitchison J. D., Rout M. P., Marelli M., Blobel G., Wozniak R. W. Two novel related yeast nucleoporins Nup170p and Nup157p: complementation with the vertebrate homologue Nup155p and functional interactions with the yeast nuclear pore-membrane protein Pom152p. J Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;131(5):1133–1148. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.5.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amberg D. C., Fleischmann M., Stagljar I., Cole C. N., Aebi M. Nuclear PRP20 protein is required for mRNA export. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):233–241. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05649.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amberg D. C., Goldstein A. L., Cole C. N. Isolation and characterization of RAT1: an essential gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae required for the efficient nucleocytoplasmic trafficking of mRNA. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1173–1189. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudin A., Ozier-Kalogeropoulos O., Denouel A., Lacroute F., Cullin C. A simple and efficient method for direct gene deletion in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 11;21(14):3329–3330. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.14.3329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belanger K. D., Kenna M. A., Wei S., Davis L. I. Genetic and physical interactions between Srp1p and nuclear pore complex proteins Nup1p and Nup2p. J Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;126(3):619–630. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.3.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belhumeur P., Lee A., Tam R., DiPaolo T., Fortin N., Clark M. W. GSP1 and GSP2, genetic suppressors of the prp20-1 mutant in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: GTP-binding proteins involved in the maintenance of nuclear organization. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2152–2161. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender A., Pringle J. R. Use of a screen for synthetic lethal and multicopy suppressee mutants to identify two new genes involved in morphogenesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1295–1305. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff F. R., Krebber H., Kempf T., Hermes I., Ponstingl H. Human RanGTPase-activating protein RanGAP1 is a homologue of yeast Rna1p involved in mRNA processing and transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 28;92(5):1749–1753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.5.1749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff F. R., Ponstingl H. Catalysis of guanine nucleotide exchange on Ran by the mitotic regulator RCC1. Nature. 1991 Nov 7;354(6348):80–82. doi: 10.1038/354080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff F. R., Ponstingl H. Mitotic regulator protein RCC1 is complexed with a nuclear ras-related polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10830–10834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogerd A. M., Hoffman J. A., Amberg D. C., Fink G. R., Davis L. I. nup1 mutants exhibit pleiotropic defects in nuclear pore complex function. J Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;127(2):319–332. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogerd H. P., Fridell R. A., Madore S., Cullen B. R. Identification of a novel cellular cofactor for the Rev/Rex class of retroviral regulatory proteins. Cell. 1995 Aug 11;82(3):485–494. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90437-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breeden L., Nasmyth K. Regulation of the yeast HO gene. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:643–650. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. A., Bharathi A., Ghosh A., Whalen W., Fitzgerald E., Dhar R. A mutation in the Schizosaccharomyces pombe rae1 gene causes defects in poly(A)+ RNA export and in the cytoskeleton. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 31;270(13):7411–7419. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.13.7411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers B., Goetsch L. Preparation of yeast cells for thin-section electron microscopy. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:602–608. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94044-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Dahlberg J. E., Lund E. Diverse effects of the guanine nucleotide exchange factor RCC1 on RNA transport. Science. 1995 Mar 24;267(5205):1807–1810. doi: 10.1126/science.7534442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chi N. C., Adam E. J., Adam S. A. Sequence and characterization of cytoplasmic nuclear protein import factor p97. J Cell Biol. 1995 Jul;130(2):265–274. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett A. H., Koepp D. M., Schlenstedt G., Lee M. S., Hopper A. K., Silver P. A. Rna1p, a Ran/TC4 GTPase activating protein, is required for nuclear import. J Cell Biol. 1995 Sep;130(5):1017–1026. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.5.1017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly T. J., Cook K. S., Gray G. S., Maione T. E., Rusche J. R. Specific binding of HIV-1 recombinant Rev protein to the Rev-responsive element in vitro. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):816–819. doi: 10.1038/342816a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. I., Blobel G. Identification and characterization of a nuclear pore complex protein. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):699–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90784-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. I., Fink G. R. The NUP1 gene encodes an essential component of the yeast nuclear pore complex. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):965–978. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90062-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. I. The nuclear pore complex. Annu Rev Biochem. 1995;64:865–896. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.64.070195.004245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayhoff M. O., Barker W. C., Hunt L. T. Establishing homologies in protein sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:524–545. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Laskey R. A. Nuclear targeting sequences--a consensus? Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Dec;16(12):478–481. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90184-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doye V., Hurt E. C. Genetic approaches to nuclear pore structure and function. Trends Genet. 1995 Jun;11(6):235–241. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(00)89057-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doye V., Wepf R., Hurt E. C. A novel nuclear pore protein Nup133p with distinct roles in poly(A)+ RNA transport and nuclear pore distribution. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 15;13(24):6062–6075. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06953.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enenkel C., Blobel G., Rexach M. Identification of a yeast karyopherin heterodimer that targets import substrate to mammalian nuclear pore complexes. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 14;270(28):16499–16502. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.28.16499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabre E., Boelens W. C., Wimmer C., Mattaj I. W., Hurt E. C. Nup145p is required for nuclear export of mRNA and binds homopolymeric RNA in vitro via a novel conserved motif. Cell. 1994 Jul 29;78(2):275–289. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Song O. A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):245–246. doi: 10.1038/340245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes D. J. Structure and function of the nuclear pore complex. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:495–527. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.002431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester W., Stutz F., Rosbash M., Wickens M. Defects in mRNA 3'-end formation, transcription initiation, and mRNA transport associated with the yeast mutation prp20: possible coupling of mRNA processing and chromatin structure. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1914–1926. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridell R. A., Fischer U., Lührmann R., Meyer B. E., Meinkoth J. L., Malim M. H., Cullen B. R. Amphibian transcription factor IIIA proteins contain a sequence element functionally equivalent to the nuclear export signal of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Rev. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Apr 2;93(7):2936–2940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.7.2936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz C. C., Zapp M. L., Green M. R. A human nucleoporin-like protein that specifically interacts with HIV Rev. Nature. 1995 Aug 10;376(6540):530–533. doi: 10.1038/376530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerace L. Nuclear export signals and the fast track to the cytoplasm. Cell. 1995 Aug 11;82(3):341–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90420-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A. L., Snay C. A., Heath C. V., Cole C. N. Pleiotropic nuclear defects associated with a conditional allele of the novel nucleoporin Rat9p/Nup85p. Mol Biol Cell. 1996 Jun;7(6):917–934. doi: 10.1091/mbc.7.6.917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorsch L. C., Dockendorff T. C., Cole C. N. A conditional allele of the novel repeat-containing yeast nucleoporin RAT7/NUP159 causes both rapid cessation of mRNA export and reversible clustering of nuclear pore complexes. J Cell Biol. 1995 May;129(4):939–955. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.4.939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandi P., Schlaich N., Tekotte H., Hurt E. C. Functional interaction of Nic96p with a core nucleoporin complex consisting of Nsp1p, Nup49p and a novel protein Nup57p. EMBO J. 1995 Jan 3;14(1):76–87. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb06977.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görlich D., Kostka S., Kraft R., Dingwall C., Laskey R. A., Hartmann E., Prehn S. Two different subunits of importin cooperate to recognize nuclear localization signals and bind them to the nuclear envelope. Curr Biol. 1995 Apr 1;5(4):383–392. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00079-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görlich D., Mattaj I. W. Nucleocytoplasmic transport. Science. 1996 Mar 15;271(5255):1513–1518. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5255.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görlich D., Prehn S., Laskey R. A., Hartmann E. Isolation of a protein that is essential for the first step of nuclear protein import. Cell. 1994 Dec 2;79(5):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görlich D., Vogel F., Mills A. D., Hartmann E., Laskey R. A. Distinct functions for the two importin subunits in nuclear protein import. Nature. 1995 Sep 21;377(6546):246–248. doi: 10.1038/377246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy C. F. Characterization of an essential Orc2p-associated factor that plays a role in DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Apr;16(4):1832–1841. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.4.1832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath C. V., Copeland C. S., Amberg D. C., Del Priore V., Snyder M., Cole C. N. Nuclear pore complex clustering and nuclear accumulation of poly(A)+ RNA associated with mutation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAT2/NUP120 gene. J Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;131(6 Pt 2):1677–1697. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.6.1677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henríquez R., Blobel G., Aris J. P. Isolation and sequencing of NOP1. A yeast gene encoding a nucleolar protein homologous to a human autoimmune antigen. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2209–2215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper A. K., Traglia H. M., Dunst R. W. The yeast RNA1 gene product necessary for RNA processing is located in the cytosol and apparently excluded from the nucleus. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):309–321. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
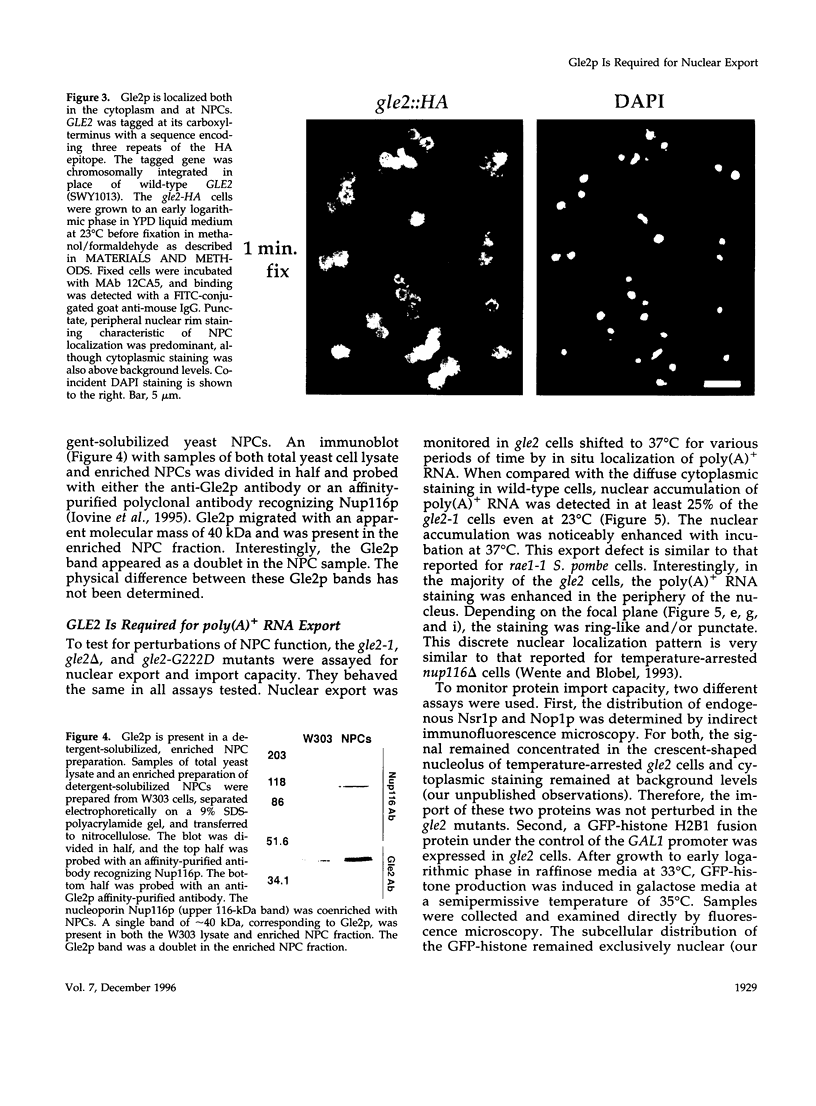
- Iovine M. K., Watkins J. L., Wente S. R. The GLFG repetitive region of the nucleoporin Nup116p interacts with Kap95p, an essential yeast nuclear import factor. J Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;131(6 Pt 2):1699–1713. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.6.1699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izaurralde E., Mattaj I. W. RNA export. Cell. 1995 Apr 21;81(2):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90323-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan E. G., Severs N. J., Williamson D. H. Nuclear pore formation and the cell cycle in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Feb;104(2):446–449. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Chen S., Hitomi M., Jacobs E., Kumagai C., Liang S., Schneiter R., Singleton D., Wisniewska J., Tartakoff A. M. Isolation and characterization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mRNA transport-defective (mtr) mutants. J Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;126(3):649–659. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.3.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Goldfarb D., Spitz L. M., Tartakoff A. M., Ohno M. Regulation of RNA processing and transport by a nuclear guanine nucleotide release protein and members of the Ras superfamily. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2929–2937. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05955.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Zhao Y., Tartakoff A. M. A conditional yeast mutant deficient in mRNA transport from nucleus to cytoplasm. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2312–2316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koepp D. M., Wong D. H., Corbett A. H., Silver P. A. Dynamic localization of the nuclear import receptor and its interactions with transport factors. J Cell Biol. 1996 Jun;133(6):1163–1176. doi: 10.1083/jcb.133.6.1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence C. W. Classical mutagenesis techniques. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:273–281. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li O., Heath C. V., Amberg D. C., Dockendorff T. C., Copeland C. S., Snyder M., Cole C. N. Mutation or deletion of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAT3/NUP133 gene causes temperature-dependent nuclear accumulation of poly(A)+ RNA and constitutive clustering of nuclear pore complexes. Mol Biol Cell. 1995 Apr;6(4):401–417. doi: 10.1091/mbc.6.4.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb J. D., Schlenstedt G., Pellman D., Kornitzer D., Silver P. A., Fink G. R. The yeast nuclear import receptor is required for mitosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 15;92(17):7647–7651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.17.7647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Hauber J., Le S. Y., Maizel J. V., Cullen B. R. The HIV-1 rev trans-activator acts through a structured target sequence to activate nuclear export of unspliced viral mRNA. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):254–257. doi: 10.1038/338254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchior F., Gerace L. Mechanisms of nuclear protein import. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Jun;7(3):310–318. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80084-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchior F., Paschal B., Evans J., Gerace L. Inhibition of nuclear protein import by nonhydrolyzable analogues of GTP and identification of the small GTPase Ran/TC4 as an essential transport factor. J Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;123(6 Pt 2):1649–1659. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.6.1649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer B. E., Malim M. H. The HIV-1 Rev trans-activator shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Genes Dev. 1994 Jul 1;8(13):1538–1547. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.13.1538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael W. M., Choi M., Dreyfuss G. A nuclear export signal in hnRNP A1: a signal-mediated, temperature-dependent nuclear protein export pathway. Cell. 1995 Nov 3;83(3):415–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90119-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. S., Blobel G. A G protein involved in nucleocytoplasmic transport: the role of Ran. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 May;19(5):211–216. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. S., Blobel G. The GTP-binding protein Ran/TC4 is required for protein import into the nucleus. Nature. 1993 Oct 14;365(6447):661–663. doi: 10.1038/365661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroianu J., Blobel G., Radu A. Previously identified protein of uncertain function is karyopherin alpha and together with karyopherin beta docks import substrate at nuclear pore complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 14;92(6):2008–2011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.6.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroianu J., Hijikata M., Blobel G., Radu A. Mammalian karyopherin alpha 1 beta and alpha 2 beta heterodimers: alpha 1 or alpha 2 subunit binds nuclear localization signal and beta subunit interacts with peptide repeat-containing nucleoporins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jul 3;92(14):6532–6536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.14.6532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy R., Wente S. R. An RNA-export mediator with an essential nuclear export signal. Nature. 1996 Sep 26;383(6598):357–360. doi: 10.1038/383357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmeyer D. D., Forbes D. J. Nuclear import can be separated into distinct steps in vitro: nuclear pore binding and translocation. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):641–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90402-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pemberton L. F., Rout M. P., Blobel G. Disruption of the nucleoporin gene NUP133 results in clustering of nuclear pore complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 14;92(4):1187–1191. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.4.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piñol-Roma S., Dreyfuss G. Shuttling of pre-mRNA binding proteins between nucleus and cytoplasm. Nature. 1992 Feb 20;355(6362):730–732. doi: 10.1038/355730a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers M. A., Forbes D. J. Cytosolic factors in nuclear transport: what's importin? Cell. 1994 Dec 16;79(6):931–934. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radu A., Blobel G., Moore M. S. Identification of a protein complex that is required for nuclear protein import and mediates docking of import substrate to distinct nucleoporins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 28;92(5):1769–1773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.5.1769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radu A., Moore M. S., Blobel G. The peptide repeat domain of nucleoporin Nup98 functions as a docking site in transport across the nuclear pore complex. Cell. 1995 Apr 21;81(2):215–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90331-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson W. D., Mills A. D., Dilworth S. M., Laskey R. A., Dingwall C. Nuclear protein migration involves two steps: rapid binding at the nuclear envelope followed by slower translocation through nuclear pores. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):655–664. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90403-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. Targeting, disruption, replacement, and allele rescue: integrative DNA transformation in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:281–301. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94022-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rout M. P., Blobel G. Isolation of the yeast nuclear pore complex. J Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;123(4):771–783. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.4.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rout M. P., Wente S. R. Pores for thought: nuclear pore complex proteins. Trends Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;4(10):357–365. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlenstedt G., Hurt E., Doye V., Silver P. A. Reconstitution of nuclear protein transport with semi-intact yeast cells. J Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;123(4):785–798. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.4.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlenstedt G., Saavedra C., Loeb J. D., Cole C. N., Silver P. A. The GTP-bound form of the yeast Ran/TC4 homologue blocks nuclear protein import and appearance of poly(A)+ RNA in the cytoplasm. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jan 3;92(1):225–229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.1.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severs N. J., Jordan E. G., Williamson D. H. Nuclear pore absence from areas of close association between nucleus and vacuole in synchronous yeast cultures. J Ultrastruct Res. 1976 Mar;54(3):374–387. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(76)80023-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simos G., Hurt E. C. Nucleocytoplasmic transport: factors and mechanisms. FEBS Lett. 1995 Aug 1;369(1):107–112. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00674-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siniossoglou S., Wimmer C., Rieger M., Doye V., Tekotte H., Weise C., Emig S., Segref A., Hurt E. C. A novel complex of nucleoporins, which includes Sec13p and a Sec13p homolog, is essential for normal nuclear pores. Cell. 1996 Jan 26;84(2):265–275. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80981-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutz F., Neville M., Rosbash M. Identification of a novel nuclear pore-associated protein as a functional target of the HIV-1 Rev protein in yeast. Cell. 1995 Aug 11;82(3):495–506. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90438-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis K., Mattaj I. W., Lamond A. I. Identification of hSRP1 alpha as a functional receptor for nuclear localization sequences. Science. 1995 May 19;268(5213):1049–1053. doi: 10.1126/science.7754385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen W., Meinkoth J. L., Tsien R. Y., Taylor S. S. Identification of a signal for rapid export of proteins from the nucleus. Cell. 1995 Aug 11;82(3):463–473. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90435-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wente S. R., Blobel G. A temperature-sensitive NUP116 null mutant forms a nuclear envelope seal over the yeast nuclear pore complex thereby blocking nucleocytoplasmic traffic. J Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;123(2):275–284. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wente S. R., Blobel G. NUP145 encodes a novel yeast glycine-leucine-phenylalanine-glycine (GLFG) nucleoporin required for nuclear envelope structure. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;125(5):955–969. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.5.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wente S. R., Rout M. P., Blobel G. A new family of yeast nuclear pore complex proteins. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(4):705–723. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.4.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimmer C., Doye V., Grandi P., Nehrbass U., Hurt E. C. A new subclass of nucleoporins that functionally interact with nuclear pore protein NSP1. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):5051–5061. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05612.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe M. P., Schatz G. Two nuclear mutations that block mitochondrial protein import in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4819–4823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano R., Oakes M., Yamaghishi M., Dodd J. A., Nomura M. Cloning and characterization of SRP1, a suppressor of temperature-sensitive RNA polymerase I mutations, in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5640–5651. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapp M. L., Green M. R. Sequence-specific RNA binding by the HIV-1 Rev protein. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):714–716. doi: 10.1038/342714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]